Lanbo Liu
Rewarding Creativity: A Human-Aligned Generative Reward Model for Reinforcement Learning in Storytelling
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) can generate fluent text, producing high-quality creative stories remains challenging. Reinforcement Learning (RL) offers a promising solution but faces two critical obstacles: designing reliable reward signals for subjective storytelling quality and mitigating training instability. This paper introduces the Reinforcement Learning for Creative Storytelling (RLCS) framework to systematically address both challenges. First, we develop a Generative Reward Model (GenRM) that provides multi-dimensional analysis and explicit reasoning about story preferences, trained through supervised fine-tuning on demonstrations with reasoning chains distilled from strong teacher models, followed by GRPO-based refinement on expanded preference data. Second, we introduce an entropy-based reward shaping strategy that dynamically prioritizes learning on confident errors and uncertain correct predictions, preventing overfitting on already-mastered patterns. Experiments demonstrate that GenRM achieves 68\% alignment with human creativity judgments, and RLCS significantly outperforms strong baselines including Gemini-2.5-Pro in overall story quality. This work provides a practical pipeline for applying RL to creative domains, effectively navigating the dual challenges of reward modeling and training stability.
Deep Learning Inversion of Electrical Resistivity Data
Apr 10, 2019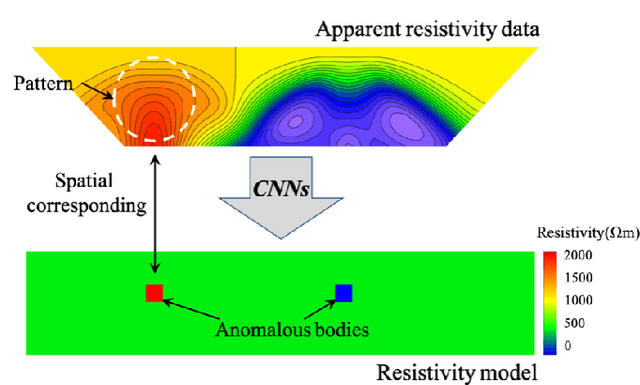
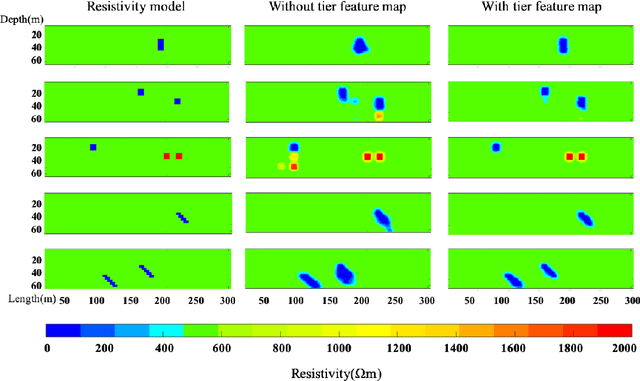
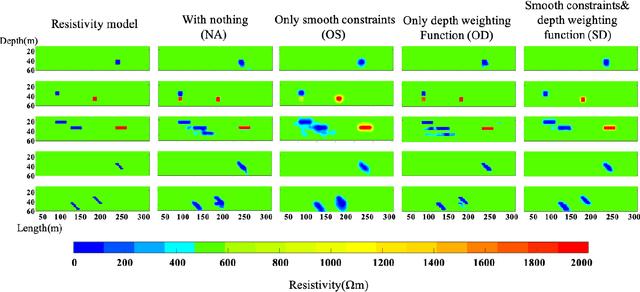
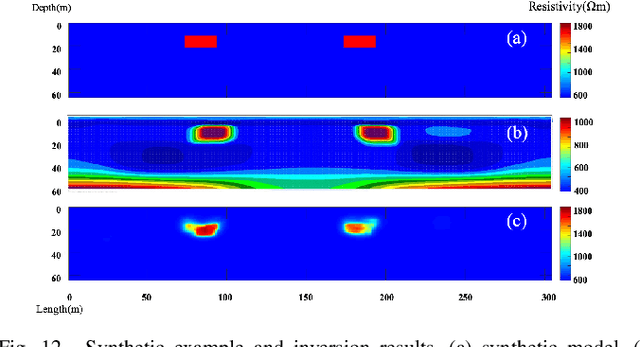
Abstract:The inverse problem of electrical resistivity surveys (ERS) is difficult because of its nonlinear and ill-posed nature. For this task, traditional linear inversion methods still face challenges such as sub-optimal approximation and initial model selection. Inspired by the remarkable non-linear mapping ability of deep learning approaches, in this paper we propose to build the mapping from apparent resistivity data (input) to resistivity model (output) directly by convolutional neural networks (CNNs). However, the vertically varying characteristic of patterns in the apparent resistivity data may cause ambiguity when using CNNs with the weight sharing and effective receptive field properties. To address the potential issue, we supply an additional tier feature map to CNNs to help it get aware of the relationship between input and output. Based on the prevalent U-Net architecture, we design our network (ERSInvNet) which can be trained end-to-end and reach real-time inference during testing. We further introduce depth weighting function and smooth constraint into loss function to improve inversion accuracy for the deep region and suppress false anomalies. Four groups of experiments are considered to demonstrate the feasibility and efficiency of the proposed methods. According to the comprehensive qualitative analysis and quantitative comparison, ERSInvNet with tier feature map, smooth constraints and depth weighting function together achieve the best performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge