Koki Yamamoto
EgoOops: A Dataset for Mistake Action Detection from Egocentric Videos with Procedural Texts
Oct 07, 2024
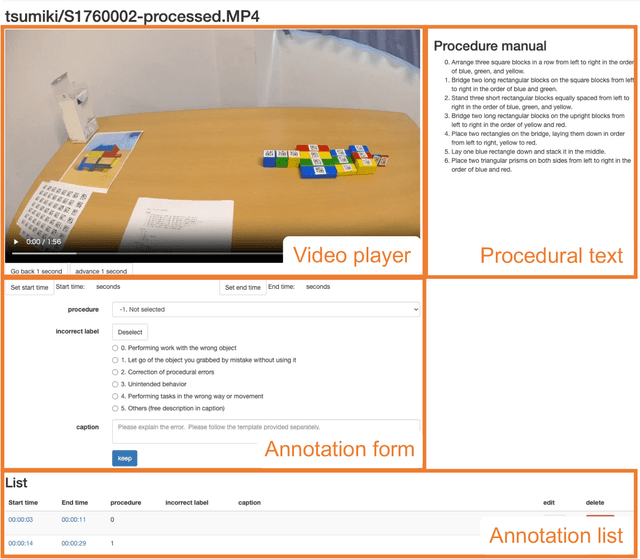

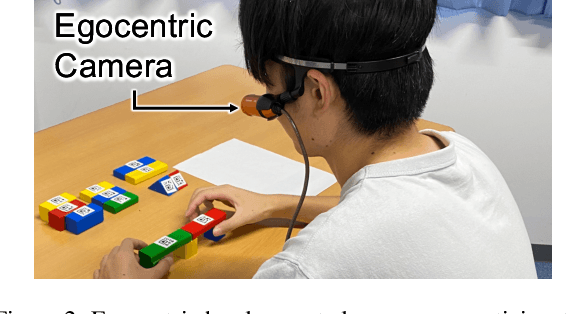
Abstract:Mistake action detection from egocentric videos is crucial for developing intelligent archives that detect workers' errors and provide feedback. Previous studies have been limited to specific domains, focused on detecting mistakes from videos without procedural texts, and analyzed whether actions are mistakes. To address these limitations, in this paper, we propose the EgoOops dataset, which includes egocentric videos, procedural texts, and three types of annotations: video-text alignment, mistake labels, and descriptions for mistakes. EgoOops covers five procedural domains and includes 50 egocentric videos. The video-text alignment allows the model to detect mistakes based on both videos and procedural texts. The mistake labels and descriptions enable detailed analysis of real-world mistakes. Based on EgoOops, we tackle two tasks: video-text alignment and mistake detection. For video-text alignment, we enhance the recent StepFormer model with an additional loss for fine-tuning. Based on the alignment results, we propose a multi-modal classifier to predict mistake labels. In our experiments, the proposed methods achieve higher performance than the baselines. In addition, our ablation study demonstrates the effectiveness of combining videos and texts. We will release the dataset and codes upon publication.
BioVL-QR: Egocentric Biochemical Video-and-Language Dataset Using Micro QR Codes
Apr 04, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces a biochemical vision-and-language dataset, which consists of 24 egocentric experiment videos, corresponding protocols, and video-and-language alignments. The key challenge in the wet-lab domain is detecting equipment, reagents, and containers is difficult because the lab environment is scattered by filling objects on the table and some objects are indistinguishable. Therefore, previous studies assume that objects are manually annotated and given for downstream tasks, but this is costly and time-consuming. To address this issue, this study focuses on Micro QR Codes to detect objects automatically. From our preliminary study, we found that detecting objects only using Micro QR Codes is still difficult because the researchers manipulate objects, causing blur and occlusion frequently. To address this, we also propose a novel object labeling method by combining a Micro QR Code detector and an off-the-shelf hand object detector. As one of the applications of our dataset, we conduct the task of generating protocols from experiment videos and find that our approach can generate accurate protocols.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge