Karima Benatchba
A Life-long Learning Intrusion Detection System for 6G-Enabled IoV
Jul 22, 2024



Abstract:The introduction of 6G technology into the Internet of Vehicles (IoV) promises to revolutionize connectivity with ultra-high data rates and seamless network coverage. However, this technological leap also brings significant challenges, particularly for the dynamic and diverse IoV landscape, which must meet the rigorous reliability and security requirements of 6G networks. Furthermore, integrating 6G will likely increase the IoV's susceptibility to a spectrum of emerging cyber threats. Therefore, it is crucial for security mechanisms to dynamically adapt and learn new attack patterns, keeping pace with the rapid evolution and diversification of these threats - a capability currently lacking in existing systems. This paper presents a novel intrusion detection system leveraging the paradigm of life-long (or continual) learning. Our methodology combines class-incremental learning with federated learning, an approach ideally suited to the distributed nature of the IoV. This strategy effectively harnesses the collective intelligence of Connected and Automated Vehicles (CAVs) and edge computing capabilities to train the detection system. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to synergize class-incremental learning with federated learning specifically for cyber attack detection. Through comprehensive experiments on a recent network traffic dataset, our system has exhibited a robust adaptability in learning new cyber attack patterns, while effectively retaining knowledge of previously encountered ones. Additionally, it has proven to maintain high accuracy and a low false positive rate.
LOOPer: A Learned Automatic Code Optimizer For Polyhedral Compilers
Mar 22, 2024



Abstract:While polyhedral compilers have shown success in implementing advanced code transformations, they still have challenges in selecting the most profitable transformations that lead to the best speedups. This has motivated the use of machine learning to build cost models to guide the search for polyhedral optimizations. State-of-the-art polyhedral compilers have demonstrated a viable proof-of-concept of this approach. While such a proof-of-concept has shown promise, it still has significant limitations. State-of-the-art polyhedral compilers that use a deep-learning cost model only support a small subset of affine transformations, limiting their ability to apply complex code transformations. They also only support simple programs that have a single loop nest and a rectangular iteration domain, limiting their applicability to many programs. These limitations significantly impact the generality of such compilers and autoschedulers and put into question the whole approach. In this paper, we introduce LOOPer, the first polyhedral autoscheduler that uses a deep-learning based cost model and covers a large set of affine transformations and programs. It supports the exploration of a large set of affine transformations, allowing the application of complex sequences of polyhedral transformations. It also supports the optimization of programs with multiple loop nests and with rectangular and non-rectangular iteration domains, allowing the optimization of an extensive set of programs. We implement and evaluate LOOPer and show that it achieves speedups over the state-of-the-art. On the Polybench benchmark, LOOPer achieves a geometric mean speedup of 1.59x over Tiramisu. LOOPer also achieves competitive speedups with a geometric mean speedup of 1.34x over Pluto, a state-of-the-art polyhedral compiler that does not use a machine-learning based cost model.
Progress Report: A Deep Learning Guided Exploration of Affine Unimodular Loop Transformations
Jun 08, 2022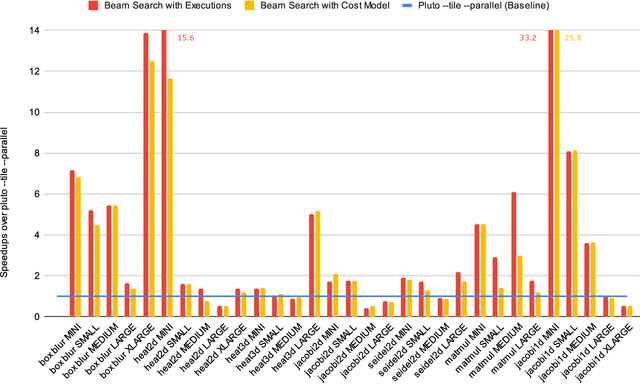
Abstract:In this paper, we present a work in progress about a deep learning based approach for automatic code optimization in polyhedral compilers. The proposed technique explores combinations of affine and non-affine loop transformations to find the sequence of transformations that minimizes the execution time of a given program. This exploration is guided by a deep learning based cost model that evaluates the speedup that each sequence of transformations would yield. Preliminary results show that the proposed techniques achieve a 2.35x geometric mean speedup over state of the art polyhedral compilers (Pluto).
A Deep Learning Based Cost Model for Automatic Code Optimization
Apr 11, 2021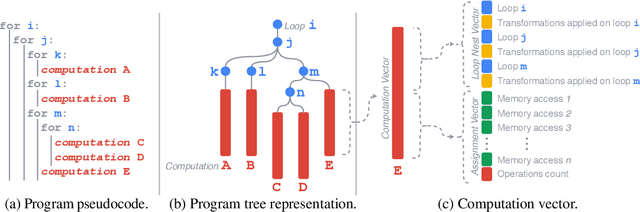
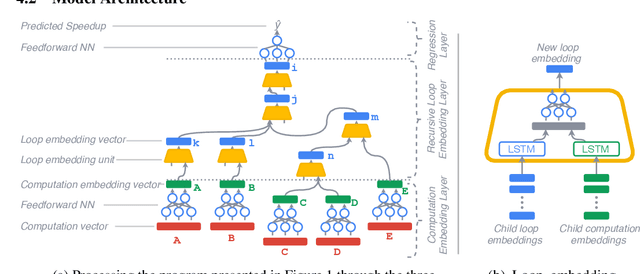
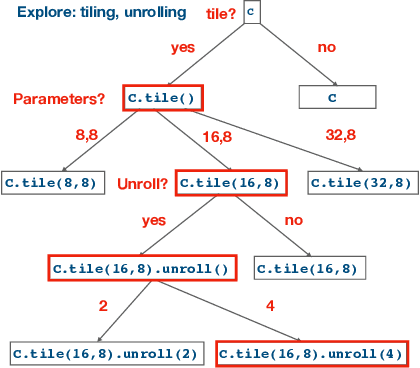
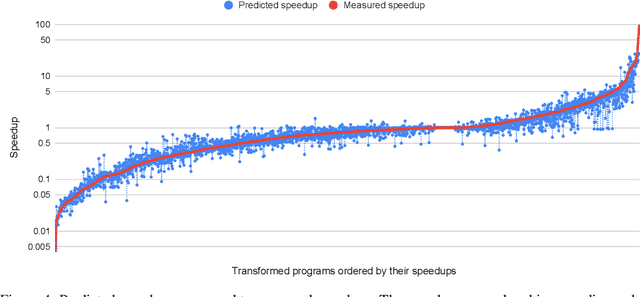
Abstract:Enabling compilers to automatically optimize code has been a longstanding goal for the compiler community. Efficiently solving this problem requires using precise cost models. These models predict whether applying a sequence of code transformations reduces the execution time of the program. Building an analytical cost model to do so is hard in modern x86 architectures due to the complexity of the microarchitecture. In this paper, we present a novel deep learning based cost model for automatic code optimization. This model was integrated in a search method and implemented in the Tiramisu compiler to select the best code transformations. The input of the proposed model is a set of simple features representing the unoptimized code and a sequence of code transformations. The model predicts the speedup expected when the code transformations are applied. Unlike previous models, the proposed one works on full programs and does not rely on any heavy feature engineering. The proposed model has only 16% of mean absolute percentage error in predicting speedups on full programs. The proposed model enables Tiramisu to automatically find code transformations that match or are better than state-of-the-art compilers without requiring the same level of heavy feature engineering required by those compilers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge