Kwanwoo Kim
ARGORA: Orchestrated Argumentation for Causally Grounded LLM Reasoning and Decision Making
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Existing multi-expert LLM systems gather diverse perspectives but combine them through simple aggregation, obscuring which arguments drove the final decision. We introduce ARGORA, a framework that organizes multi-expert discussions into explicit argumentation graphs showing which arguments support or attack each other. By casting these graphs as causal models, ARGORA can systematically remove individual arguments and recompute outcomes, identifying which reasoning chains were necessary and whether decisions would change under targeted modifications. We further introduce a correction mechanism that aligns internal reasoning with external judgments when they disagree. Across diverse benchmarks and an open-ended use case, ARGORA achieves competitive accuracy and demonstrates corrective behavior: when experts initially disagree, the framework resolves disputes toward correct answers more often than it introduces new errors, while providing causal diagnostics of decisive arguments.
Hetero-SCAN: Towards Social Context Aware Fake News Detection via Heterogeneous Graph Neural Network
Sep 13, 2021

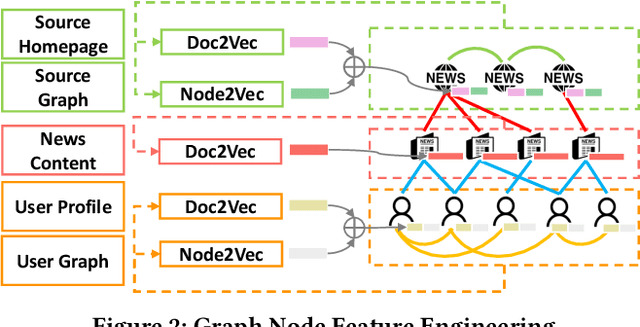

Abstract:Fake news, false or misleading information presented as news, has a great impact on many aspects of society, such as politics and healthcare. To handle this emerging problem, many fake news detection methods have been proposed, applying Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques on the article text. Considering that even people cannot easily distinguish fake news by news content, these text-based solutions are insufficient. To further improve fake news detection, researchers suggested graph-based solutions, utilizing the social context information such as user engagement or publishers information. However, existing graph-based methods still suffer from the following four major drawbacks: 1) expensive computational cost due to a large number of user nodes in the graph, 2) the error in sub-tasks, such as textual encoding or stance detection, 3) loss of rich social context due to homogeneous representation of news graphs, and 4) the absence of temporal information utilization. In order to overcome the aforementioned issues, we propose a novel social context aware fake news detection method, Hetero-SCAN, based on a heterogeneous graph neural network. Hetero-SCAN learns the news representation from the heterogeneous graph of news in an end-to-end manner. We demonstrate that Hetero-SCAN yields significant improvement over state-of-the-art text-based and graph-based fake news detection methods in terms of performance and efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge