Kevin Lang
Streaming Quantiles Algorithms with Small Space and Update Time
Jun 29, 2019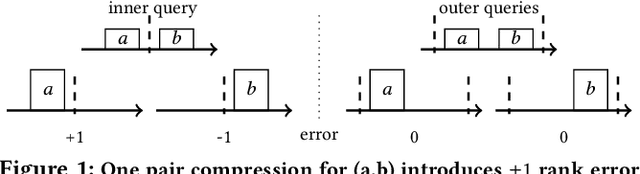
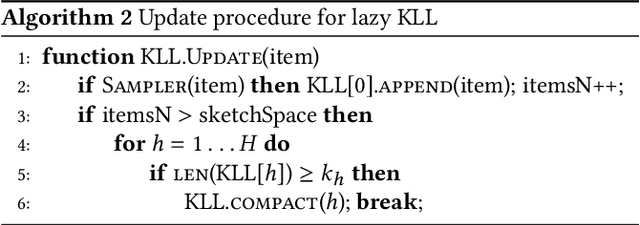
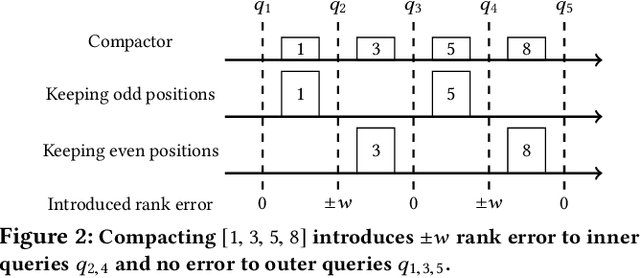
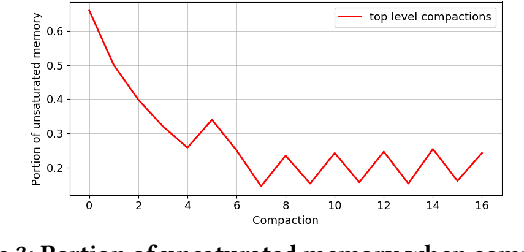
Abstract:Approximating quantiles and distributions over streaming data has been studied for roughly two decades now. Recently, Karnin, Lang, and Liberty proposed the first asymptotically optimal algorithm for doing so. This manuscript complements their theoretical result by providing a practical variants of their algorithm with improved constants. For a given sketch size, our techniques provably reduce the upper bound on the sketch error by a factor of two. These improvements are verified experimentally. Our modified quantile sketch improves the latency as well by reducing the worst case update time from $O(1/\varepsilon)$ down to $O(\log (1/\varepsilon))$. We also suggest two algorithms for weighted item streams which offer improved asymptotic update times compared to na\"ive extensions. Finally, we provide a specialized data structure for these sketches which reduces both their memory footprints and update times.
Bargaining for Revenue Shares on Tree Trading Networks
Apr 22, 2013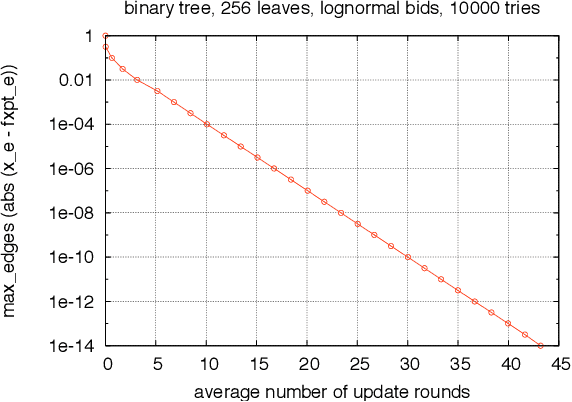
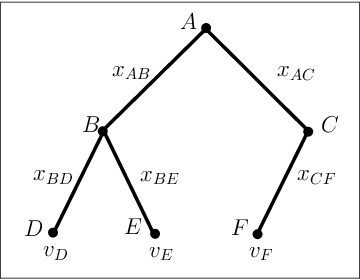
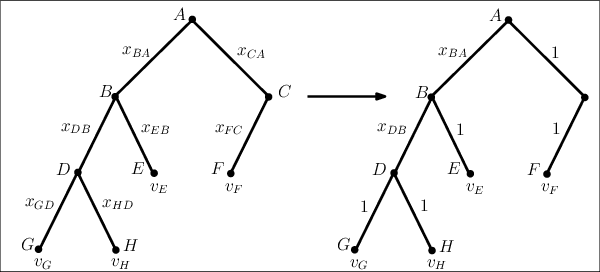
Abstract:We study trade networks with a tree structure, where a seller with a single indivisible good is connected to buyers, each with some value for the good, via a unique path of intermediaries. Agents in the tree make multiplicative revenue share offers to their parent nodes, who choose the best offer and offer part of it to their parent, and so on; the winning path is determined by who finally makes the highest offer to the seller. In this paper, we investigate how these revenue shares might be set via a natural bargaining process between agents on the tree, specifically, egalitarian bargaining between endpoints of each edge in the tree. We investigate the fixed point of this system of bargaining equations and prove various desirable for this solution concept, including (i) existence, (ii) uniqueness, (iii) efficiency, (iv) membership in the core, (v) strict monotonicity, (vi) polynomial-time computability to any given accuracy. Finally, we present numerical evidence that asynchronous dynamics with randomly ordered updates always converges to the fixed point, indicating that the fixed point shares might arise from decentralized bargaining amongst agents on the trade network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge