Katie Atkinson
Towards Supporting Legal Argumentation with NLP: Is More Data Really All You Need?
Jun 16, 2024Abstract:Modeling legal reasoning and argumentation justifying decisions in cases has always been central to AI & Law, yet contemporary developments in legal NLP have increasingly focused on statistically classifying legal conclusions from text. While conceptually simpler, these approaches often fall short in providing usable justifications connecting to appropriate legal concepts. This paper reviews both traditional symbolic works in AI & Law and recent advances in legal NLP, and distills possibilities of integrating expert-informed knowledge to strike a balance between scalability and explanation in symbolic vs. data-driven approaches. We identify open challenges and discuss the potential of modern NLP models and methods that integrate
Using Argumentation Schemes to Model Legal Reasoning
Oct 01, 2022Abstract:We present argumentation schemes to model reasoning with legal cases. We provide schemes for each of the three stages that take place after the facts are established: factor ascription, issue resolution and outcome determination. The schemes are illustrated with examples from a specific legal domain, US Trade Secrets law, and the wider applicability of these schemes is discussed.
Combining Long Short Term Memory and Convolutional Neural Network for Cross-Sentence n-ary Relation Extraction
Nov 02, 2018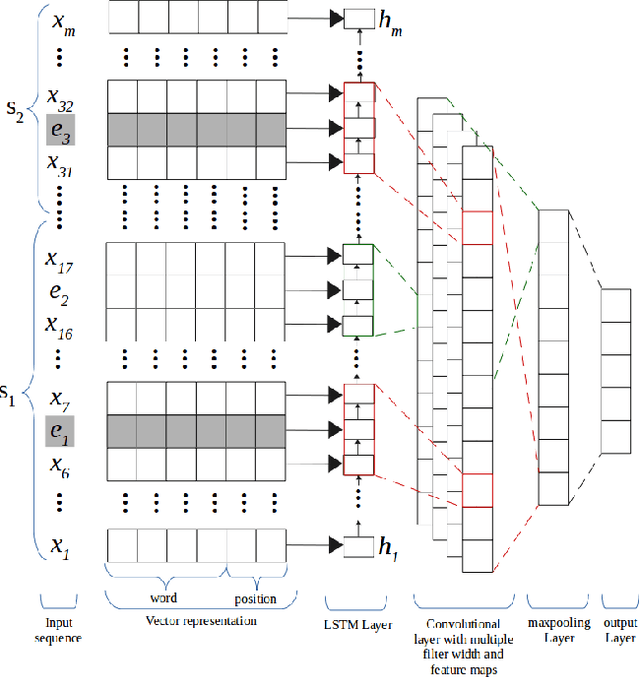
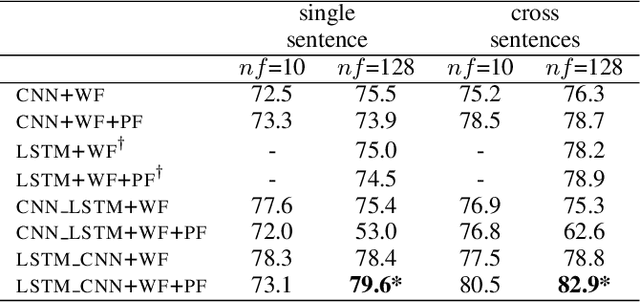
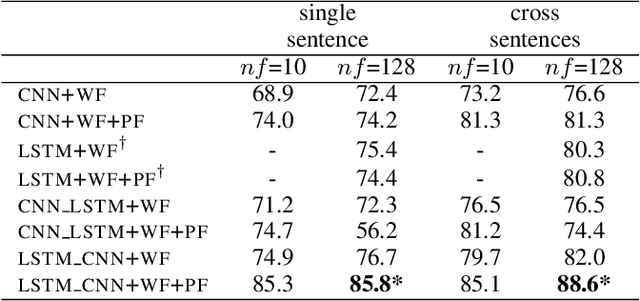
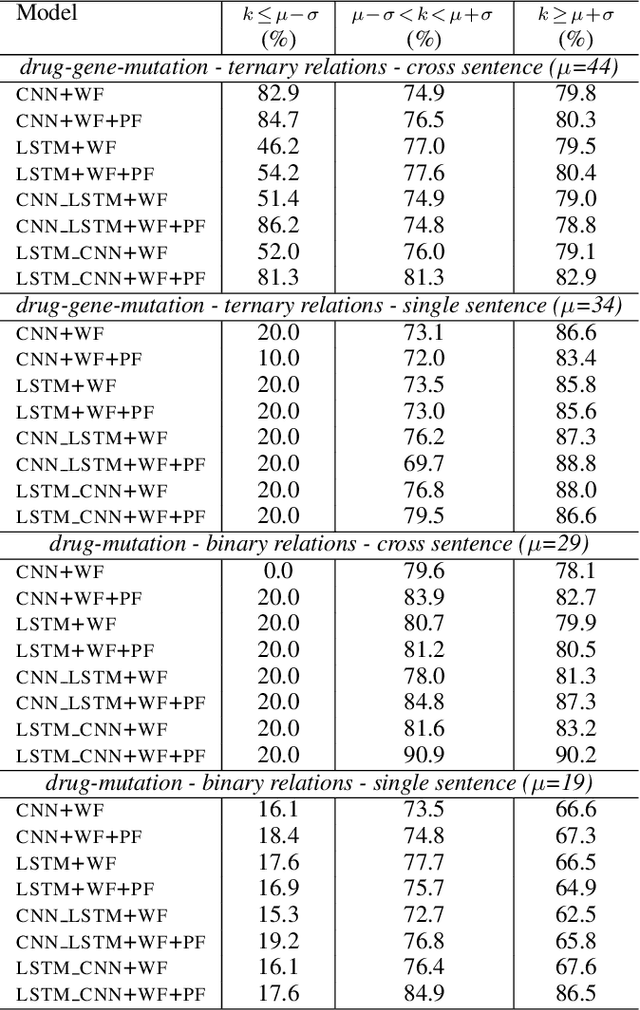
Abstract:We propose in this paper a combined model of Long Short Term Memory and Convolutional Neural Networks (LSTM-CNN) that exploits word embeddings and positional embeddings for cross-sentence n-ary relation extraction. The proposed model brings together the properties of both LSTMs and CNNs, to simultaneously exploit long-range sequential information and capture most informative features, essential for cross-sentence n-ary relation extraction. The LSTM-CNN model is evaluated on standard dataset on cross-sentence n-ary relation extraction, where it significantly outperforms baselines such as CNNs, LSTMs and also a combined CNN-LSTM model. The paper also shows that the LSTM-CNN model outperforms the current state-of-the-art methods on cross-sentence n-ary relation extraction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge