Kate M. Knill
Assessment of L2 Oral Proficiency using Speech Large Language Models
May 27, 2025Abstract:The growing population of L2 English speakers has increased the demand for developing automatic graders for spoken language assessment (SLA). Historically, statistical models, text encoders, and self-supervised speech models have been utilised for this task. However, cascaded systems suffer from the loss of information, while E2E graders also have limitations. With the recent advancements of multi-modal large language models (LLMs), we aim to explore their potential as L2 oral proficiency graders and overcome these issues. In this work, we compare various training strategies using regression and classification targets. Our results show that speech LLMs outperform all previous competitive baselines, achieving superior performance on two datasets. Furthermore, the trained grader demonstrates strong generalisation capabilities in the cross-part or cross-task evaluation, facilitated by the audio understanding knowledge acquired during LLM pre-training.
Scaling and Prompting for Improved End-to-End Spoken Grammatical Error Correction
May 27, 2025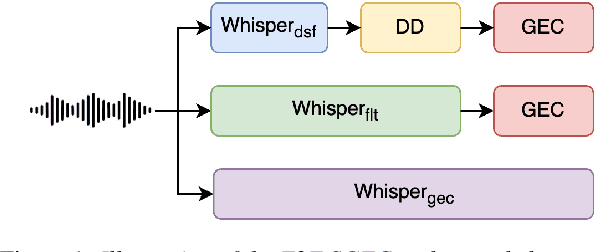
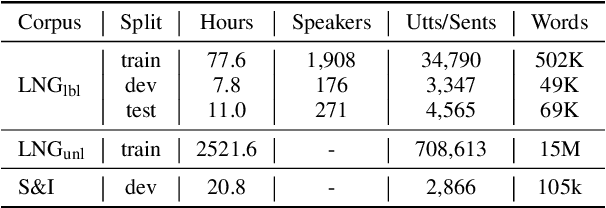
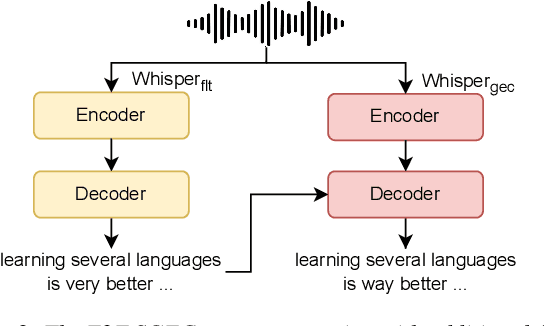
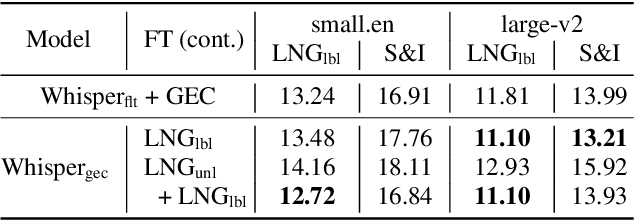
Abstract:Spoken Grammatical Error Correction (SGEC) and Feedback (SGECF) are crucial for second language learners, teachers and test takers. Traditional SGEC systems rely on a cascaded pipeline consisting of an ASR, a module for disfluency detection (DD) and removal and one for GEC. With the rise of end-to-end (E2E) speech foundation models, we investigate their effectiveness in SGEC and feedback generation. This work introduces a pseudo-labelling process to address the challenge of limited labelled data, expanding the training data size from 77 hours to approximately 2500 hours, leading to improved performance. Additionally, we prompt an E2E Whisper-based SGEC model with fluent transcriptions, showing a slight improvement in SGEC performance, with more significant gains in feedback generation. Finally, we assess the impact of increasing model size, revealing that while pseudo-labelled data does not yield performance gain for a larger Whisper model, training with prompts proves beneficial.
Training Articulatory Inversion Models for Inter-Speaker Consistency
May 26, 2025Abstract:Acoustic-to-Articulatory Inversion (AAI) attempts to model the inverse mapping from speech to articulation. Exact articulatory prediction from speech alone may be impossible, as speakers can choose different forms of articulation seemingly without reference to their vocal tract structure. However, once a speaker has selected an articulatory form, their productions vary minimally. Recent works in AAI have proposed adapting Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) models to single-speaker datasets, claiming that these single-speaker models provide a universal articulatory template. In this paper, we investigate whether SSL-adapted models trained on single and multi-speaker data produce articulatory targets which are consistent across speaker identities for English and Russian. We do this through the use of a novel evaluation method which extracts articulatory targets using minimal pair sets. We also present a training method which can improve inter-speaker consistency using only speech data.
Learn and Don't Forget: Adding a New Language to ASR Foundation Models
Jul 09, 2024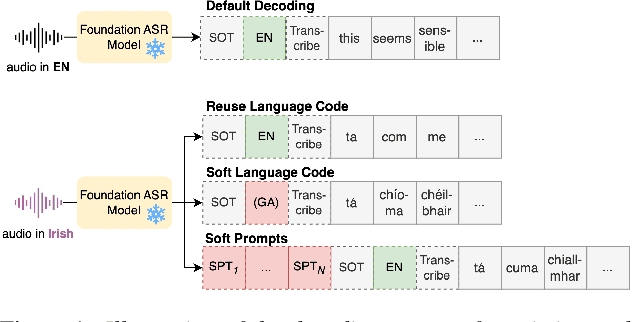
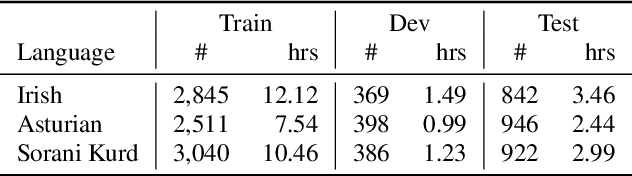
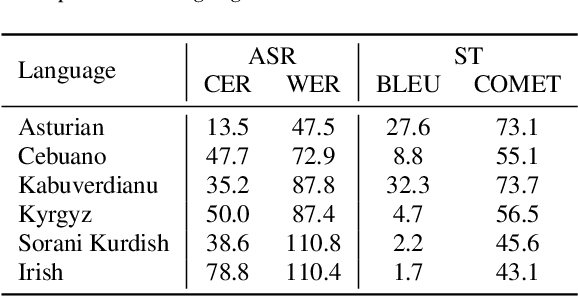
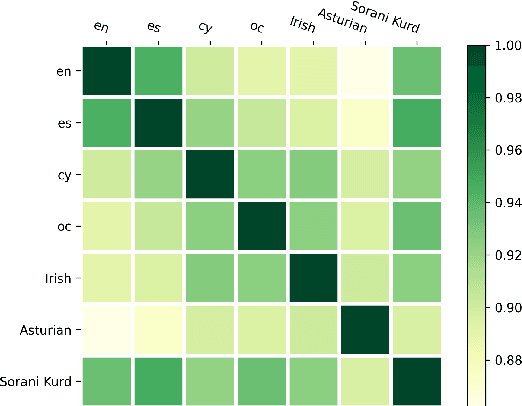
Abstract:Foundation ASR models often support many languages, e.g. 100 languages in Whisper. However, there has been limited work on integrating an additional, typically low-resource, language, while maintaining performance on the original language set. Fine-tuning, while simple, may degrade the accuracy of the original set. We compare three approaches that exploit adaptation parameters: soft language code tuning, train only the language code; soft prompt tuning, train prepended tokens; and LoRA where a small set of additional parameters are optimised. Elastic Weight Consolidation (EWC) offers an alternative compromise with the potential to maintain performance in specific target languages. Results show that direct fine-tuning yields the best performance for the new language but degrades existing language capabilities. EWC can address this issue for specific languages. If only adaptation parameters are used, the language capabilities are maintained but at the cost of performance in the new language.
Can GPT-4 do L2 analytic assessment?
Apr 29, 2024Abstract:Automated essay scoring (AES) to evaluate second language (L2) proficiency has been a firmly established technology used in educational contexts for decades. Although holistic scoring has seen advancements in AES that match or even exceed human performance, analytic scoring still encounters issues as it inherits flaws and shortcomings from the human scoring process. The recent introduction of large language models presents new opportunities for automating the evaluation of specific aspects of L2 writing proficiency. In this paper, we perform a series of experiments using GPT-4 in a zero-shot fashion on a publicly available dataset annotated with holistic scores based on the Common European Framework of Reference and aim to extract detailed information about their underlying analytic components. We observe significant correlations between the automatically predicted analytic scores and multiple features associated with the individual proficiency components.
Investigating the Emergent Audio Classification Ability of ASR Foundation Models
Nov 15, 2023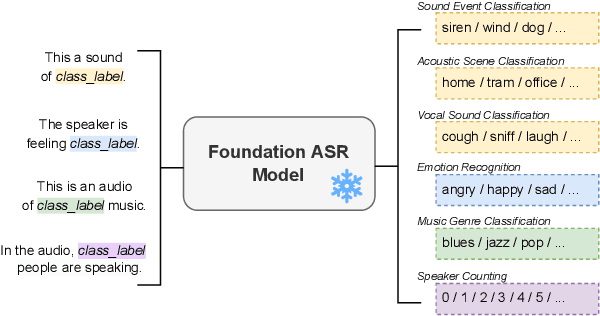
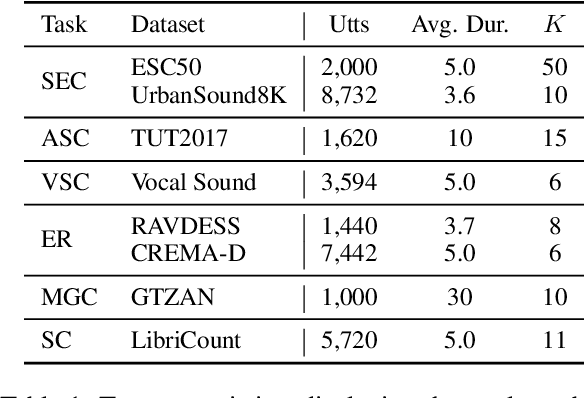
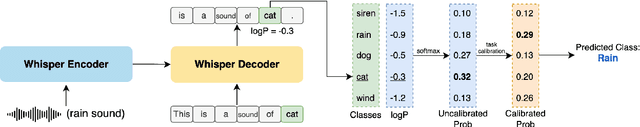

Abstract:Text and vision foundation models can perform many tasks in a zero-shot setting, a desirable property that enables these systems to be applied in general and low-resource settings. However, there has been significantly less work on the zero-shot abilities of ASR foundation models, with these systems typically fine-tuned to specific tasks or constrained to applications that match their training criterion and data annotation. In this work we investigate the ability of Whisper and MMS, ASR foundation models trained primarily for speech recognition, to perform zero-shot audio classification. We use simple template-based text prompts at the decoder and use the resulting decoding probabilities to generate zero-shot predictions. Without training the model on extra data or adding any new parameters, we demonstrate that Whisper shows promising zero-shot classification performance on a range of 8 audio-classification datasets, outperforming existing state-of-the-art zero-shot baseline's accuracy by an average of 9%. One important step to unlock the emergent ability is debiasing, where a simple unsupervised reweighting method of the class probabilities yields consistent significant performance gains. We further show that performance increases with model size, implying that as ASR foundation models scale up, they may exhibit improved zero-shot performance.
Towards End-to-End Spoken Grammatical Error Correction
Nov 09, 2023Abstract:Grammatical feedback is crucial for L2 learners, teachers, and testers. Spoken grammatical error correction (GEC) aims to supply feedback to L2 learners on their use of grammar when speaking. This process usually relies on a cascaded pipeline comprising an ASR system, disfluency removal, and GEC, with the associated concern of propagating errors between these individual modules. In this paper, we introduce an alternative "end-to-end" approach to spoken GEC, exploiting a speech recognition foundation model, Whisper. This foundation model can be used to replace the whole framework or part of it, e.g., ASR and disfluency removal. These end-to-end approaches are compared to more standard cascaded approaches on the data obtained from a free-speaking spoken language assessment test, Linguaskill. Results demonstrate that end-to-end spoken GEC is possible within this architecture, but the lack of available data limits current performance compared to a system using large quantities of text-based GEC data. Conversely, end-to-end disfluency detection and removal, which is easier for the attention-based Whisper to learn, does outperform cascaded approaches. Additionally, the paper discusses the challenges of providing feedback to candidates when using end-to-end systems for spoken GEC.
Zero-shot Audio Topic Reranking using Large Language Models
Sep 14, 2023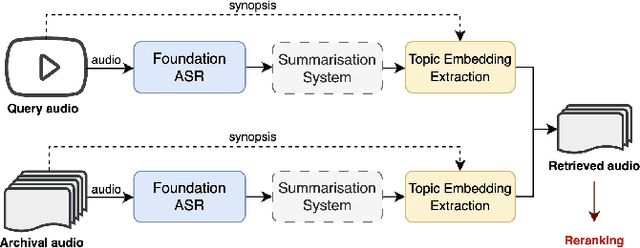

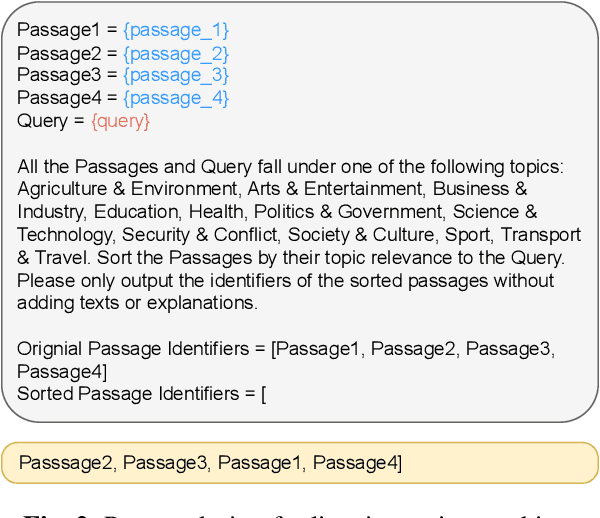

Abstract:The Multimodal Video Search by Examples (MVSE) project investigates using video clips as the query term for information retrieval, rather than the more traditional text query. This enables far richer search modalities such as images, speaker, content, topic, and emotion. A key element for this process is highly rapid, flexible, search to support large archives, which in MVSE is facilitated by representing video attributes by embeddings. This work aims to mitigate any performance loss from this rapid archive search by examining reranking approaches. In particular, zero-shot reranking methods using large language models are investigated as these are applicable to any video archive audio content. Performance is evaluated for topic-based retrieval on a publicly available video archive, the BBC Rewind corpus. Results demonstrate that reranking can achieve improved retrieval ranking without the need for any task-specific training data.
Adapting an ASR Foundation Model for Spoken Language Assessment
Jul 13, 2023



Abstract:A crucial part of an accurate and reliable spoken language assessment system is the underlying ASR model. Recently, large-scale pre-trained ASR foundation models such as Whisper have been made available. As the output of these models is designed to be human readable, punctuation is added, numbers are presented in Arabic numeric form and abbreviations are included. Additionally, these models have a tendency to skip disfluencies and hesitations in the output. Though useful for readability, these attributes are not helpful for assessing the ability of a candidate and providing feedback. Here a precise transcription of what a candidate said is needed. In this paper, we give a detailed analysis of Whisper outputs and propose two solutions: fine-tuning and soft prompt tuning. Experiments are conducted on both public speech corpora and an English learner dataset. Results show that we can effectively alter the decoding behaviour of Whisper to generate the exact words spoken in the response.
Adapting an Unadaptable ASR System
Jun 01, 2023



Abstract:As speech recognition model sizes and training data requirements grow, it is increasingly common for systems to only be available via APIs from online service providers rather than having direct access to models themselves. In this scenario it is challenging to adapt systems to a specific target domain. To address this problem we consider the recently released OpenAI Whisper ASR as an example of a large-scale ASR system to assess adaptation methods. An error correction based approach is adopted, as this does not require access to the model, but can be trained from either 1-best or N-best outputs that are normally available via the ASR API. LibriSpeech is used as the primary target domain for adaptation. The generalization ability of the system in two distinct dimensions are then evaluated. First, whether the form of correction model is portable to other speech recognition domains, and secondly whether it can be used for ASR models having a different architecture.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge