Ferdous Ahmed Barbhuiya
Handloom Design Generation Using Generative Networks
May 20, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes deep learning techniques of generating designs for clothing, focused on handloom fabric and discusses the associated challenges along with its application. The capability of generative neural network models in understanding artistic designs and synthesizing those is not yet explored well. In this work, multiple methods are employed incorporating the current state of the art generative models and style transfer algorithms to study and observe their performance for the task. The results are then evaluated through user score. This work also provides a new dataset NeuralLoom for the task of the design generation.
NBF at SemEval-2025 Task 5: Light-Burst Attention Enhanced System for Multilingual Subject Recommendation
May 06, 2025Abstract:We present our system submission for SemEval 2025 Task 5, which focuses on cross-lingual subject classification in the English and German academic domains. Our approach leverages bilingual data during training, employing negative sampling and a margin-based retrieval objective. We demonstrate that a dimension-as-token self-attention mechanism designed with significantly reduced internal dimensions can effectively encode sentence embeddings for subject retrieval. In quantitative evaluation, our system achieved an average recall rate of 32.24% in the general quantitative setting (all subjects), 43.16% and 31.53% of the general qualitative evaluation methods with minimal GPU usage, highlighting their competitive performance. Our results demonstrate that our approach is effective in capturing relevant subject information under resource constraints, although there is still room for improvement.
Text Simplification for Comprehension-based Question-Answering
Sep 28, 2021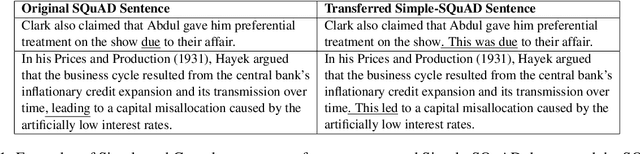
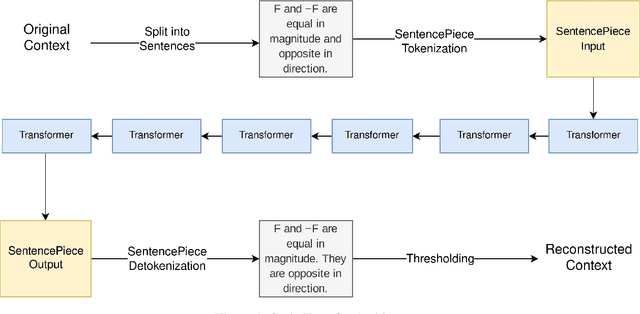
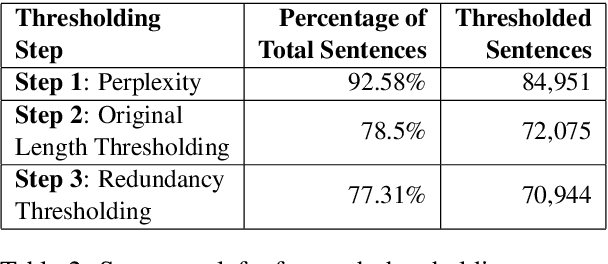
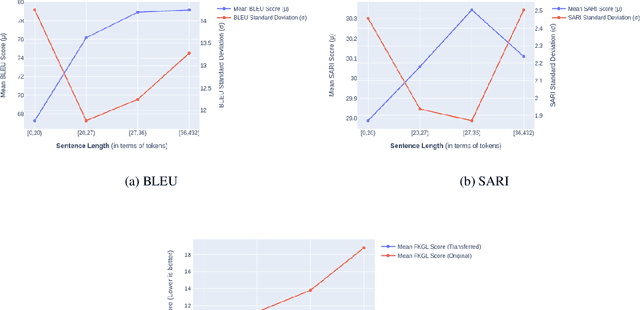
Abstract:Text simplification is the process of splitting and rephrasing a sentence to a sequence of sentences making it easier to read and understand while preserving the content and approximating the original meaning. Text simplification has been exploited in NLP applications like machine translation, summarization, semantic role labeling, and information extraction, opening a broad avenue for its exploitation in comprehension-based question-answering downstream tasks. In this work, we investigate the effect of text simplification in the task of question-answering using a comprehension context. We release Simple-SQuAD, a simplified version of the widely-used SQuAD dataset. Firstly, we outline each step in the dataset creation pipeline, including style transfer, thresholding of sentences showing correct transfer, and offset finding for each answer. Secondly, we verify the quality of the transferred sentences through various methodologies involving both automated and human evaluation. Thirdly, we benchmark the newly created corpus and perform an ablation study for examining the effect of the simplification process in the SQuAD-based question answering task. Our experiments show that simplification leads to up to 2.04% and 1.74% increase in Exact Match and F1, respectively. Finally, we conclude with an analysis of the transfer process, investigating the types of edits made by the model, and the effect of sentence length on the transfer model.
Predicting Popularity of Images Over 30 Days
Aug 03, 2021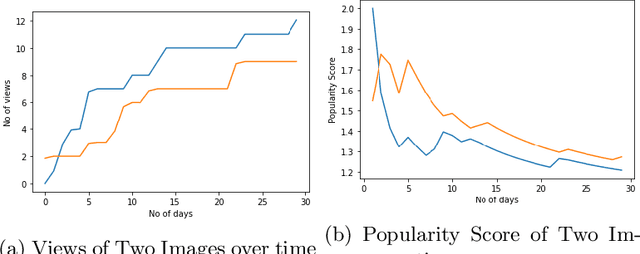
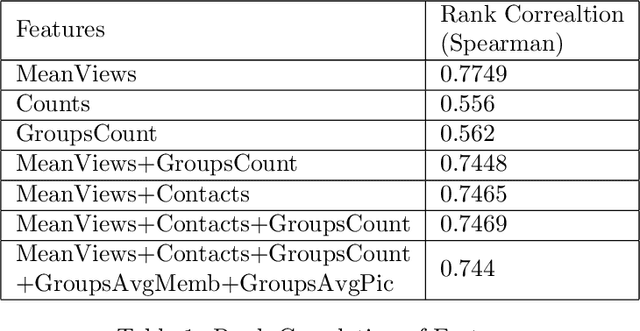
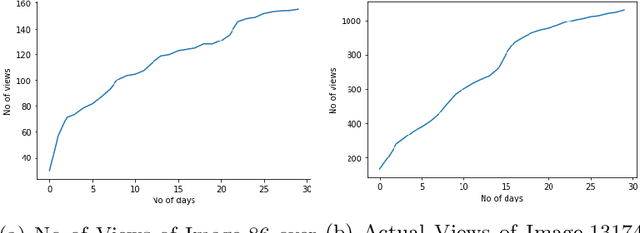
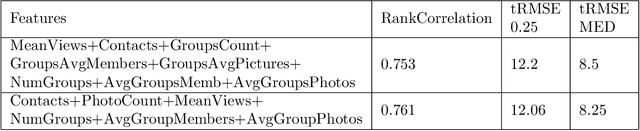
Abstract:The current work deals with the problem of attempting to predict the popularity of images before even being uploaded. This method is specifically focused on Flickr images. Social features of each image as well as that of the user who had uploaded it, have been recorded. The dataset also includes the engagement score of each image which is the ground truth value of the views obtained by each image over a period of 30 days. The work aims to predict the popularity of images on Flickr over a period of 30 days using the social features of the user and the image, as well as the visual features of the images. The method states that the engagement sequence of an image can be said to depend on two independent quantities, namely scale and shape of an image. Once the shape and scale of an image have been predicted, combining them the predicted sequence of an image over 30 days is obtained. The current work follows a previous work done in the same direction, with certain speculations and suggestions of improvement.
IIITG-ADBU@HASOC-Dravidian-CodeMix-FIRE2020: Offensive Content Detection in Code-Mixed Dravidian Text
Jul 29, 2021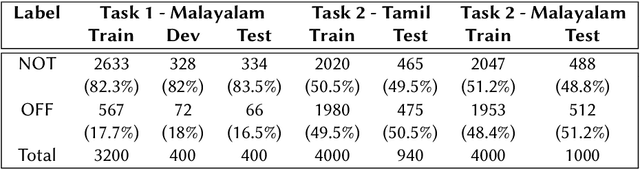
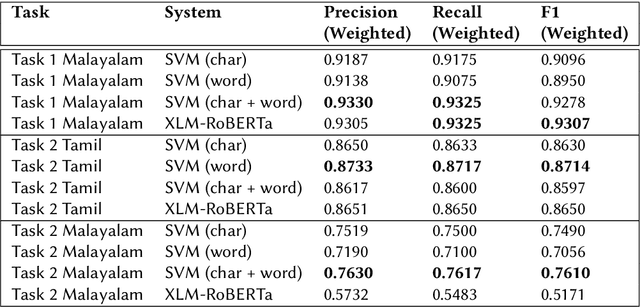
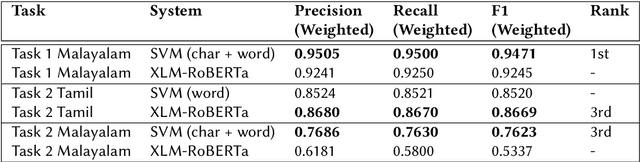
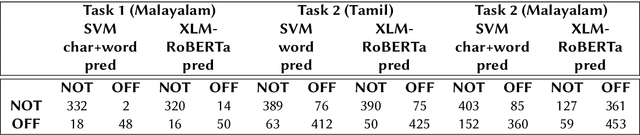
Abstract:This paper presents the results obtained by our SVM and XLM-RoBERTa based classifiers in the shared task Dravidian-CodeMix-HASOC 2020. The SVM classifier trained using TF-IDF features of character and word n-grams performed the best on the code-mixed Malayalam text. It obtained a weighted F1 score of 0.95 (1st Rank) and 0.76 (3rd Rank) on the YouTube and Twitter dataset respectively. The XLM-RoBERTa based classifier performed the best on the code-mixed Tamil text. It obtained a weighted F1 score of 0.87 (3rd Rank) on the code-mixed Tamil Twitter dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge