Kazuhiro Kosuge
RTFF: Random-to-Target Fabric Flattening Policy using Dual-Arm Manipulator
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Robotic fabric manipulation in garment production for sewing, cutting, and ironing requires reliable flattening and alignment, yet remains challenging due to fabric deformability, effectively infinite degrees of freedom, and frequent occlusions from wrinkles, folds, and the manipulator's End-Effector (EE) and arm. To address these issues, this paper proposes the first Random-to-Target Fabric Flattening (RTFF) policy, which aligns a random wrinkled fabric state to an arbitrary wrinkle-free target state. The proposed policy adopts a hybrid Imitation Learning-Visual Servoing (IL-VS) framework, where IL learns with explicit fabric models for coarse alignment of the wrinkled fabric toward a wrinkle-free state near the target, and VS ensures fine alignment to the target. Central to this framework is a template-based mesh that offers precise target state representation, wrinkle-aware geometry prediction, and consistent vertex correspondence across RTFF manipulation steps, enabling robust manipulation and seamless IL-VS switching. Leveraging the power of mesh, a novel IL solution for RTFF-Mesh Action Chunking Transformer (MACT)-is then proposed by conditioning the mesh information into a Transformer-based policy. The RTFF policy is validated on a real dual-arm tele-operation system, showing zero-shot alignment to different targets, high accuracy, and strong generalization across fabrics and scales. Project website: https://kaitang98.github.io/RTFF_Policy/
Automated Action Generation based on Action Field for Robotic Garment Manipulation
May 06, 2025Abstract:Garment manipulation using robotic systems is a challenging task due to the diverse shapes and deformable nature of fabric. In this paper, we propose a novel method for robotic garment manipulation that significantly improves the accuracy while reducing computational time compared to previous approaches. Our method features an action generator that directly interprets scene images and generates pixel-wise end-effector action vectors using a neural network. The network also predicts a manipulation score map that ranks potential actions, allowing the system to select the most effective action. Extensive simulation experiments demonstrate that our method achieves higher unfolding and alignment performances and faster computation time than previous approaches. Real-world experiments show that the proposed method generalizes well to different garment types and successfully flattens garments.
SIS: Seam-Informed Strategy for T-shirt Unfolding
Sep 12, 2024Abstract:Seams are information-rich components of garments. The presence of different types of seams and their combinations helps to select grasping points for garment handling. In this paper, we propose a new Seam-Informed Strategy (SIS) for finding actions for handling a garment, such as grasping and unfolding a T-shirt. Candidates for a pair of grasping points for a dual-arm manipulator system are extracted using the proposed Seam Feature Extraction Method (SFEM). A pair of grasping points for the robot system is selected by the proposed Decision Matrix Iteration Method (DMIM). The decision matrix is first computed by multiple human demonstrations and updated by the robot execution results to improve the grasping and unfolding performance of the robot. Note that the proposed scheme is trained on real data without relying on simulation. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed strategy. The project video is available at https://github.com/lancexz/sis.
FPCC-Net: Fast Point Cloud Clustering for Instance Segmentation
Jan 19, 2021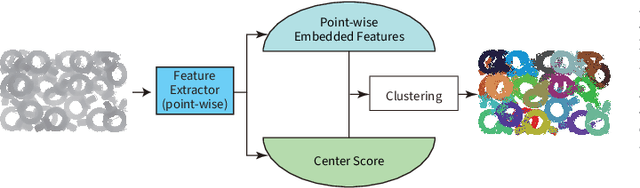

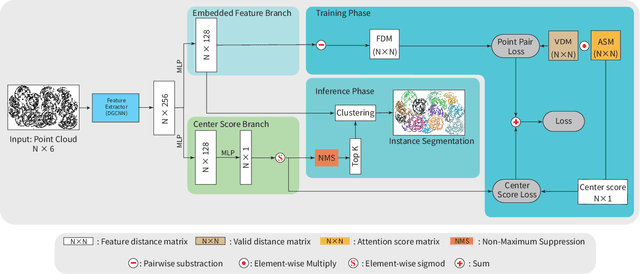
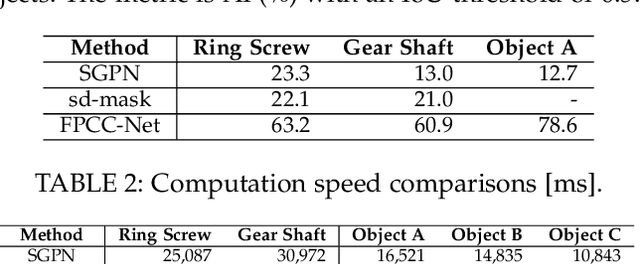
Abstract:Instance segmentation is an important pre-processing task in numerous real-world applications, such as robotics, autonomous vehicles, and human-computer interaction. However, there has been little research on 3D point cloud instance segmentation of bin-picking scenes in which multiple objects of the same class are stacked together. Compared with the rapid development of deep learning for two-dimensional (2D) image tasks, deep learning-based 3D point cloud segmentation still has a lot of room for development. In such a situation, distinguishing a large number of occluded objects of the same class is a highly challenging problem. In a usual bin-picking scene, an object model is known and the number of object type is one. Thus, the semantic information can be ignored; instead, the focus is put on the segmentation of instances. Based on this task requirement, we propose a network (FPCC-Net) that infers feature centers of each instance and then clusters the remaining points to the closest feature center in feature embedding space. FPCC-Net includes two subnets, one for inferring the feature centers for clustering and the other for describing features of each point. The proposed method is compared with existing 3D point cloud and 2D segmentation methods in some bin-picking scenes. It is shown that FPCC-Net improves average precision (AP) by about 40\% than SGPN and can process about 60,000 points in about 0.8 [s].
Dance Teaching by a Robot: Combining Cognitive and Physical Human-Robot Interaction for Supporting the Skill Learning Process
Oct 29, 2018



Abstract:This letter presents a physical human-robot interaction scenario in which a robot guides and performs the role of a teacher within a defined dance training framework. A combined cognitive and physical feedback of performance is proposed for assisting the skill learning process. Direct contact cooperation has been designed through an adaptive impedance-based controller that adjusts according to the partner's performance in the task. In measuring performance, a scoring system has been designed using the concept of progressive teaching (PT). The system adjusts the difficulty based on the user's number of practices and performance history. Using the proposed method and a baseline constant controller, comparative experiments have shown that the PT presents better performance in the initial stage of skill learning. An analysis of the subjects' perception of comfort, peace of mind, and robot performance have shown a significant difference at the p < .01 level, favoring the PT algorithm.
* Presented at IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation ICRA-2017
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge