Leonard Hackel
Technische Universität Berlin, Berlin Institute for the Foundations of Learning and Data
How Much of a Model Do We Need? Redundancy and Slimmability in Remote Sensing Foundation Models
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Large-scale foundation models (FMs) in remote sensing (RS) are developed based on the paradigms established in computer vision (CV) and have shown promise for various Earth observation applications. However, the direct transfer of scaling assumptions from CV to RS has not been adequately examined. We hypothesize that RS FMs enter an overparameterized regime at substantially smaller scales than their CV counterparts, where increasing parameter count primarily induces redundant representations rather than qualitatively new abstractions. To test this hypothesis, we use post-hoc slimming, where we uniformly reduce the width of pretrained encoder, as a tool to measure representational redundancy across six state-of-the-art RS FMs on four downstream classification tasks. Our findings reveal a significant contrast with those in the CV domain: while a post-hoc slimmed masked autoencoder (MAE) trained on ImageNet retains less than 10% accuracy at 1% FLOPs, RS FMs maintain over 71% relative accuracy at the same budget. This sevenfold difference provides strong empirical support for our hypothesis. We further demonstrate that learned slimmable training can improve both Momentum Contrast (MoCo)- and MAE- based models. In addition, through the explained variance ratio and the feature correlation analysis, we provide mechanistic explanations showing that RS FMs distribute task-relevant information with high redundancy. Our findings establish post-hoc slimmability as both a practical deployment strategy for resource-constrained environments and a diagnostic tool that challenges the prevailing scaling paradigm in RS. Upon acceptance, we will publish all code.
Rank-based Geographical Regularization: Revisiting Contrastive Self-Supervised Learning for Multispectral Remote Sensing Imagery
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) has become a powerful paradigm for learning from large, unlabeled datasets, particularly in computer vision (CV). However, applying SSL to multispectral remote sensing (RS) images presents unique challenges and opportunities due to the geographical and temporal variability of the data. In this paper, we introduce GeoRank, a novel regularization method for contrastive SSL that improves upon prior techniques by directly optimizing spherical distances to embed geographical relationships into the learned feature space. GeoRank outperforms or matches prior methods that integrate geographical metadata and consistently improves diverse contrastive SSL algorithms (e.g., BYOL, DINO). Beyond this, we present a systematic investigation of key adaptations of contrastive SSL for multispectral RS images, including the effectiveness of data augmentations, the impact of dataset cardinality and image size on performance, and the task dependency of temporal views. Code is available at https://github.com/tomburgert/georank.
CSMoE: An Efficient Remote Sensing Foundation Model with Soft Mixture-of-Experts
Sep 17, 2025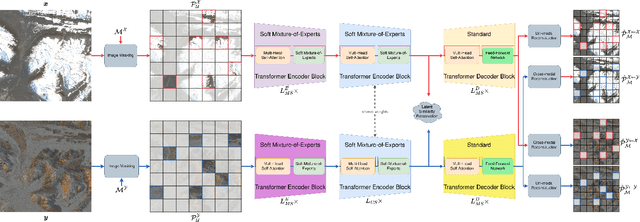
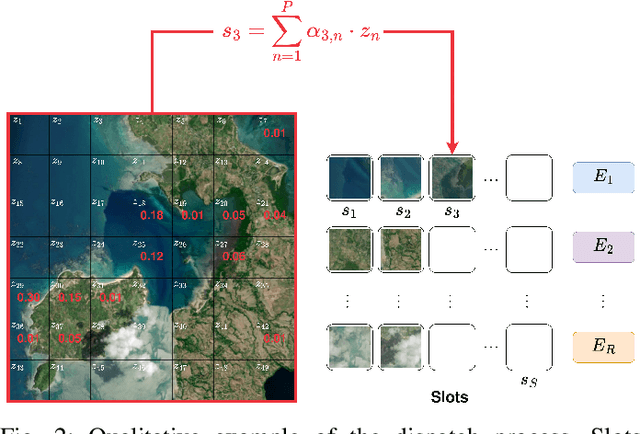
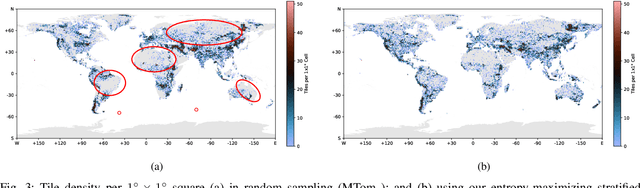

Abstract:Self-supervised learning through masked autoencoders has attracted great attention for remote sensing (RS) foundation model (FM) development, enabling improved representation learning across diverse sensors and downstream tasks. However, existing RS FMs often either suffer from substantial computational complexity during both training and inference or exhibit limited representational capacity. These issues restrict their practical applicability in RS. To address this limitation, we propose an adaptation for enhancing the efficiency of RS FMs by integrating the Soft mixture-of-experts (MoE) mechanism into the FM. The integration of Soft MoEs into the FM allows modality-specific expert specialization alongside shared cross-sensor representation learning. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our adaptation, we apply it on the Cross-Sensor Masked Autoencoder (CSMAE) model, resulting in the Cross-Sensor Mixture-of-Experts (CSMoE) model. In addition, we introduce a thematic-climatic descriptor-driven sampling strategy for the construction of a representative and diverse training set to train our CSMoE model. Extensive experiments on scene classification, semantic segmentation, and content-based image retrieval demonstrate that our adaptation yields a reduction in computational requirements while maintaining or improving representational performance. Compared to state-of-the-art RS FMs, CSMoE achieves a superior trade-off between representational capacity, accuracy, and computational efficiency. On average, CSMoE achieves more than twice the computational efficiency of existing RS FMs, while maintaining competitive performance across all experiments. These results show the effectiveness of the proposed adaptation for creating computationally efficient RS FMs. The code for the model, the training set creation, and the model weights will be available at https://git.tu-berlin.de/rsim/csmoe.
Redundancy-Aware Pretraining of Vision-Language Foundation Models in Remote Sensing
May 16, 2025Abstract:The development of foundation models through pretraining of vision-language models (VLMs) has recently attracted great attention in remote sensing (RS). VLM pretraining aims to learn image and language alignments from a large number of image-text pairs. Each pretraining image is often associated with multiple captions containing redundant information due to repeated or semantically similar phrases, resulting in increased pretraining and inference time. To overcome this, we introduce a weighted feature aggregation (WFA) strategy for VLM pretraining in RS. Our strategy aims to extract and exploit complementary information from multiple captions per image while reducing redundancies through feature aggregation with importance weighting. To calculate adaptive importance weights for different captions of each image, we propose two techniques: (i) non-parametric uniqueness and (ii) learning-based attention. In the first technique, importance weights are calculated based on the bilingual evaluation understudy (BLEU) scores of the captions to emphasize unique sentences and reduce the influence of repetitive ones. In the second technique, importance weights are learned through an attention mechanism instead of relying on hand-crafted features. The effectiveness of the proposed WFA strategy with the two techniques is analyzed in terms of downstream performance on text-to-image retrieval in RS. Experimental results show that the proposed strategy enables efficient and effective pretraining of VLMs in RS. Based on the experimental analysis, we derive guidelines for selecting appropriate techniques depending on downstream task requirements and resource constraints. The code of this work is publicly available at https://git.tu-berlin.de/rsim/redundacy-aware-rs-vlm.
reBEN: Refined BigEarthNet Dataset for Remote Sensing Image Analysis
Jul 04, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents refined BigEarthNet (reBEN) that is a large-scale, multi-modal remote sensing dataset constructed to support deep learning (DL) studies for remote sensing image analysis. The reBEN dataset consists of 549,488 pairs of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 image patches. To construct reBEN, we initially consider the Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 tiles used to construct the BigEarthNet dataset and then divide them into patches of size 1200 m x 1200 m. We apply atmospheric correction to the Sentinel-2 patches using the latest version of the sen2cor tool, resulting in higher-quality patches compared to those present in BigEarthNet. Each patch is then associated with a pixel-level reference map and scene-level multi-labels. This makes reBEN suitable for pixel- and scene-based learning tasks. The labels are derived from the most recent CORINE Land Cover (CLC) map of 2018 by utilizing the 19-class nomenclature as in BigEarthNet. The use of the most recent CLC map results in overcoming the label noise present in BigEarthNet. Furthermore, we introduce a new geographical-based split assignment algorithm that significantly reduces the spatial correlation among the train, validation, and test sets with respect to those present in BigEarthNet. This increases the reliability of the evaluation of DL models. To minimize the DL model training time, we introduce software tools that convert the reBEN dataset into a DL-optimized data format. In our experiments, we show the potential of reBEN for multi-modal multi-label image classification problems by considering several state-of-the-art DL models. The pre-trained model weights, associated code, and complete dataset are available at https://bigearth.net.
LiT-4-RSVQA: Lightweight Transformer-based Visual Question Answering in Remote Sensing
Jun 02, 2023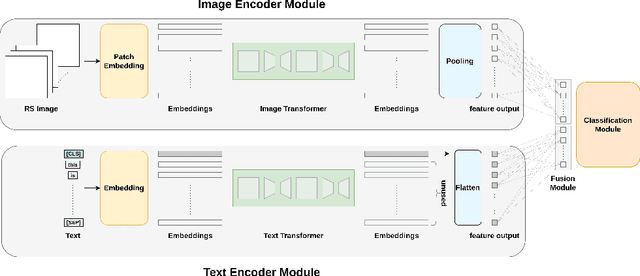
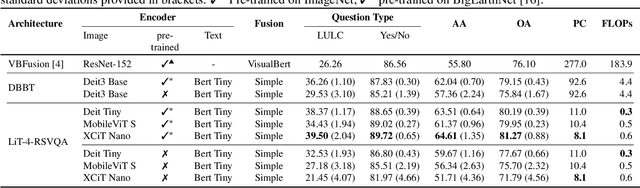
Abstract:Visual question answering (VQA) methods in remote sensing (RS) aim to answer natural language questions with respect to an RS image. Most of the existing methods require a large amount of computational resources, which limits their application in operational scenarios in RS. To address this issue, in this paper we present an effective lightweight transformer-based VQA in RS (LiT-4-RSVQA) architecture for efficient and accurate VQA in RS. Our architecture consists of: i) a lightweight text encoder module; ii) a lightweight image encoder module; iii) a fusion module; and iv) a classification module. The experimental results obtained on a VQA benchmark dataset demonstrate that our proposed LiT-4-RSVQA architecture provides accurate VQA results while significantly reducing the computational requirements on the executing hardware. Our code is publicly available at https://git.tu-berlin.de/rsim/lit4rsvqa.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge