Leizhen Dong
Category-Aware Transformer Network for Better Human-Object Interaction Detection
Apr 11, 2022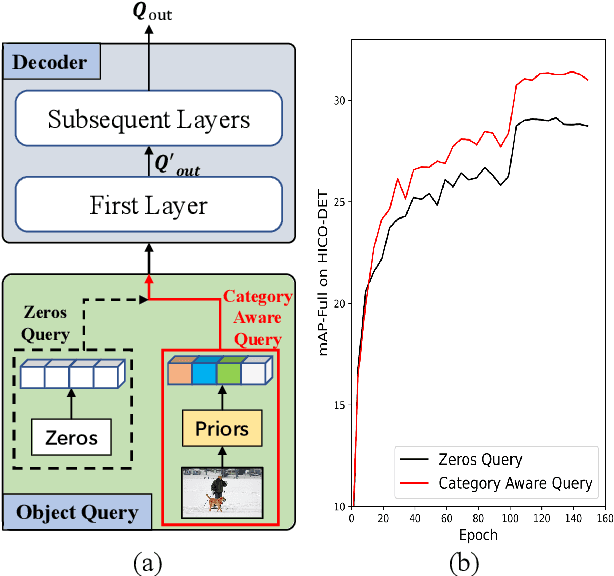
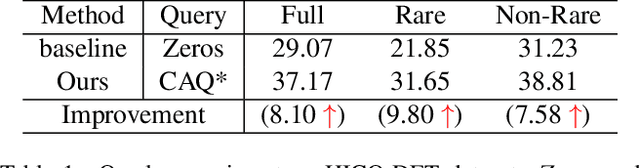
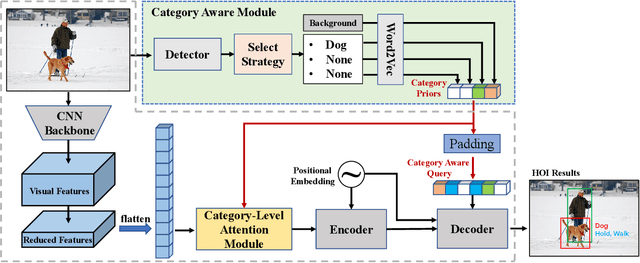
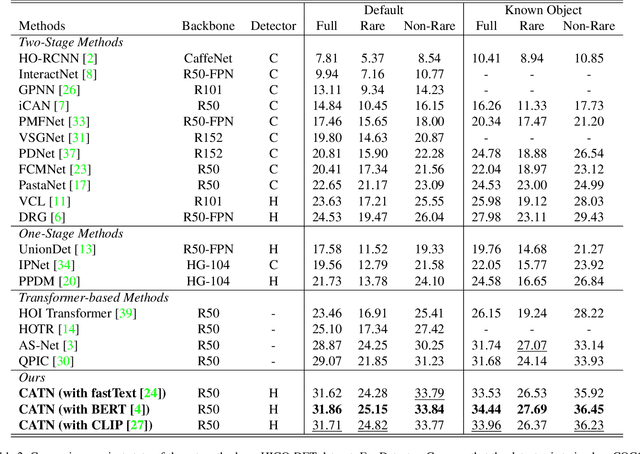
Abstract:Human-Object Interactions (HOI) detection, which aims to localize a human and a relevant object while recognizing their interaction, is crucial for understanding a still image. Recently, transformer-based models have significantly advanced the progress of HOI detection. However, the capability of these models has not been fully explored since the Object Query of the model is always simply initialized as just zeros, which would affect the performance. In this paper, we try to study the issue of promoting transformer-based HOI detectors by initializing the Object Query with category-aware semantic information. To this end, we innovatively propose the Category-Aware Transformer Network (CATN). Specifically, the Object Query would be initialized via category priors represented by an external object detection model to yield better performance. Moreover, such category priors can be further used for enhancing the representation ability of features via the attention mechanism. We have firstly verified our idea via the Oracle experiment by initializing the Object Query with the groundtruth category information. And then extensive experiments have been conducted to show that a HOI detection model equipped with our idea outperforms the baseline by a large margin to achieve a new state-of-the-art result.
Effective Actor-centric Human-object Interaction Detection
Feb 24, 2022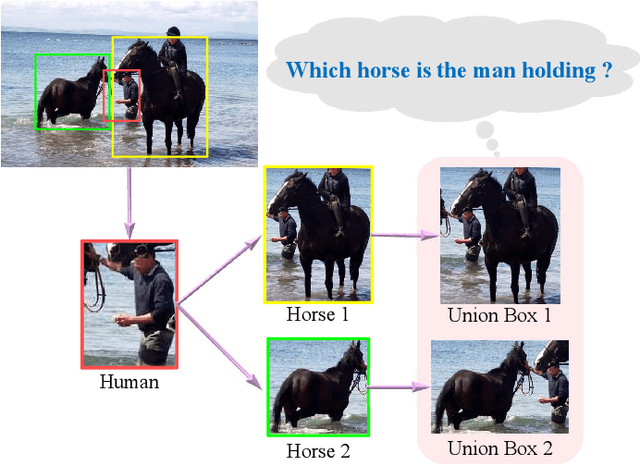
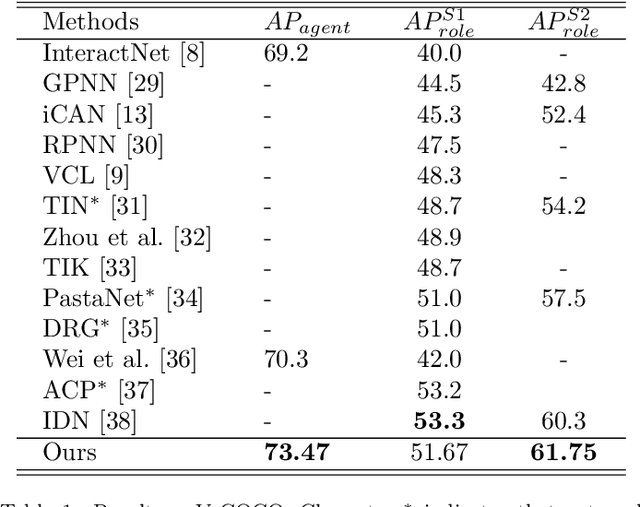
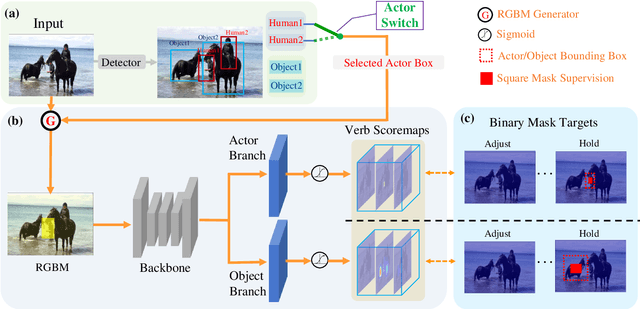
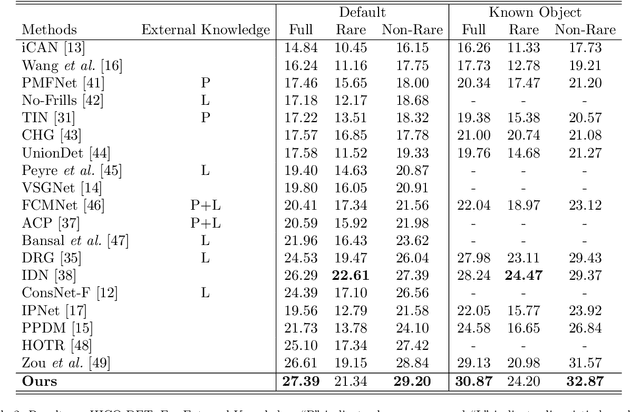
Abstract:While Human-Object Interaction(HOI) Detection has achieved tremendous advances in recent, it still remains challenging due to complex interactions with multiple humans and objects occurring in images, which would inevitably lead to ambiguities. Most existing methods either generate all human-object pair candidates and infer their relationships by cropped local features successively in a two-stage manner, or directly predict interaction points in a one-stage procedure. However, the lack of spatial configurations or reasoning steps of two- or one- stage methods respectively limits their performance in such complex scenes. To avoid this ambiguity, we propose a novel actor-centric framework. The main ideas are that when inferring interactions: 1) the non-local features of the entire image guided by actor position are obtained to model the relationship between the actor and context, and then 2) we use an object branch to generate pixel-wise interaction area prediction, where the interaction area denotes the object central area. Moreover, we also use an actor branch to get interaction prediction of the actor and propose a novel composition strategy based on center-point indexing to generate the final HOI prediction. Thanks to the usage of the non-local features and the partly-coupled property of the human-objects composition strategy, our proposed framework can detect HOI more accurately especially for complex images. Extensive experimental results show that our method achieves the state-of-the-art on the challenging V-COCO and HICO-DET benchmarks and is more robust especially in multiple persons and/or objects scenes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge