Léo Jacqmin
LIS
Are cascade dialogue state tracking models speaking out of turn in spoken dialogues?
Nov 03, 2023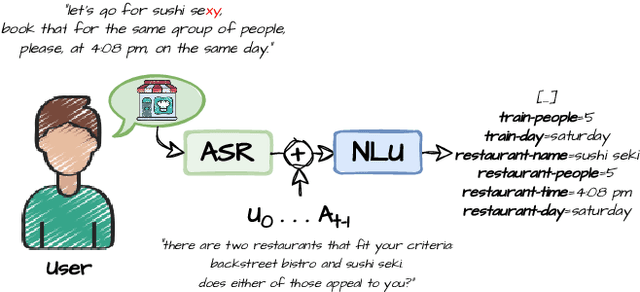

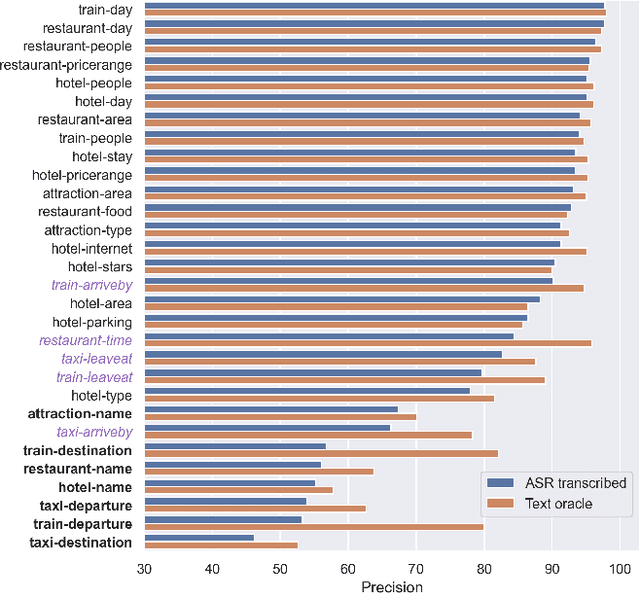
Abstract:In Task-Oriented Dialogue (TOD) systems, correctly updating the system's understanding of the user's needs is key to a smooth interaction. Traditionally TOD systems are composed of several modules that interact with one another. While each of these components is the focus of active research communities, their behavior in interaction can be overlooked. This paper proposes a comprehensive analysis of the errors of state of the art systems in complex settings such as Dialogue State Tracking which highly depends on the dialogue context. Based on spoken MultiWoz, we identify that errors on non-categorical slots' values are essential to address in order to bridge the gap between spoken and chat-based dialogue systems. We explore potential solutions to improve transcriptions and help dialogue state tracking generative models correct such errors.
OLISIA: a Cascade System for Spoken Dialogue State Tracking
Apr 20, 2023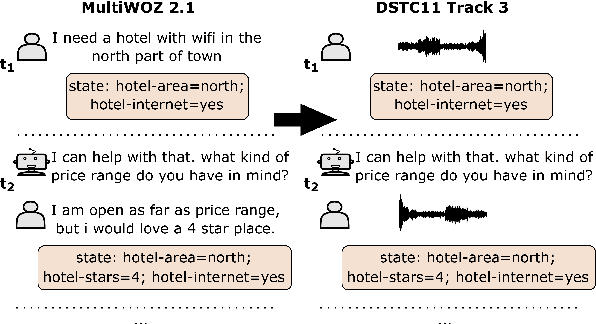
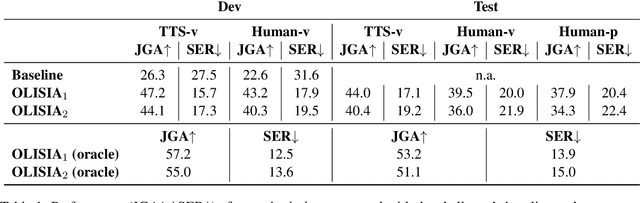

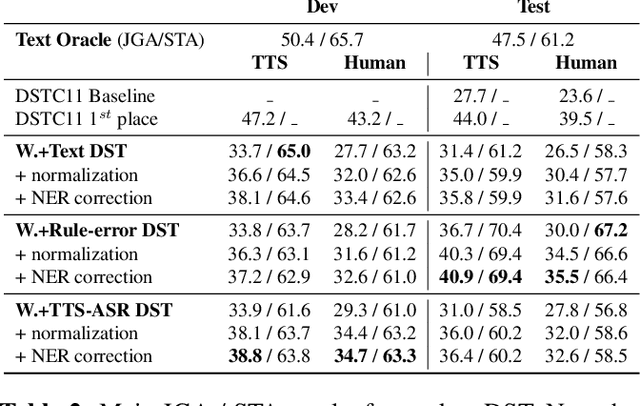
Abstract:Though Dialogue State Tracking (DST) is a core component of spoken dialogue systems, recent work on this task mostly deals with chat corpora, disregarding the discrepancies between spoken and written language.In this paper, we propose OLISIA, a cascade system which integrates an Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) model and a DST model. We introduce several adaptations in the ASR and DST modules to improve integration and robustness to spoken conversations.With these adaptations, our system ranked first in DSTC11 Track 3, a benchmark to evaluate spoken DST. We conduct an in-depth analysis of the results and find that normalizing the ASR outputs and adapting the DST inputs through data augmentation, along with increasing the pre-trained models size all play an important role in reducing the performance discrepancy between written and spoken conversations.
"Do you follow me?": A Survey of Recent Approaches in Dialogue State Tracking
Jul 29, 2022



Abstract:While communicating with a user, a task-oriented dialogue system has to track the user's needs at each turn according to the conversation history. This process called dialogue state tracking (DST) is crucial because it directly informs the downstream dialogue policy. DST has received a lot of interest in recent years with the text-to-text paradigm emerging as the favored approach. In this review paper, we first present the task and its associated datasets. Then, considering a large number of recent publications, we identify highlights and advances of research in 2021-2022. Although neural approaches have enabled significant progress, we argue that some critical aspects of dialogue systems such as generalizability are still underexplored. To motivate future studies, we propose several research avenues.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge