Konstantinos Balaskas
Exploration of Low-Power Flexible Stress Monitoring Classifiers for Conformal Wearables
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Conventional stress monitoring relies on episodic, symptom-focused interventions, missing the need for continuous, accessible, and cost-efficient solutions. State-of-the-art approaches use rigid, silicon-based wearables, which, though capable of multitasking, are not optimized for lightweight, flexible wear, limiting their practicality for continuous monitoring. In contrast, flexible electronics (FE) offer flexibility and low manufacturing costs, enabling real-time stress monitoring circuits. However, implementing complex circuits like machine learning (ML) classifiers in FE is challenging due to integration and power constraints. Previous research has explored flexible biosensors and ADCs, but classifier design for stress detection remains underexplored. This work presents the first comprehensive design space exploration of low-power, flexible stress classifiers. We cover various ML classifiers, feature selection, and neural simplification algorithms, with over 1200 flexible classifiers. To optimize hardware efficiency, fully customized circuits with low-precision arithmetic are designed in each case. Our exploration provides insights into designing real-time stress classifiers that offer higher accuracy than current methods, while being low-cost, conformable, and ensuring low power and compact size.
Invited Paper: Feature-to-Classifier Co-Design for Mixed-Signal Smart Flexible Wearables for Healthcare at the Extreme Edge
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Flexible Electronics (FE) offer a promising alternative to rigid silicon-based hardware for wearable healthcare devices, enabling lightweight, conformable, and low-cost systems. However, their limited integration density and large feature sizes impose strict area and power constraints, making ML-based healthcare systems-integrating analog frontend, feature extraction and classifier-particularly challenging. Existing FE solutions often neglect potential system-wide solutions and focus on the classifier, overlooking the substantial hardware cost of feature extraction and Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs)-both major contributors to area and power consumption. In this work, we present a holistic mixed-signal feature-to-classifier co-design framework for flexible smart wearable systems. To the best of our knowledge, we design the first analog feature extractors in FE, significantly reducing feature extraction cost. We further propose an hardware-aware NAS-inspired feature selection strategy within ML training, enabling efficient, application-specific designs. Our evaluation on healthcare benchmarks shows our approach delivers highly accurate, ultra-area-efficient flexible systems-ideal for disposable, low-power wearable monitoring.
Arbitrary Precision Printed Ternary Neural Networks with Holistic Evolutionary Approximation
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Printed electronics offer a promising alternative for applications beyond silicon-based systems, requiring properties like flexibility, stretchability, conformality, and ultra-low fabrication costs. Despite the large feature sizes in printed electronics, printed neural networks have attracted attention for meeting target application requirements, though realizing complex circuits remains challenging. This work bridges the gap between classification accuracy and area efficiency in printed neural networks, covering the entire processing-near-sensor system design and co-optimization from the analog-to-digital interface-a major area and power bottleneck-to the digital classifier. We propose an automated framework for designing printed Ternary Neural Networks with arbitrary input precision, utilizing multi-objective optimization and holistic approximation. Our circuits outperform existing approximate printed neural networks by 17x in area and 59x in power on average, being the first to enable printed-battery-powered operation with under 5% accuracy loss while accounting for analog-to-digital interfacing costs.
Carbon-Efficient 3D DNN Acceleration: Optimizing Performance and Sustainability
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:As Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) continue to drive advancements in artificial intelligence, the design of hardware accelerators faces growing concerns over embodied carbon footprint due to complex fabrication processes. 3D integration improves performance but introduces sustainability challenges, making carbon-aware optimization essential. In this work, we propose a carbon-efficient design methodology for 3D DNN accelerators, leveraging approximate computing and genetic algorithm-based design space exploration to optimize Carbon Delay Product (CDP). By integrating area-efficient approximate multipliers into Multiply-Accumulate (MAC) units, our approach effectively reduces silicon area and fabrication overhead while maintaining high computational accuracy. Experimental evaluations across three technology nodes (45nm, 14nm, and 7nm) show that our method reduces embodied carbon by up to 30% with negligible accuracy drop.
Compact Yet Highly Accurate Printed Classifiers Using Sequential Support Vector Machine Circuits
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:Printed Electronics (PE) technology has emerged as a promising alternative to silicon-based computing. It offers attractive properties such as on-demand ultra-low-cost fabrication, mechanical flexibility, and conformality. However, PE are governed by large feature sizes, prohibiting the realization of complex printed Machine Learning (ML) classifiers. Leveraging PE's ultra-low non-recurring engineering and fabrication costs, designers can fully customize hardware to a specific ML model and dataset, significantly reducing circuit complexity. Despite significant advancements, state-of-the-art solutions achieve area efficiency at the expense of considerable accuracy loss. Our work mitigates this by designing area- and power-efficient printed ML classifiers with little to no accuracy degradation. Specifically, we introduce the first sequential Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifiers, exploiting the hardware efficiency of bespoke control and storage units and a single Multiply-Accumulate compute engine. Our SVMs yield on average 6x lower area and 4.6% higher accuracy compared to the printed state of the art.
Late Breaking Results: Energy-Efficient Printed Machine Learning Classifiers with Sequential SVMs
Jan 28, 2025

Abstract:Printed Electronics (PE) provide a mechanically flexible and cost-effective solution for machine learning (ML) circuits, compared to silicon-based technologies. However, due to large feature sizes, printed classifiers are limited by high power, area, and energy overheads, which restricts the realization of battery-powered systems. In this work, we design sequential printed bespoke Support Vector Machine (SVM) circuits that adhere to the power constraints of existing printed batteries while minimizing energy consumption, thereby boosting battery life. Our results show 6.5x energy savings while maintaining higher accuracy compared to the state of the art.
Hardware-Aware DNN Compression via Diverse Pruning and Mixed-Precision Quantization
Dec 23, 2023



Abstract:Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) have shown significant advantages in a wide variety of domains. However, DNNs are becoming computationally intensive and energy hungry at an exponential pace, while at the same time, there is a vast demand for running sophisticated DNN-based services on resource constrained embedded devices. In this paper, we target energy-efficient inference on embedded DNN accelerators. To that end, we propose an automated framework to compress DNNs in a hardware-aware manner by jointly employing pruning and quantization. We explore, for the first time, per-layer fine- and coarse-grained pruning, in the same DNN architecture, in addition to low bit-width mixed-precision quantization for weights and activations. Reinforcement Learning (RL) is used to explore the associated design space and identify the pruning-quantization configuration so that the energy consumption is minimized whilst the prediction accuracy loss is retained at acceptable levels. Using our novel composite RL agent we are able to extract energy-efficient solutions without requiring retraining and/or fine tuning. Our extensive experimental evaluation over widely used DNNs and the CIFAR-10/100 and ImageNet datasets demonstrates that our framework achieves $39\%$ average energy reduction for $1.7\%$ average accuracy loss and outperforms significantly the state-of-the-art approaches.
Approximate Decision Trees For Machine Learning Classification on Tiny Printed Circuits
Mar 15, 2022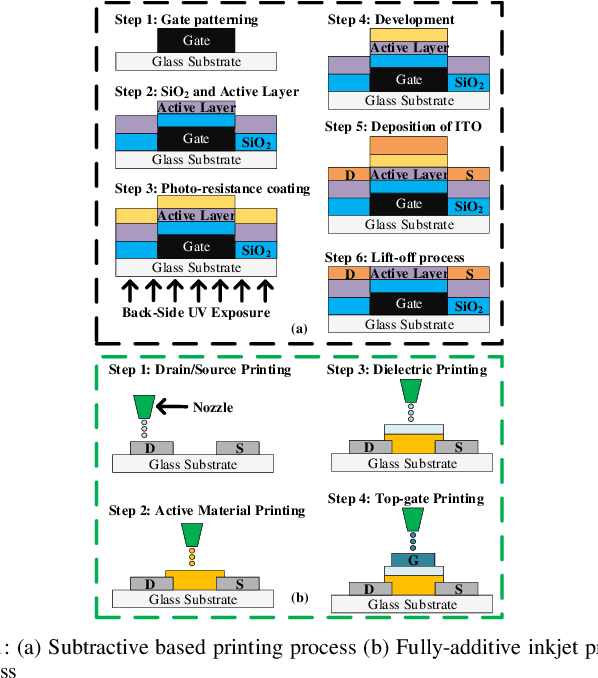
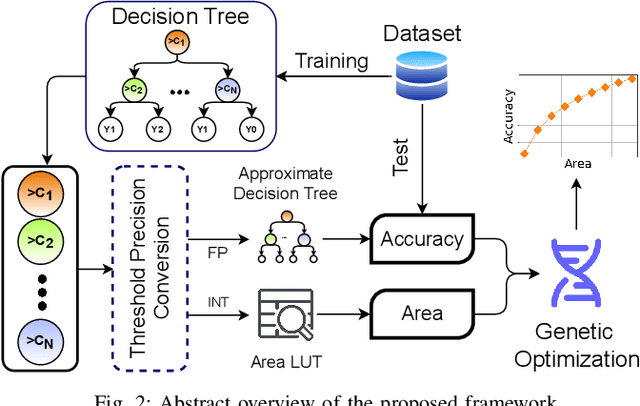
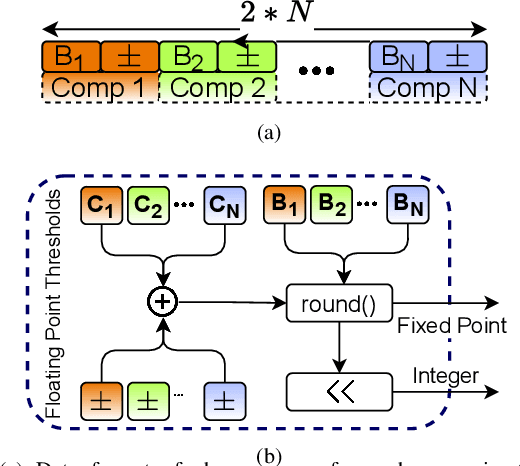
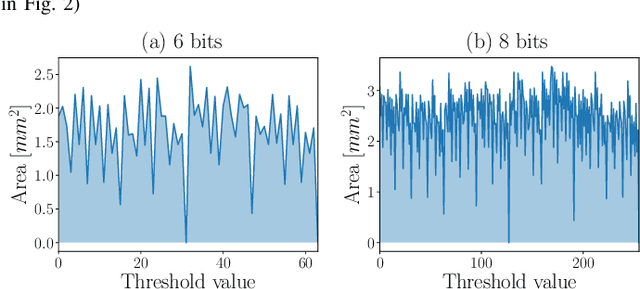
Abstract:Although Printed Electronics (PE) cannot compete with silicon-based systems in conventional evaluation metrics, e.g., integration density, area and performance, PE offers attractive properties such as on-demand ultra-low-cost fabrication, flexibility and non-toxicity. As a result, it targets application domains that are untouchable by lithography-based silicon electronics and thus have not yet seen much proliferation of computing. However, despite the attractive characteristics of PE, the large feature sizes in PE prohibit the realization of complex printed circuits, such as Machine Learning (ML) classifiers. In this work, we exploit the hardware-friendly nature of Decision Trees for machine learning classification and leverage the hardware-efficiency of the approximate design in order to generate approximate ML classifiers that are suitable for tiny, ultra-resource constrained, and battery-powered printed applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge