Lewis Mervin
Temporal Distribution Shift in Real-World Pharmaceutical Data: Implications for Uncertainty Quantification in QSAR Models
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:The estimation of uncertainties associated with predictions from quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) models can accelerate the drug discovery process by identifying promising experiments and allowing an efficient allocation of resources. Several computational tools exist that estimate the predictive uncertainty in machine learning models. However, deviations from the i.i.d. setting have been shown to impair the performance of these uncertainty quantification methods. We use a real-world pharmaceutical dataset to address the pressing need for a comprehensive, large-scale evaluation of uncertainty estimation methods in the context of realistic distribution shifts over time. We investigate the performance of several uncertainty estimation methods, including ensemble-based and Bayesian approaches. Furthermore, we use this real-world setting to systematically assess the distribution shifts in label and descriptor space and their impact on the capability of the uncertainty estimation methods. Our study reveals significant shifts over time in both label and descriptor space and a clear connection between the magnitude of the shift and the nature of the assay. Moreover, we show that pronounced distribution shifts impair the performance of popular uncertainty estimation methods used in QSAR models. This work highlights the challenges of identifying uncertainty quantification methods that remain reliable under distribution shifts introduced by real-world data.
Publishing Neural Networks in Drug Discovery Might Compromise Training Data Privacy
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:This study investigates the risks of exposing confidential chemical structures when machine learning models trained on these structures are made publicly available. We use membership inference attacks, a common method to assess privacy that is largely unexplored in the context of drug discovery, to examine neural networks for molecular property prediction in a black-box setting. Our results reveal significant privacy risks across all evaluated datasets and neural network architectures. Combining multiple attacks increases these risks. Molecules from minority classes, often the most valuable in drug discovery, are particularly vulnerable. We also found that representing molecules as graphs and using message-passing neural networks may mitigate these risks. We provide a framework to assess privacy risks of classification models and molecular representations. Our findings highlight the need for careful consideration when sharing neural networks trained on proprietary chemical structures, informing organisations and researchers about the trade-offs between data confidentiality and model openness.
Enhancing Uncertainty Quantification in Drug Discovery with Censored Regression Labels
Sep 06, 2024



Abstract:In the early stages of drug discovery, decisions regarding which experiments to pursue can be influenced by computational models. These decisions are critical due to the time-consuming and expensive nature of the experiments. Therefore, it is becoming essential to accurately quantify the uncertainty in machine learning predictions, such that resources can be used optimally and trust in the models improves. While computational methods for drug discovery often suffer from limited data and sparse experimental observations, additional information can exist in the form of censored labels that provide thresholds rather than precise values of observations. However, the standard approaches that quantify uncertainty in machine learning cannot fully utilize censored labels. In this work, we adapt ensemble-based, Bayesian, and Gaussian models with tools to learn from censored labels by using the Tobit model from survival analysis. Our results demonstrate that despite the partial information available in censored labels, they are essential to accurately and reliably model the real pharmaceutical setting.
Achieving Well-Informed Decision-Making in Drug Discovery: A Comprehensive Calibration Study using Neural Network-Based Structure-Activity Models
Jul 19, 2024



Abstract:In the drug discovery process, where experiments can be costly and time-consuming, computational models that predict drug-target interactions are valuable tools to accelerate the development of new therapeutic agents. Estimating the uncertainty inherent in these neural network predictions provides valuable information that facilitates optimal decision-making when risk assessment is crucial. However, such models can be poorly calibrated, which results in unreliable uncertainty estimates that do not reflect the true predictive uncertainty. In this study, we compare different metrics, including accuracy and calibration scores, used for model hyperparameter tuning to investigate which model selection strategy achieves well-calibrated models. Furthermore, we propose to use a computationally efficient Bayesian uncertainty estimation method named Bayesian Linear Probing (BLP), which generates Hamiltonian Monte Carlo (HMC) trajectories to obtain samples for the parameters of a Bayesian Logistic Regression fitted to the hidden layer of the baseline neural network. We report that BLP improves model calibration and achieves the performance of common uncertainty quantification methods by combining the benefits of uncertainty estimation and probability calibration methods. Finally, we show that combining post hoc calibration method with well-performing uncertainty quantification approaches can boost model accuracy and calibration.
Industry-Scale Orchestrated Federated Learning for Drug Discovery
Oct 17, 2022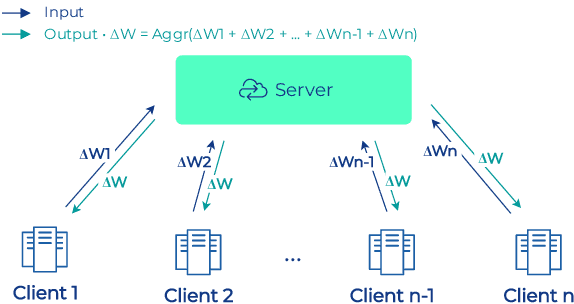
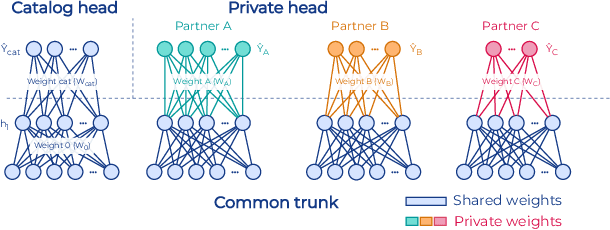
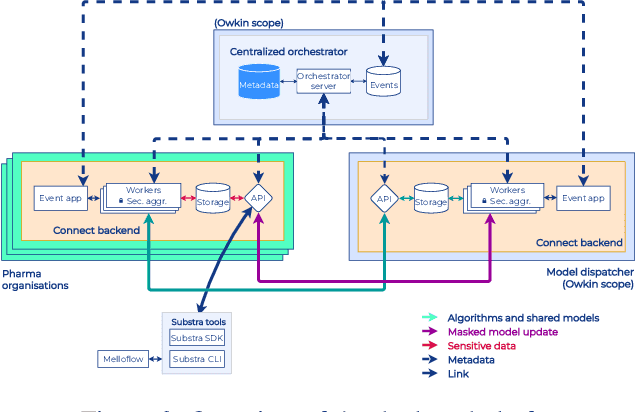
Abstract:To apply federated learning to drug discovery we developed a novel platform in the context of European Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) project MELLODDY (grant n{\deg}831472), which was comprised of 10 pharmaceutical companies, academic research labs, large industrial companies and startups. To the best of our knowledge, The MELLODDY platform was the first industry-scale platform to enable the creation of a global federated model for drug discovery without sharing the confidential data sets of the individual partners. The federated model was trained on the platform by aggregating the gradients of all contributing partners in a cryptographic, secure way following each training iteration. The platform was deployed on an Amazon Web Services (AWS) multi-account architecture running Kubernetes clusters in private subnets. Organisationally, the roles of the different partners were codified as different rights and permissions on the platform and administrated in a decentralized way. The MELLODDY platform generated new scientific discoveries which are described in a companion paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge