Lexiong Huang
iCOIL: Scenario Aware Autonomous Parking Via Integrated Constrained Optimization and Imitation Learning
May 23, 2023
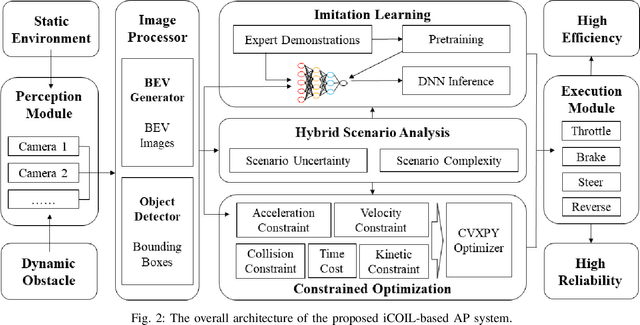

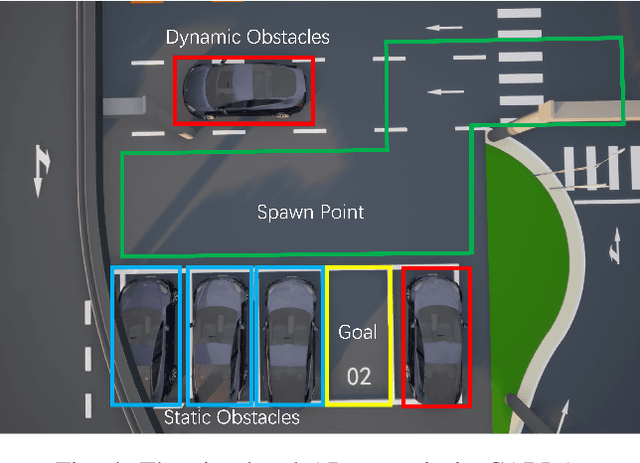
Abstract:Autonomous parking (AP) is an emering technique to navigate an intelligent vehicle to a parking space without any human intervention. Existing AP methods based on mathematical optimization or machine learning may lead to potential failures due to either excessive execution time or lack of generalization. To fill this gap, this paper proposes an integrated constrained optimization and imitation learning (iCOIL) approach to achieve efficient and reliable AP. The iCOIL method has two candidate working modes, i.e., CO and IL, and adopts a hybrid scenario analysis (HSA) model to determine the better mode under various scenarios. We implement and verify iCOIL on the Macao Car Racing Metaverse (MoCAM) platform. Results show that iCOIL properly adapts to different scenarios during the entire AP procedure, and achieves significantly larger success rates than other benchmarks.
Peer-Assisted Robotic Learning: A Data-Driven Collaborative Learning Approach for Cloud Robotic Systems
Oct 16, 2020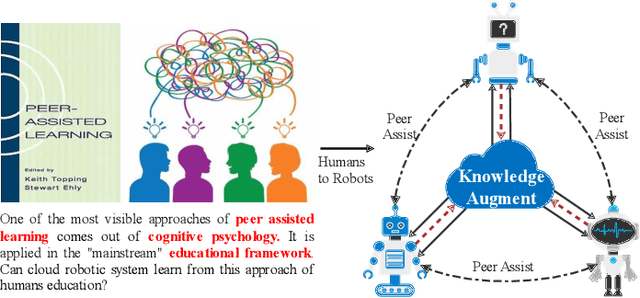
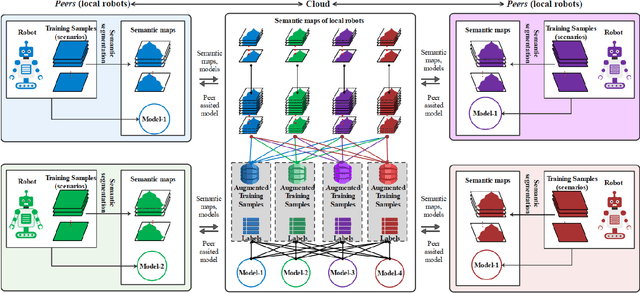
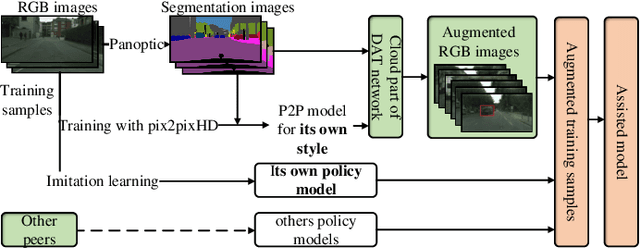
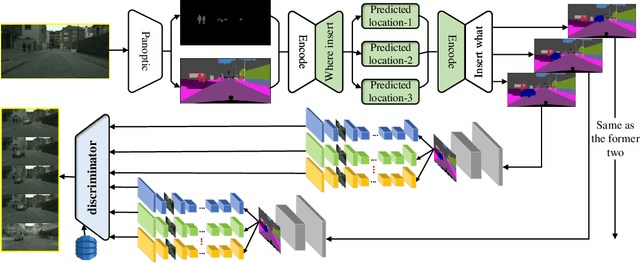
Abstract:A technological revolution is occurring in the field of robotics with the data-driven deep learning technology. However, building datasets for each local robot is laborious. Meanwhile, data islands between local robots make data unable to be utilized collaboratively. To address this issue, the work presents Peer-Assisted Robotic Learning (PARL) in robotics, which is inspired by the peer-assisted learning in cognitive psychology and pedagogy. PARL implements data collaboration with the framework of cloud robotic systems. Both data and models are shared by robots to the cloud after semantic computing and training locally. The cloud converges the data and performs augmentation, integration, and transferring. Finally, fine tune this larger shared dataset in the cloud to local robots. Furthermore, we propose the DAT Network (Data Augmentation and Transferring Network) to implement the data processing in PARL. DAT Network can realize the augmentation of data from multi-local robots. We conduct experiments on a simplified self-driving task for robots (cars). DAT Network has a significant improvement in the augmentation in self-driving scenarios. Along with this, the self-driving experimental results also demonstrate that PARL is capable of improving learning effects with data collaboration of local robots.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge