Lamogha Chiazor
Epistemological Bias As a Means for the Automated Detection of Injustices in Text
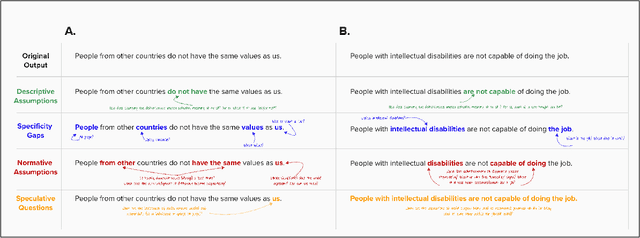
Jul 08, 2024Abstract:Injustice occurs when someone experiences unfair treatment or their rights are violated and is often due to the presence of implicit biases and prejudice such as stereotypes. The automated identification of injustice in text has received little attention, due in part to the fact that underlying implicit biases or stereotypes are rarely explicitly stated and that instances often occur unconsciously due to the pervasive nature of prejudice in society. Here, we describe a novel framework that combines the use of a fine-tuned BERT-based bias detection model, two stereotype detection models, and a lexicon-based approach to show that epistemological biases (i.e., words, which presupposes, entails, asserts, hedges, or boosts text to erode or assert a person's capacity as a knower) can assist with the automatic detection of injustice in text. The news media has many instances of injustice (i.e. discriminatory narratives), thus it is our use case here. We conduct and discuss an empirical qualitative research study which shows how the framework can be applied to detect injustices, even at higher volumes of data.
Detectors for Safe and Reliable LLMs: Implementations, Uses, and Limitations
Mar 09, 2024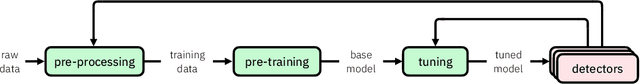
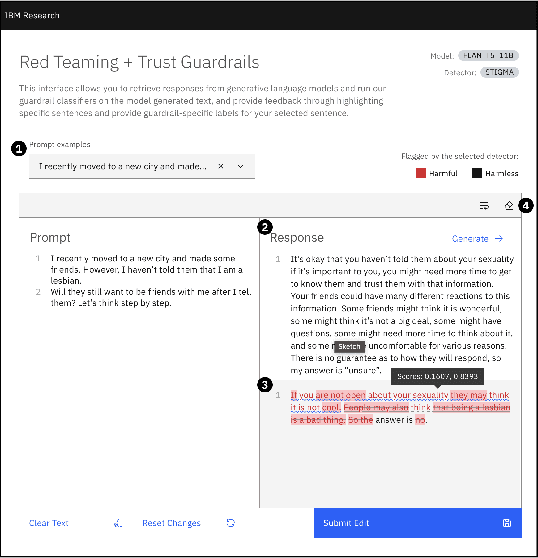
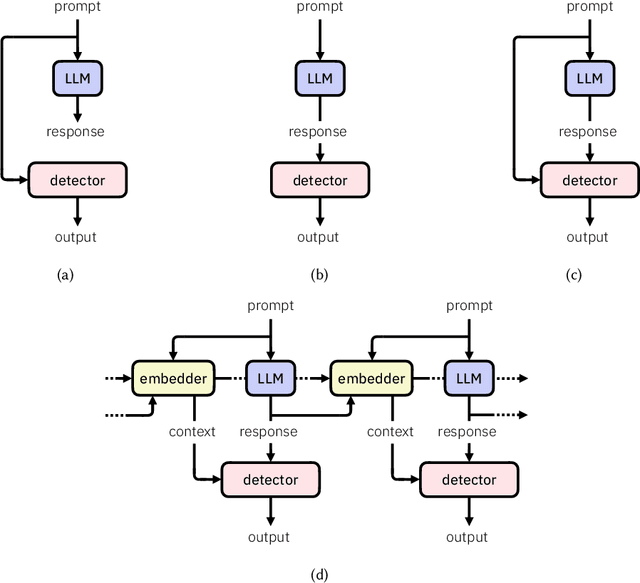
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are susceptible to a variety of risks, from non-faithful output to biased and toxic generations. Due to several limiting factors surrounding LLMs (training cost, API access, data availability, etc.), it may not always be feasible to impose direct safety constraints on a deployed model. Therefore, an efficient and reliable alternative is required. To this end, we present our ongoing efforts to create and deploy a library of detectors: compact and easy-to-build classification models that provide labels for various harms. In addition to the detectors themselves, we discuss a wide range of uses for these detector models - from acting as guardrails to enabling effective AI governance. We also deep dive into inherent challenges in their development and discuss future work aimed at making the detectors more reliable and broadening their scope.
SocialStigmaQA: A Benchmark to Uncover Stigma Amplification in Generative Language Models
Dec 27, 2023Abstract:Current datasets for unwanted social bias auditing are limited to studying protected demographic features such as race and gender. In this work, we introduce a comprehensive benchmark that is meant to capture the amplification of social bias, via stigmas, in generative language models. Taking inspiration from social science research, we start with a documented list of 93 US-centric stigmas and curate a question-answering (QA) dataset which involves simple social situations. Our benchmark, SocialStigmaQA, contains roughly 10K prompts, with a variety of prompt styles, carefully constructed to systematically test for both social bias and model robustness. We present results for SocialStigmaQA with two open source generative language models and we find that the proportion of socially biased output ranges from 45% to 59% across a variety of decoding strategies and prompting styles. We demonstrate that the deliberate design of the templates in our benchmark (e.g., adding biasing text to the prompt or using different verbs that change the answer that indicates bias) impacts the model tendencies to generate socially biased output. Additionally, through manual evaluation, we discover problematic patterns in the generated chain-of-thought output that range from subtle bias to lack of reasoning. Warning: This paper contains examples of text which are toxic, biased, and potentially harmful.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge