Lane McIntosh
From deep learning to mechanistic understanding in neuroscience: the structure of retinal prediction
Dec 12, 2019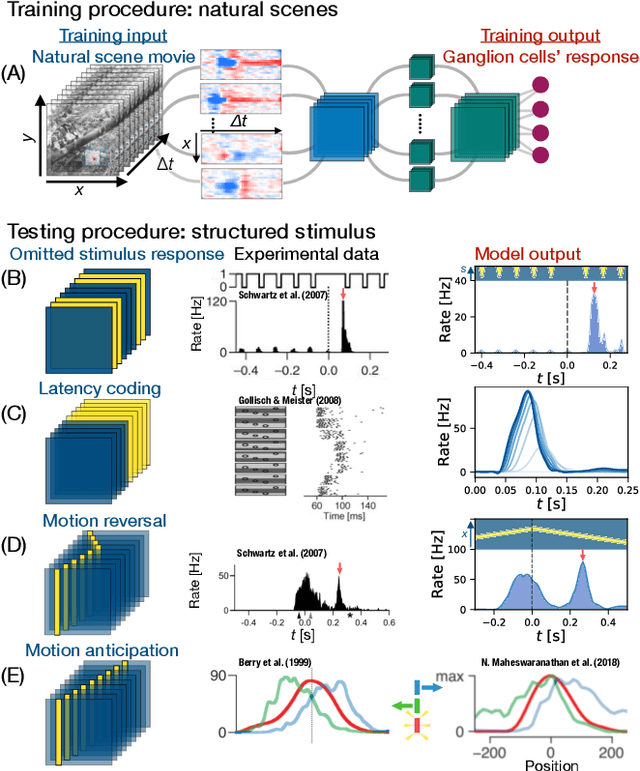
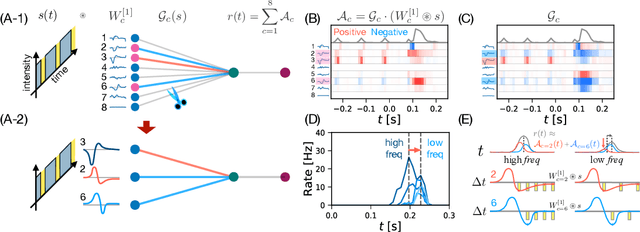
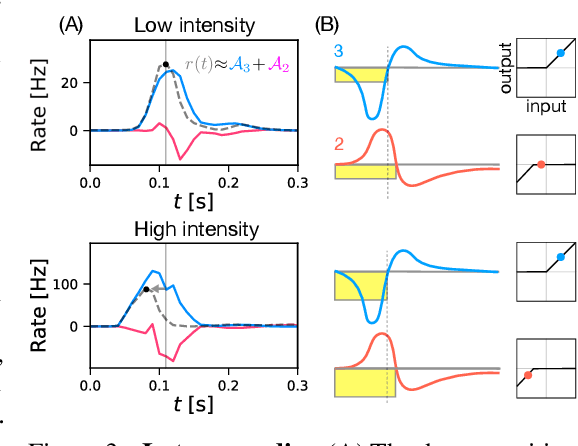
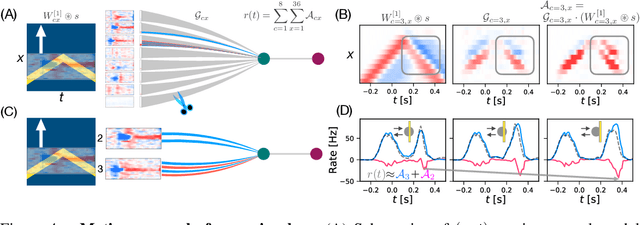
Abstract:Recently, deep feedforward neural networks have achieved considerable success in modeling biological sensory processing, in terms of reproducing the input-output map of sensory neurons. However, such models raise profound questions about the very nature of explanation in neuroscience. Are we simply replacing one complex system (a biological circuit) with another (a deep network), without understanding either? Moreover, beyond neural representations, are the deep network's computational mechanisms for generating neural responses the same as those in the brain? Without a systematic approach to extracting and understanding computational mechanisms from deep neural network models, it can be difficult both to assess the degree of utility of deep learning approaches in neuroscience, and to extract experimentally testable hypotheses from deep networks. We develop such a systematic approach by combining dimensionality reduction and modern attribution methods for determining the relative importance of interneurons for specific visual computations. We apply this approach to deep network models of the retina, revealing a conceptual understanding of how the retina acts as a predictive feature extractor that signals deviations from expectations for diverse spatiotemporal stimuli. For each stimulus, our extracted computational mechanisms are consistent with prior scientific literature, and in one case yields a new mechanistic hypothesis. Thus overall, this work not only yields insights into the computational mechanisms underlying the striking predictive capabilities of the retina, but also places the framework of deep networks as neuroscientific models on firmer theoretical foundations, by providing a new roadmap to go beyond comparing neural representations to extracting and understand computational mechanisms.
Recurrent Segmentation for Variable Computational Budgets
Mar 15, 2018
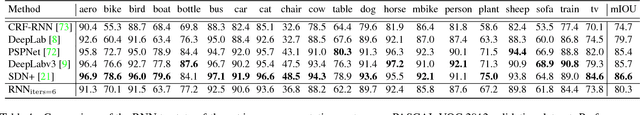
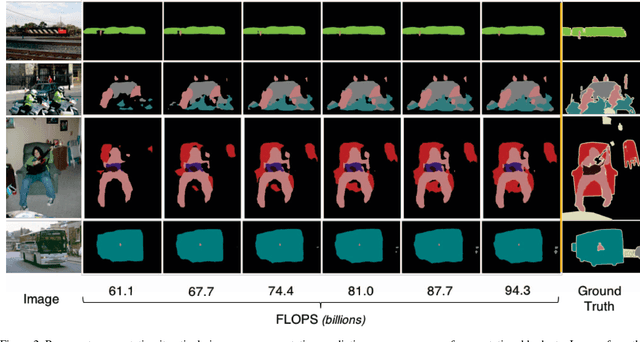
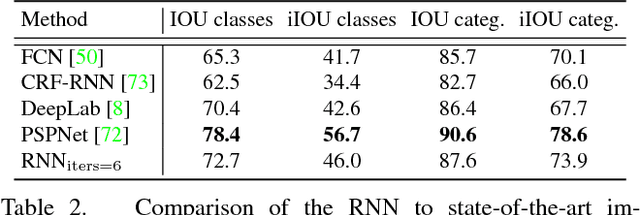
Abstract:State-of-the-art systems for semantic image segmentation use feed-forward pipelines with fixed computational costs. Building an image segmentation system that works across a range of computational budgets is challenging and time-intensive as new architectures must be designed and trained for every computational setting. To address this problem we develop a recurrent neural network that successively improves prediction quality with each iteration. Importantly, the RNN may be deployed across a range of computational budgets by merely running the model for a variable number of iterations. We find that this architecture is uniquely suited for efficiently segmenting videos. By exploiting the segmentation of past frames, the RNN can perform video segmentation at similar quality but reduced computational cost compared to state-of-the-art image segmentation methods. When applied to static images in the PASCAL VOC 2012 and Cityscapes segmentation datasets, the RNN traces out a speed-accuracy curve that saturates near the performance of state-of-the-art segmentation methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge