Kartikey Pant
Text Simplification for Comprehension-based Question-Answering
Sep 28, 2021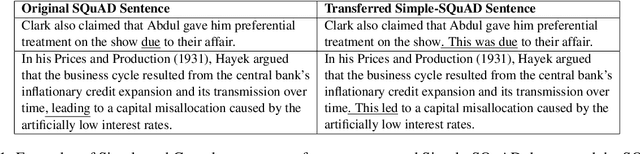
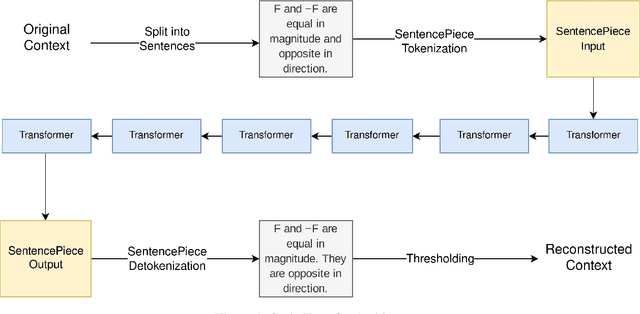
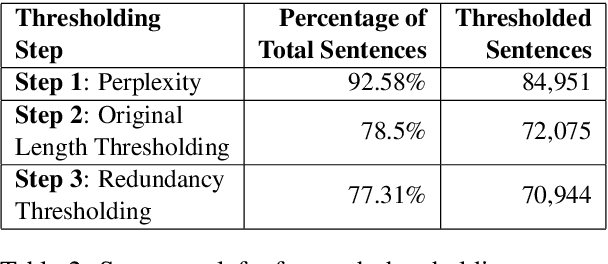
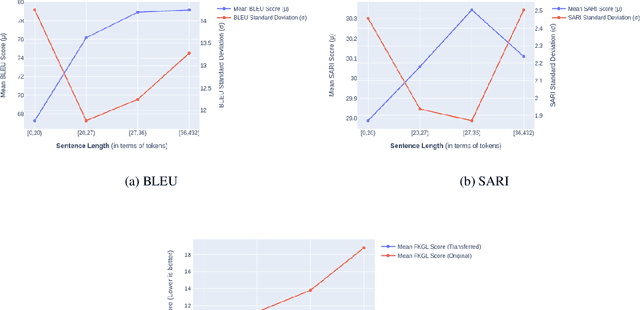
Abstract:Text simplification is the process of splitting and rephrasing a sentence to a sequence of sentences making it easier to read and understand while preserving the content and approximating the original meaning. Text simplification has been exploited in NLP applications like machine translation, summarization, semantic role labeling, and information extraction, opening a broad avenue for its exploitation in comprehension-based question-answering downstream tasks. In this work, we investigate the effect of text simplification in the task of question-answering using a comprehension context. We release Simple-SQuAD, a simplified version of the widely-used SQuAD dataset. Firstly, we outline each step in the dataset creation pipeline, including style transfer, thresholding of sentences showing correct transfer, and offset finding for each answer. Secondly, we verify the quality of the transferred sentences through various methodologies involving both automated and human evaluation. Thirdly, we benchmark the newly created corpus and perform an ablation study for examining the effect of the simplification process in the SQuAD-based question answering task. Our experiments show that simplification leads to up to 2.04% and 1.74% increase in Exact Match and F1, respectively. Finally, we conclude with an analysis of the transfer process, investigating the types of edits made by the model, and the effect of sentence length on the transfer model.
Towards Code-switched Classification Exploiting Constituent Language Resources
Nov 03, 2020



Abstract:Code-switching is a commonly observed communicative phenomenon denoting a shift from one language to another within the same speech exchange. The analysis of code-switched data often becomes an assiduous task, owing to the limited availability of data. We propose converting code-switched data into its constituent high resource languages for exploiting both monolingual and cross-lingual settings in this work. This conversion allows us to utilize the higher resource availability for its constituent languages for multiple downstream tasks. We perform experiments for two downstream tasks, sarcasm detection and hate speech detection, in the English-Hindi code-switched setting. These experiments show an increase in 22% and 42.5% in F1-score for sarcasm detection and hate speech detection, respectively, compared to the state-of-the-art.
Cross-lingual Inductive Transfer to Detect Offensive Language
Jul 07, 2020



Abstract:With the growing use of social media and its availability, many instances of the use of offensive language have been observed across multiple languages and domains. This phenomenon has given rise to the growing need to detect the offensive language used in social media cross-lingually. In OffensEval 2020, the organizers have released the \textit{multilingual Offensive Language Identification Dataset} (mOLID), which contains tweets in five different languages, to detect offensive language. In this work, we introduce a cross-lingual inductive approach to identify the offensive language in tweets using the contextual word embedding \textit{XLM-RoBERTa} (XLM-R). We show that our model performs competitively on all five languages, obtaining the fourth position in the English task with an F1-score of $0.919$ and eighth position in the Turkish task with an F1-score of $0.781$. Further experimentation proves that our model works competitively in a zero-shot learning environment, and is extensible to other languages.
BERT-based Ensembles for Modeling Disclosure and Support in Conversational Social Media Text
Jun 01, 2020



Abstract:There is a growing interest in understanding how humans initiate and hold conversations. The affective understanding of conversations focuses on the problem of how speakers use emotions to react to a situation and to each other. In the CL-Aff Shared Task, the organizers released Get it #OffMyChest dataset, which contains Reddit comments from casual and confessional conversations, labeled for their disclosure and supportiveness characteristics. In this paper, we introduce a predictive ensemble model exploiting the finetuned contextualized word embeddings, RoBERTa and ALBERT. We show that our model outperforms the base models in all considered metrics, achieving an improvement of $3\%$ in the F1 score. We further conduct statistical analysis and outline deeper insights into the given dataset while providing a new characterization of impact for the dataset.
Sarcasm Detection using Context Separators in Online Discourse
Jun 01, 2020



Abstract:Sarcasm is an intricate form of speech, where meaning is conveyed implicitly. Being a convoluted form of expression, detecting sarcasm is an assiduous problem. The difficulty in recognition of sarcasm has many pitfalls, including misunderstandings in everyday communications, which leads us to an increasing focus on automated sarcasm detection. In the second edition of the Figurative Language Processing (FigLang 2020) workshop, the shared task of sarcasm detection released two datasets, containing responses along with their context sampled from Twitter and Reddit. In this work, we use RoBERTa_large to detect sarcasm in both the datasets. We further assert the importance of context in improving the performance of contextual word embedding based models by using three different types of inputs - Response-only, Context-Response, and Context-Response (Separated). We show that our proposed architecture performs competitively for both the datasets. We also show that the addition of a separation token between context and target response results in an improvement of 5.13% in the F1-score in the Reddit dataset.
Towards Detection of Subjective Bias using Contextualized Word Embeddings
Feb 16, 2020
Abstract:Subjective bias detection is critical for applications like propaganda detection, content recommendation, sentiment analysis, and bias neutralization. This bias is introduced in natural language via inflammatory words and phrases, casting doubt over facts, and presupposing the truth. In this work, we perform comprehensive experiments for detecting subjective bias using BERT-based models on the Wiki Neutrality Corpus(WNC). The dataset consists of $360k$ labeled instances, from Wikipedia edits that remove various instances of the bias. We further propose BERT-based ensembles that outperform state-of-the-art methods like $BERT_{large}$ by a margin of $5.6$ F1 score.
SmokEng: Towards Fine-grained Classification of Tobacco-related Social Media Text
Oct 12, 2019



Abstract:Contemporary datasets on tobacco consumption focus on one of two topics, either public health mentions and disease surveillance, or sentiment analysis on topical tobacco products and services. However, two primary considerations are not accounted for, the language of the demographic affected and a combination of the topics mentioned above in a fine-grained classification mechanism. In this paper, we create a dataset of 3144 tweets, which are selected based on the presence of colloquial slang related to smoking and analyze it based on the semantics of the tweet. Each class is created and annotated based on the content of the tweets such that further hierarchical methods can be easily applied. Further, we prove the efficacy of standard text classification methods on this dataset, by designing experiments which do both binary as well as multi-class classification. Our experiments tackle the identification of either a specific topic (such as tobacco product promotion), a general mention (cigarettes and related products) or a more fine-grained classification. This methodology paves the way for further analysis, such as understanding sentiment or style, which makes this dataset a vital contribution to both disease surveillance and tobacco use research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge