Kerem Can Tezcan
Modelling the Distribution of 3D Brain MRI using a 2D Slice VAE
Jul 09, 2020



Abstract:Probabilistic modelling has been an essential tool in medical image analysis, especially for analyzing brain Magnetic Resonance Images (MRI). Recent deep learning techniques for estimating high-dimensional distributions, in particular Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), opened up new avenues for probabilistic modeling. Modelling of volumetric data has remained a challenge, however, because constraints on available computation and training data make it difficult effectively leverage VAEs, which are well-developed for 2D images. We propose a method to model 3D MR brain volumes distribution by combining a 2D slice VAE with a Gaussian model that captures the relationships between slices. We do so by estimating the sample mean and covariance in the latent space of the 2D model over the slice direction. This combined model lets us sample new coherent stacks of latent variables to decode into slices of a volume. We also introduce a novel evaluation method for generated volumes that quantifies how well their segmentations match those of true brain anatomy. We demonstrate that our proposed model is competitive in generating high quality volumes at high resolutions according to both traditional metrics and our proposed evaluation.
Unsupervised Lesion Detection via Image Restoration with a Normative Prior
Apr 30, 2020


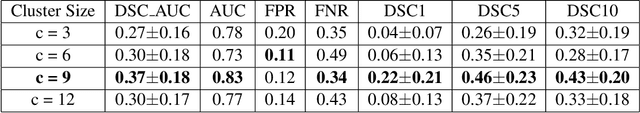
Abstract:Unsupervised lesion detection is a challenging problem that requires accurately estimating normative distributions of healthy anatomy and detecting lesions as outliers without training examples. Recently, this problem has received increased attention from the research community following the advances in unsupervised learning with deep learning. Such advances allow the estimation of high-dimensional distributions, such as normative distributions, with higher accuracy than previous methods.The main approach of the recently proposed methods is to learn a latent-variable model parameterized with networks to approximate the normative distribution using example images showing healthy anatomy, perform prior-projection, i.e. reconstruct the image with lesions using the latent-variable model, and determine lesions based on the differences between the reconstructed and original images. While being promising, the prior-projection step often leads to a large number of false positives. In this work, we approach unsupervised lesion detection as an image restoration problem and propose a probabilistic model that uses a network-based prior as the normative distribution and detect lesions pixel-wise using MAP estimation. The probabilistic model punishes large deviations between restored and original images, reducing false positives in pixel-wise detections. Experiments with gliomas and stroke lesions in brain MRI using publicly available datasets show that the proposed approach outperforms the state-of-the-art unsupervised methods by a substantial margin, +0.13 (AUC), for both glioma and stroke detection. Extensive model analysis confirms the effectiveness of MAP-based image restoration.
Visual Feature Attribution using Wasserstein GANs
Jun 26, 2018



Abstract:Attributing the pixels of an input image to a certain category is an important and well-studied problem in computer vision, with applications ranging from weakly supervised localisation to understanding hidden effects in the data. In recent years, approaches based on interpreting a previously trained neural network classifier have become the de facto state-of-the-art and are commonly used on medical as well as natural image datasets. In this paper, we discuss a limitation of these approaches which may lead to only a subset of the category specific features being detected. To address this problem we develop a novel feature attribution technique based on Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Networks (WGAN), which does not suffer from this limitation. We show that our proposed method performs substantially better than the state-of-the-art for visual attribution on a synthetic dataset and on real 3D neuroimaging data from patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer's disease (AD). For AD patients the method produces compellingly realistic disease effect maps which are very close to the observed effects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge