Kyle Martin
iSee: Advancing Multi-Shot Explainable AI Using Case-based Recommendations
Aug 23, 2024



Abstract:Explainable AI (XAI) can greatly enhance user trust and satisfaction in AI-assisted decision-making processes. Recent findings suggest that a single explainer may not meet the diverse needs of multiple users in an AI system; indeed, even individual users may require multiple explanations. This highlights the necessity for a "multi-shot" approach, employing a combination of explainers to form what we introduce as an "explanation strategy". Tailored to a specific user or a user group, an "explanation experience" describes interactions with personalised strategies designed to enhance their AI decision-making processes. The iSee platform is designed for the intelligent sharing and reuse of explanation experiences, using Case-based Reasoning to advance best practices in XAI. The platform provides tools that enable AI system designers, i.e. design users, to design and iteratively revise the most suitable explanation strategy for their AI system to satisfy end-user needs. All knowledge generated within the iSee platform is formalised by the iSee ontology for interoperability. We use a summative mixed methods study protocol to evaluate the usability and utility of the iSee platform with six design users across varying levels of AI and XAI expertise. Our findings confirm that the iSee platform effectively generalises across applications and its potential to promote the adoption of XAI best practices.
XEQ Scale for Evaluating XAI Experience Quality Grounded in Psychometric Theory
Jul 15, 2024Abstract:Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) aims to improve the transparency of autonomous decision-making through explanations. Recent literature has emphasised users' need for holistic "multi-shot" explanations and the ability to personalise their engagement with XAI systems. We refer to this user-centred interaction as an XAI Experience. Despite advances in creating XAI experiences, evaluating them in a user-centred manner has remained challenging. To address this, we introduce the XAI Experience Quality (XEQ) Scale (pronounced "Seek" Scale), for evaluating the user-centred quality of XAI experiences. Furthermore, XEQ quantifies the quality of experiences across four evaluation dimensions: learning, utility, fulfilment and engagement. These contributions extend the state-of-the-art of XAI evaluation, moving beyond the one-dimensional metrics frequently developed to assess single-shot explanations. In this paper, we present the XEQ scale development and validation process, including content validation with XAI experts as well as discriminant and construct validation through a large-scale pilot study. Out pilot study results offer strong evidence that establishes the XEQ Scale as a comprehensive framework for evaluating user-centred XAI experiences.
Tell me more: Intent Fulfilment Framework for Enhancing User Experiences in Conversational XAI
May 16, 2024Abstract:The evolution of Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) has emphasised the significance of meeting diverse user needs. The approaches to identifying and addressing these needs must also advance, recognising that explanation experiences are subjective, user-centred processes that interact with users towards a better understanding of AI decision-making. This paper delves into the interrelations in multi-faceted XAI and examines how different types of explanations collaboratively meet users' XAI needs. We introduce the Intent Fulfilment Framework (IFF) for creating explanation experiences. The novelty of this paper lies in recognising the importance of "follow-up" on explanations for obtaining clarity, verification and/or substitution. Moreover, the Explanation Experience Dialogue Model integrates the IFF and "Explanation Followups" to provide users with a conversational interface for exploring their explanation needs, thereby creating explanation experiences. Quantitative and qualitative findings from our comparative user study demonstrate the impact of the IFF in improving user engagement, the utility of the AI system and the overall user experience. Overall, we reinforce the principle that "one explanation does not fit all" to create explanation experiences that guide the complex interaction through conversation.
CBR-RAG: Case-Based Reasoning for Retrieval Augmented Generation in LLMs for Legal Question Answering
Apr 04, 2024Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances Large Language Model (LLM) output by providing prior knowledge as context to input. This is beneficial for knowledge-intensive and expert reliant tasks, including legal question-answering, which require evidence to validate generated text outputs. We highlight that Case-Based Reasoning (CBR) presents key opportunities to structure retrieval as part of the RAG process in an LLM. We introduce CBR-RAG, where CBR cycle's initial retrieval stage, its indexing vocabulary, and similarity knowledge containers are used to enhance LLM queries with contextually relevant cases. This integration augments the original LLM query, providing a richer prompt. We present an evaluation of CBR-RAG, and examine different representations (i.e. general and domain-specific embeddings) and methods of comparison (i.e. inter, intra and hybrid similarity) on the task of legal question-answering. Our results indicate that the context provided by CBR's case reuse enforces similarity between relevant components of the questions and the evidence base leading to significant improvements in the quality of generated answers.
Clinical Dialogue Transcription Error Correction using Seq2Seq Models
May 26, 2022



Abstract:Good communication is critical to good healthcare. Clinical dialogue is a conversation between health practitioners and their patients, with the explicit goal of obtaining and sharing medical information. This information contributes to medical decision-making regarding the patient and plays a crucial role in their healthcare journey. The reliance on note taking and manual scribing processes are extremely inefficient and leads to manual transcription errors when digitizing notes. Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) plays a significant role in speech-to-text applications, and can be directly used as a text generator in conversational applications. However, recording clinical dialogue presents a number of general and domain-specific challenges. In this paper, we present a seq2seq learning approach for ASR transcription error correction of clinical dialogues. We introduce a new Gastrointestinal Clinical Dialogue (GCD) Dataset which was gathered by healthcare professionals from a NHS Inflammatory Bowel Disease clinic and use this in a comparative study with four commercial ASR systems. Using self-supervision strategies, we fine-tune a seq2seq model on a mask-filling task using a domain-specific PubMed dataset which we have shared publicly for future research. The BART model fine-tuned for mask-filling was able to correct transcription errors and achieve lower word error rates for three out of four commercial ASR outputs.
DisCERN:Discovering Counterfactual Explanations using Relevance Features from Neighbourhoods
Sep 13, 2021



Abstract:Counterfactual explanations focus on "actionable knowledge" to help end-users understand how a machine learning outcome could be changed to a more desirable outcome. For this purpose a counterfactual explainer needs to discover input dependencies that relate to outcome changes. Identifying the minimum subset of feature changes needed to action an output change in the decision is an interesting challenge for counterfactual explainers. The DisCERN algorithm introduced in this paper is a case-based counter-factual explainer. Here counterfactuals are formed by replacing feature values from a nearest unlike neighbour (NUN) until an actionable change is observed. We show how widely adopted feature relevance-based explainers (i.e. LIME, SHAP), can inform DisCERN to identify the minimum subset of "actionable features". We demonstrate our DisCERN algorithm on five datasets in a comparative study with the widely used optimisation-based counterfactual approach DiCE. Our results demonstrate that DisCERN is an effective strategy to minimise actionable changes necessary to create good counterfactual explanations.
FitChat: Conversational Artificial Intelligence Interventions for Encouraging Physical Activity in Older Adults
Apr 29, 2020


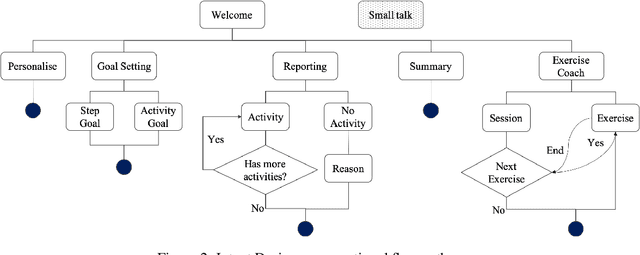
Abstract:Delivery of digital behaviour change interventions which encourage physical activity has been tried in many forms. Most often interventions are delivered as text notifications, but these do not promote interaction. Advances in conversational AI have improved natural language understanding and generation, allowing AI chatbots to provide an engaging experience with the user. For this reason, chatbots have recently been seen in healthcare delivering digital interventions through free text or choice selection. In this work, we explore the use of voice-based AI chatbots as a novel mode of intervention delivery, specifically targeting older adults to encourage physical activity. We co-created "FitChat", an AI chatbot, with older adults and we evaluate the first prototype using Think Aloud Sessions. Our thematic evaluation suggests that older adults prefer voice-based chat over text notifications or free text entry and that voice is a powerful mode for encouraging motivation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge