Ki Won Sung
Detecting Multiple Targets with Distributed Sensing and Communication in Cell-Free Massive MIMO
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates multi-target detection in an integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) system within a cell-free massive MIMO (CF-mMIMO) framework. We adopt a user-centric approach for communication user equipments (UEs) and a distributed sensing approach for multi-target detection. A heuristic access point (AP) mode selection algorithm and a channel-aware distributed sensing scheme are proposed, where local measurements at receive APs (RX-APs) are weighted based on the received signals signal-to-interference ratio (SIR). A maximum a posteriori ratio test (MAPRT) detector is applied under two awareness levels at RX-APs. To balance the communication-sensing trade-off, we develop a power allocation algorithm to jointly maximize the minimum detection probability and communication signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) while satisfying power constraints. The proposed scheme outperforms non-weighted methods. Adding test statistics from more RX-APs can degrade sensing performance due to weaker channels, but this effect can be mitigated by optimizing the weighting exponent. Additionally, assigning more sensing RX-APs to a sensing area results in approximately 10 dB loss in minimum communication SINR due to limited communication resources.
Beam Misalignment in 3GPP mmWave NR
Apr 15, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents an analytical framework for evaluating beam misalignment in 3GPP mmWave NR systems implementing analog beamforming. Our approach captures the interaction between user mobility, beam sweeping mechanisms, and deployment configurations, focusing on long-term average performance metrics. Specifically, we model the beam misalignment rates at both the base station (BS) and user equipment (UE) as Poisson processes and derive expressions for the expected misalignment duration, misalignment fraction, and overall beamforming gain. The framework accounts for practical constraints in NR such as Synchronization Signal Blocks (SSB) periodicity, TDD frame structures, and SSB overhead. Through numerical evaluation based on 3GPP mmWave parameters, we identify key trade-offs between beam counts, user mobility, and SSB timing, providing actionable design insights for robust and efficient beam management in future high-frequency networks.
Interplay between Sensing and Communication in Cell-Free Massive MIMO with URLLC Users
Jan 18, 2024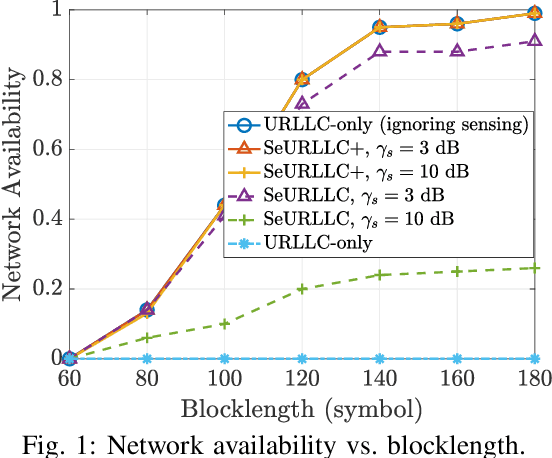


Abstract:This paper studies integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) in the downlink of a cell-free massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) system with multi-static sensing and ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) users. We propose a successive convex approximation-based power allocation algorithm that maximizes energy efficiency while satisfying the sensing and URLLC requirements. In addition, we provide a new definition for network availability, which accounts for both sensing and URLLC requirements. The impact of blocklength, sensing requirement, and required reliability as a function of decoding error probability on network availability and energy efficiency is investigated. The proposed power allocation algorithm is compared to a communication-centric approach where only the URLLC requirement is considered. It is shown that the URLLC-only approach is incapable of meeting sensing requirements, while the proposed ISAC algorithm fulfills both sensing and URLLC requirements, albeit with an associated increase in energy consumption. This increment can be reduced up to 75% by utilizing additional symbols for sensing. It is also demonstrated that larger blocklengths enhance network availability and offer greater robustness against stringent reliability requirements.
Joint Processing and Transmission Energy Optimization for ISAC in Cell-Free Massive MIMO with URLLC
Jan 18, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we explore the concept of integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) within a downlink cell-free massive MIMO (multiple-input multiple-output) system featuring multi-static sensing and users requiring ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC). Our focus involves the formulation of two non-convex algorithms that jointly solve power and blocklength allocation for end-to-end (E2E) minimization. The objectives are to jointly minimize sensing/communication processing and transmission energy consumption, while simultaneously meeting the requirements for sensing and URLLC. To address the inherent non-convexity of these optimization problems, we utilize techniques such as the Feasible Point Pursuit - Successive Convex Approximation (FPP-SCA), Concave-Convex Programming (CCP), and fractional programming. We conduct a comparative analysis of the performance of these algorithms in ISAC scenarios and against a URLLC-only scenario where sensing is not integrated. Our numerical results highlight the superior performance of the E2E energy minimization algorithm, especially in scenarios without sensing capability. Additionally, our study underscores the increasing prominence of energy consumption associated with sensing processing tasks as the number of sensing receive access points rises. Furthermore, the results emphasize that a higher sensing signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio threshold is associated with an escalation in E2E energy consumption, thereby narrowing the performance gap between the two proposed algorithms.
Multi-Static Target Detection and Power Allocation for Integrated Sensing and Communication in Cell-Free Massive MIMO
May 21, 2023Abstract:This paper studies an integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) system for single-target detection in a cloud radio access network architecture. The system considers downlink communication and multi-static sensing approach, where ISAC transmit access points (APs) jointly serve the user equipments (UEs) and optionally steer a beam toward the target. A centralized operation of cell-free massive MIMO (multiple-input multiple-output) is considered for communication and sensing purposes. A maximum a posteriori ratio test detector is developed to detect the target in the presence of clutter, so-called target-free signals. Moreover, a power allocation algorithm is proposed to maximize the sensing signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) while ensuring a minimum communication SINR value for each UE and meeting per-AP power constraints. Two ISAC setups are studied: i) using only existing communication beams for sensing and ii) using additional sensing beams. The proposed algorithm's efficiency is investigated in both realistic and idealistic scenarios, corresponding to the presence and absence of the target-free channels, respectively. Although detection probability degrades in the presence of target-free channels that act as interference, the proposed algorithm significantly outperforms the interference-unaware benchmark by exploiting the statistics of the clutter. It has also been shown that the proposed algorithm outperforms the fully communication-centric algorithm, both in the presence and absence of clutter. Moreover, using an additional sensing beam improves the detection performance for a target with lower radar cross-section variances compared to the case without sensing beams.
Power Allocation for Joint Communication and Sensing in Cell-Free Massive MIMO
Sep 05, 2022



Abstract:This paper studies a joint communication and sensing (JCAS) system with downlink communication and multi-static sensing for single-target detection in a cloud radio access network architecture. A centralized operation of cell-free massive MIMO is considered for communication and sensing purposes. The JCAS transmit access points (APs) jointly serve the user equipments (UEs) and optionally steer a beam towards the target. A maximum a posteriori ratio test detector is derived to detect the target using signals received at distributed APs. We propose a power allocation algorithm to maximize the sensing signal-to-noise ratio under the condition that a minimal signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio value for each UE is guaranteed. Numerical results show that, compared to the fully communication-centric power allocation, the detection probability under a certain false alarm probability can be increased significantly by the proposed algorithm for both JCAS setups: i) using additional sensing symbols or ii) using only existing communication symbols.
Sparse Channel Estimation in Wideband Systems with Geometric Sequence Decomposition
Apr 09, 2021

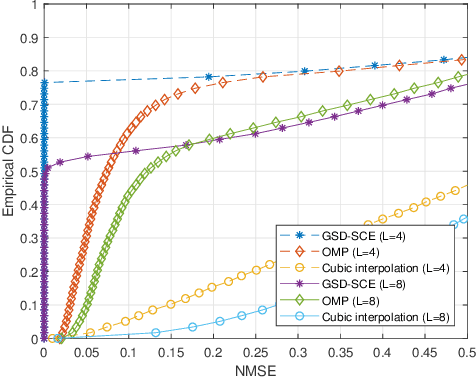
Abstract:The sparsity of multipaths in wideband channel has motivated the use of compressed sensing for channel estimation. In this letter, we propose an entirely different approach to sparse channel estimation. We exploit the fact that $L$ taps of channel impulse response in time domain constitute a non-orthogonal superposition of $L$ geometric sequences in frequency domain. This converts the channel estimation problem into the extraction of the parameters of geometric sequences. Notably, the proposed scheme achieves the error-free estimation of the whole bandwidth with a few pilot symbols if the excess delay is bounded to a certain value.
Noise Learning Based Denoising Autoencoder
Jan 20, 2021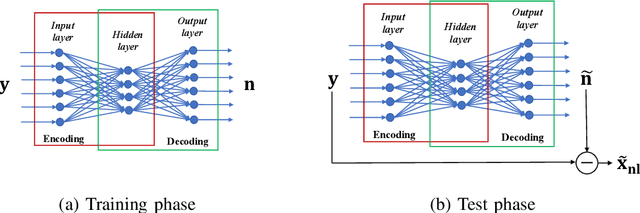
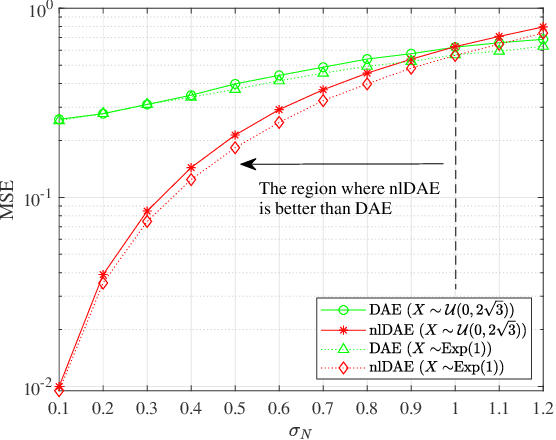
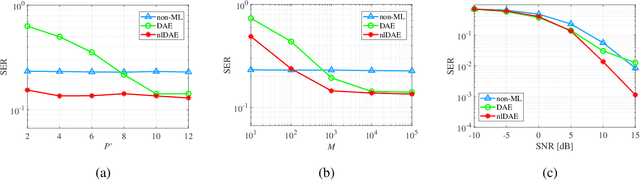
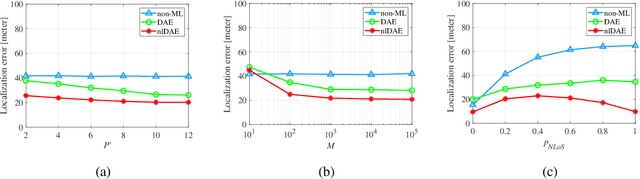
Abstract:This letter introduces a new denoiser that modifies the structure of denoising autoencoder (DAE), namely noise learning based DAE (nlDAE). The proposed nlDAE learns the noise instead of the original data. Then, the denoising is performed by subtracting the regenerated noise from the noisy input. Hence, nlDAE is more effective than DAE when the noise is simpler to regenerate than the original data. To validate the performance of nlDAE, we provide two case studies: symbol demodulation and precise localization. Numerical results suggest that nlDAE requires smaller latent space dimension and less training dataset compared to DAE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge