Katherine Lawler
Parallel Multi-Scale Networks with Deep Supervision for Hand Keypoint Detection
Dec 19, 2021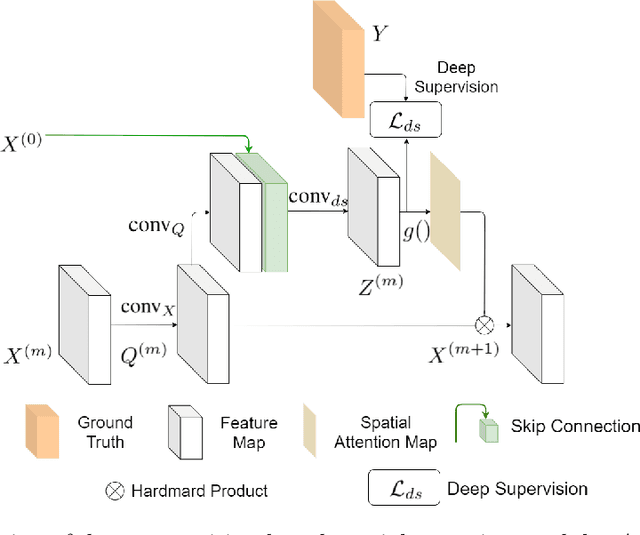
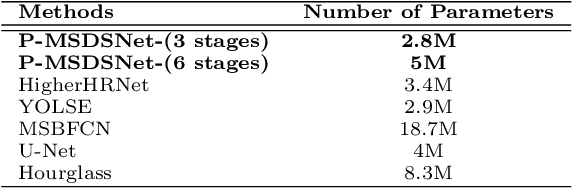
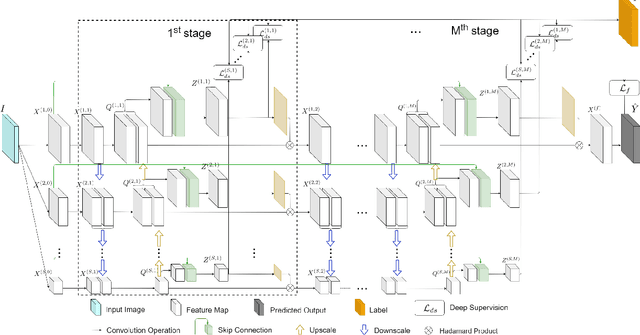
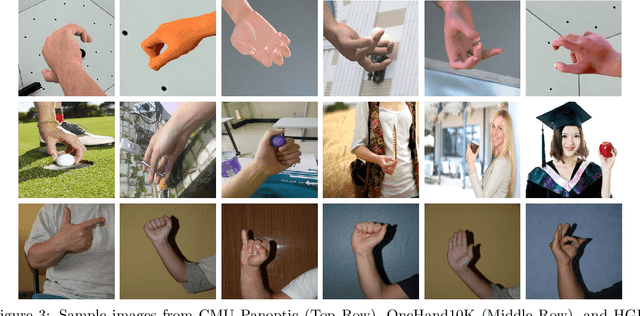
Abstract:Keypoint detection plays an important role in a wide range of applications. However, predicting keypoints of small objects such as human hands is a challenging problem. Recent works fuse feature maps of deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), either via multi-level feature integration or multi-resolution aggregation. Despite achieving some success, the feature fusion approaches increase the complexity and the opacity of CNNs. To address this issue, we propose a novel CNN model named Multi-Scale Deep Supervision Network (P-MSDSNet) that learns feature maps at different scales with deep supervisions to produce attention maps for adaptive feature propagation from layers to layers. P-MSDSNet has a multi-stage architecture which makes it scalable while its deep supervision with spatial attention improves transparency to the feature learning at each stage. We show that P-MSDSNet outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches on benchmark datasets while requiring fewer number of parameters. We also show the application of P-MSDSNet to quantify finger tapping hand movements in a neuroscience study.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence to aid detection of dementia: a narrative review on current capabilities and future directions
Apr 29, 2021



Abstract:With populations ageing, the number of people with dementia worldwide is expected to triple to 152 million by 2050. Seventy percent of cases are due to Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology and there is a 10-20 year 'pre-clinical' period before significant cognitive decline occurs. We urgently need, cost effective, objective methods to detect AD, and other dementias, at an early stage. Risk factor modification could prevent 40% of cases and drug trials would have greater chances of success if participants are recruited at an earlier stage. Currently, detection of dementia is largely by pen and paper cognitive tests but these are time consuming and insensitive to pre-clinical phases. Specialist brain scans and body fluid biomarkers can detect the earliest stages of dementia but are too invasive or expensive for widespread use. With the advancement of technology, Artificial Intelligence (AI) shows promising results in assisting with detection of early-stage dementia. Existing AI-aided methods and potential future research directions are reviewed and discussed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge