Kata Naszadi
Communicating with Speakers and Listeners of Different Pragmatic Levels
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:This paper explores the impact of variable pragmatic competence on communicative success through simulating language learning and conversing between speakers and listeners with different levels of reasoning abilities. Through studying this interaction, we hypothesize that matching levels of reasoning between communication partners would create a more beneficial environment for communicative success and language learning. Our research findings indicate that learning from more explicit, literal language is advantageous, irrespective of the learner's level of pragmatic competence. Furthermore, we find that integrating pragmatic reasoning during language learning, not just during evaluation, significantly enhances overall communication performance. This paper provides key insights into the importance of aligning reasoning levels and incorporating pragmatic reasoning in optimizing communicative interactions.
Interactive Grounded Language Understanding in a Collaborative Environment: IGLU 2021
May 05, 2022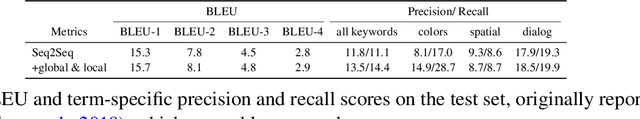
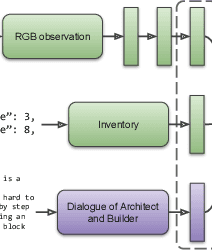
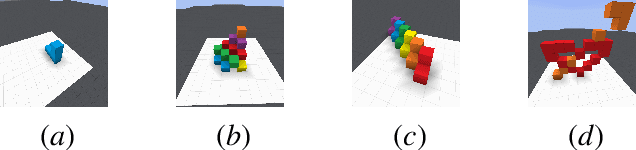
Abstract:Human intelligence has the remarkable ability to quickly adapt to new tasks and environments. Starting from a very young age, humans acquire new skills and learn how to solve new tasks either by imitating the behavior of others or by following provided natural language instructions. To facilitate research in this direction, we propose \emph{IGLU: Interactive Grounded Language Understanding in a Collaborative Environment}. The primary goal of the competition is to approach the problem of how to build interactive agents that learn to solve a task while provided with grounded natural language instructions in a collaborative environment. Understanding the complexity of the challenge, we split it into sub-tasks to make it feasible for participants.
* arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2110.06536
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge