Liang-Chih Yu
DimABSA: Building Multilingual and Multidomain Datasets for Dimensional Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis (ABSA) focuses on extracting sentiment at a fine-grained aspect level and has been widely applied across real-world domains. However, existing ABSA research relies on coarse-grained categorical labels (e.g., positive, negative), which limits its ability to capture nuanced affective states. To address this limitation, we adopt a dimensional approach that represents sentiment with continuous valence-arousal (VA) scores, enabling fine-grained analysis at both the aspect and sentiment levels. To this end, we introduce DimABSA, the first multilingual, dimensional ABSA resource annotated with both traditional ABSA elements (aspect terms, aspect categories, and opinion terms) and newly introduced VA scores. This resource contains 76,958 aspect instances across 42,590 sentences, spanning six languages and four domains. We further introduce three subtasks that combine VA scores with different ABSA elements, providing a bridge from traditional ABSA to dimensional ABSA. Given that these subtasks involve both categorical and continuous outputs, we propose a new unified metric, continuous F1 (cF1), which incorporates VA prediction error into standard F1. We provide a comprehensive benchmark using both prompted and fine-tuned large language models across all subtasks. Our results show that DimABSA is a challenging benchmark and provides a foundation for advancing multilingual dimensional ABSA.
DimStance: Multilingual Datasets for Dimensional Stance Analysis
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Stance detection is an established task that classifies an author's attitude toward a specific target into categories such as Favor, Neutral, and Against. Beyond categorical stance labels, we leverage a long-established affective science framework to model stance along real-valued dimensions of valence (negative-positive) and arousal (calm-active). This dimensional approach captures nuanced affective states underlying stance expressions, enabling fine-grained stance analysis. To this end, we introduce DimStance, the first dimensional stance resource with valence-arousal (VA) annotations. This resource comprises 11,746 target aspects in 7,365 texts across five languages (English, German, Chinese, Nigerian Pidgin, and Swahili) and two domains (politics and environmental protection). To facilitate the evaluation of stance VA prediction, we formulate the dimensional stance regression task, analyze cross-lingual VA patterns, and benchmark pretrained and large language models under regression and prompting settings. Results show competitive performance of fine-tuned LLM regressors, persistent challenges in low-resource languages, and limitations of token-based generation. DimStance provides a foundation for multilingual, emotion-aware, stance analysis and benchmarking.
Multi-Attribute Multi-Grained Adaptation of Pre-Trained Language Models for Text Understanding from Bayesian Perspective
Mar 08, 2025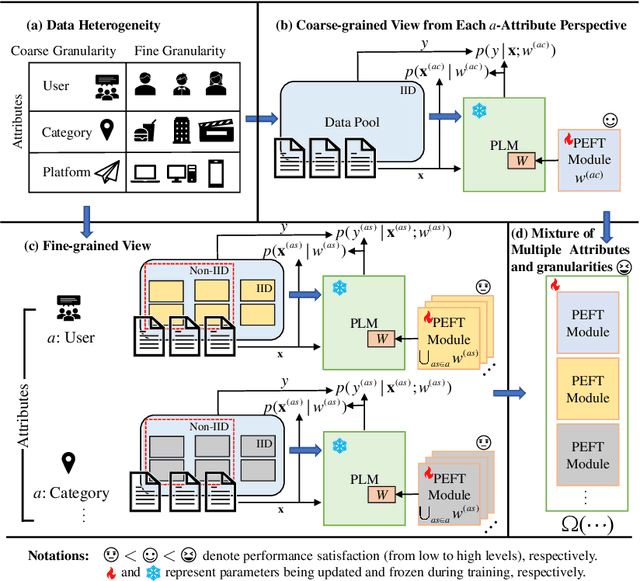
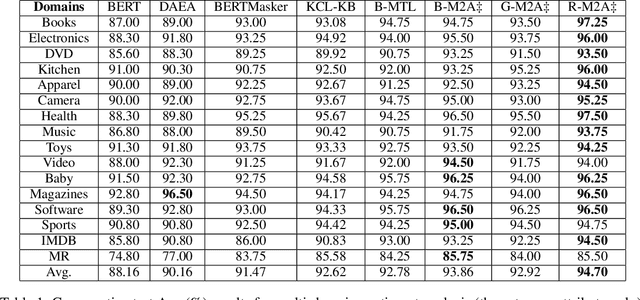
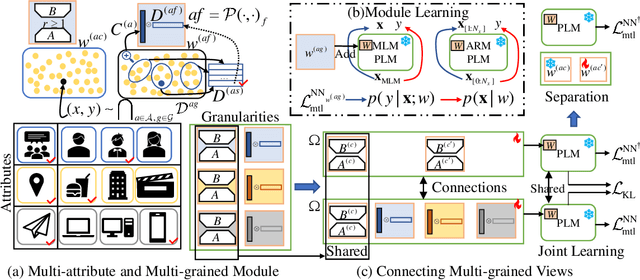
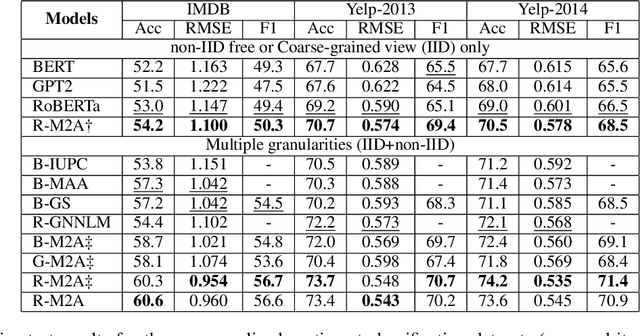
Abstract:Current neural networks often employ multi-domain-learning or attribute-injecting mechanisms to incorporate non-independent and identically distributed (non-IID) information for text understanding tasks by capturing individual characteristics and the relationships among samples. However, the extent of the impact of non-IID information and how these methods affect pre-trained language models (PLMs) remains unclear. This study revisits the assumption that non-IID information enhances PLMs to achieve performance improvements from a Bayesian perspective, which unearths and integrates non-IID and IID features. Furthermore, we proposed a multi-attribute multi-grained framework for PLM adaptations (M2A), which combines multi-attribute and multi-grained views to mitigate uncertainty in a lightweight manner. We evaluate M2A through prevalent text-understanding datasets and demonstrate its superior performance, mainly when data are implicitly non-IID, and PLMs scale larger.
Instruction Tuning with Retrieval-based Examples Ranking for Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis
May 29, 2024



Abstract:Aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA) identifies sentiment information related to specific aspects and provides deeper market insights to businesses and organizations. With the emergence of large language models (LMs), recent studies have proposed using fixed examples for instruction tuning to reformulate ABSA as a generation task. However, the performance is sensitive to the selection of in-context examples; several retrieval methods are based on surface similarity and are independent of the LM generative objective. This study proposes an instruction learning method with retrieval-based example ranking for ABSA tasks. For each target sample, an LM was applied as a scorer to estimate the likelihood of the output given the input and a candidate example as the prompt, and training examples were labeled as positive or negative by ranking the scores. An alternating training schema is proposed to train both the retriever and LM. Instructional prompts can be constructed using high-quality examples. The LM is used for both scoring and inference, improving the generation efficiency without incurring additional computational costs or training difficulties. Extensive experiments on three ABSA subtasks verified the effectiveness of the proposed method, demonstrating its superiority over various strong baseline models. Code and data are released at https://github.com/zgMin/IT-RER-ABSA.
SoftMCL: Soft Momentum Contrastive Learning for Fine-grained Sentiment-aware Pre-training
May 03, 2024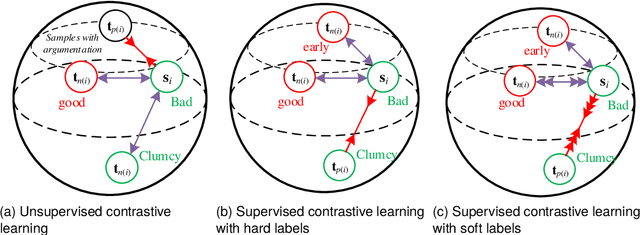

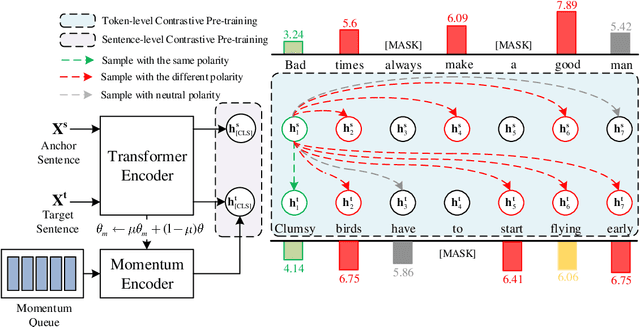

Abstract:The pre-training for language models captures general language understanding but fails to distinguish the affective impact of a particular context to a specific word. Recent works have sought to introduce contrastive learning (CL) for sentiment-aware pre-training in acquiring affective information. Nevertheless, these methods present two significant limitations. First, the compatibility of the GPU memory often limits the number of negative samples, hindering the opportunities to learn good representations. In addition, using only a few sentiment polarities as hard labels, e.g., positive, neutral, and negative, to supervise CL will force all representations to converge to a few points, leading to the issue of latent space collapse. This study proposes a soft momentum contrastive learning (SoftMCL) for fine-grained sentiment-aware pre-training. Instead of hard labels, we introduce valence ratings as soft-label supervision for CL to fine-grained measure the sentiment similarities between samples. The proposed SoftMCL is conducted on both the word- and sentence-level to enhance the model's ability to learn affective information. A momentum queue was introduced to expand the contrastive samples, allowing storing and involving more negatives to overcome the limitations of hardware platforms. Extensive experiments were conducted on four different sentiment-related tasks, which demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed SoftMCL method. The code and data of the proposed SoftMCL is available at: https://www.github.com/wangjin0818/SoftMCL/.
Personalized LoRA for Human-Centered Text Understanding
Mar 10, 2024Abstract:Effectively and efficiently adapting a pre-trained language model (PLM) for human-centered text understanding (HCTU) is challenging since user tokens are million-level in most personalized applications and do not have concrete explicit semantics. A standard and parameter-efficient approach (e.g., LoRA) necessitates memorizing numerous suits of adapters for each user. In this work, we introduce a personalized LoRA (PLoRA) with a plug-and-play (PnP) framework for the HCTU task. PLoRA is effective, parameter-efficient, and dynamically deploying in PLMs. Moreover, a personalized dropout and a mutual information maximizing strategies are adopted and hence the proposed PLoRA can be well adapted to few/zero-shot learning scenarios for the cold-start issue. Experiments conducted on four benchmark datasets show that the proposed method outperforms existing methods in full/few/zero-shot learning scenarios for the HCTU task, even though it has fewer trainable parameters. For reproducibility, the code for this paper is available at: https://github.com/yoyo-yun/PLoRA.
Learning to Memorize Entailment and Discourse Relations for Persona-Consistent Dialogues
Jan 12, 2023Abstract:Maintaining engagement and consistency is particularly important in dialogue systems. Existing works have improved the performance of dialogue systems by intentionally learning interlocutor personas with sophisticated network structures. One issue with this approach is that it requires more personal corpora with annotations. Additionally, these models typically perform the next utterance prediction to generate a response but neglect the discourse coherence in the entire conversation. To address these issues, this study proposes a method of learning to memorize entailment and discourse relations for persona-consistent dialogue tasks. Entailment text pairs in natural language inference dataset were applied to learn latent entailment relations as external memories by premise-to-hypothesis generation task. Furthermore, an internal memory with a similar architecture was applied to the discourse information in the dialogue. Placing orthogonality restrictions on these two memory spaces ensures that the latent entailment relations remain dialogue-independent. Both memories collaborate to obtain entailment and discourse representation for the generation, allowing a deeper understanding of both consistency and coherence. Experiments on two large public datasets, PersonaChat and DSTC7-AVSD, demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed method. Both automatic and human evaluations indicate that the proposed model outperforms several strong baselines in terms of both persona consistency and response coherence. Our source code is available at https://github.com/Chenrj233/LMEDR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge