Karim R. Lakhani
Time Dependency, Data Flow, and Competitive Advantage
Mar 17, 2022



Abstract:Data is fundamental to machine learning-based products and services and is considered strategic due to its externalities for businesses, governments, non-profits, and more generally for society. It is renowned that the value of organizations (businesses, government agencies and programs, and even industries) scales with the volume of available data. What is often less appreciated is that the data value in making useful organizational predictions will range widely and is prominently a function of data characteristics and underlying algorithms. In this research, our goal is to study how the value of data changes over time and how this change varies across contexts and business areas (e.g. next word prediction in the context of history, sports, politics). We focus on data from Reddit.com and compare the value's time-dependency across various Reddit topics (Subreddits). We make this comparison by measuring the rate at which user-generated text data loses its relevance to the algorithmic prediction of conversations. We show that different subreddits have different rates of relevance decline over time. Relating the text topics to various business areas of interest, we argue that competing in a business area in which data value decays rapidly alters strategies to acquire competitive advantage. When data value decays rapidly, access to a continuous flow of data will be more valuable than access to a fixed stock of data. In this kind of setting, improving user engagement and increasing user-base help creating and maintaining a competitive advantage.
Detecting Figures and Part Labels in Patents: Competition-Based Development of Image Processing Algorithms
Nov 11, 2014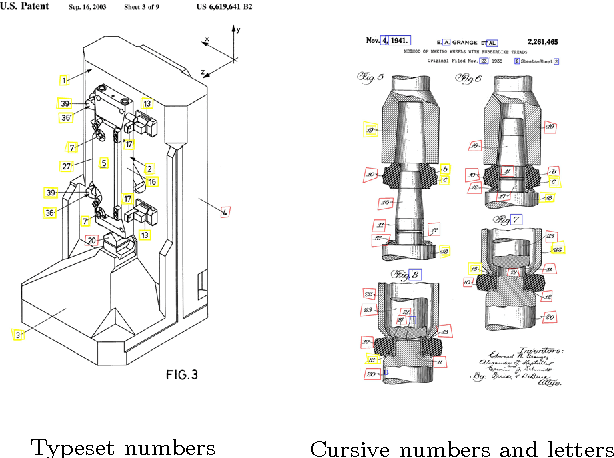

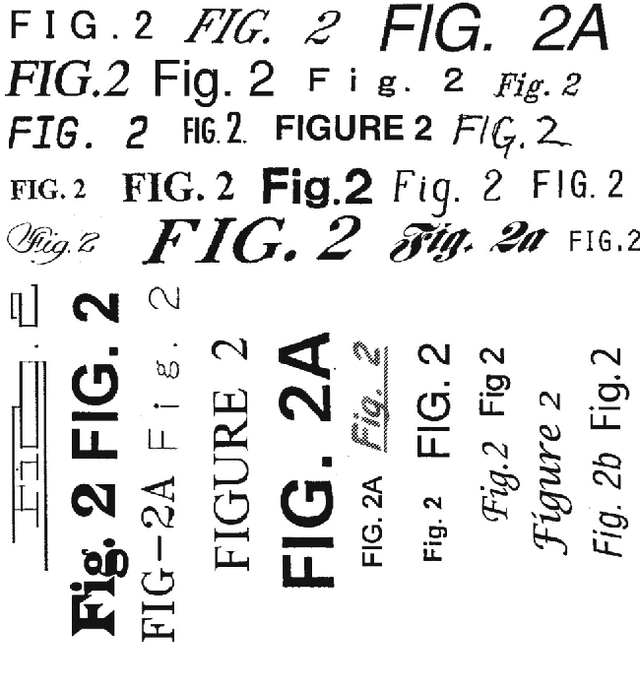
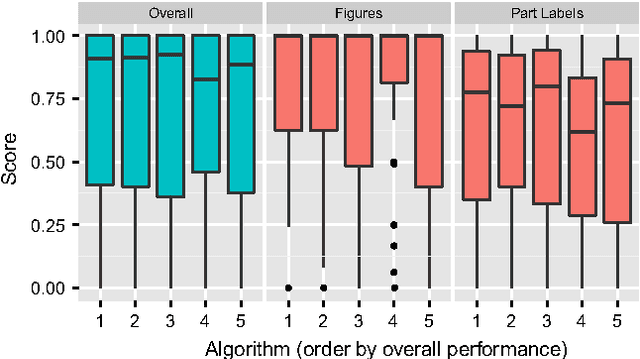
Abstract:We report the findings of a month-long online competition in which participants developed algorithms for augmenting the digital version of patent documents published by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO). The goal was to detect figures and part labels in U.S. patent drawing pages. The challenge drew 232 teams of two, of which 70 teams (30%) submitted solutions. Collectively, teams submitted 1,797 solutions that were compiled on the competition servers. Participants reported spending an average of 63 hours developing their solutions, resulting in a total of 5,591 hours of development time. A manually labeled dataset of 306 patents was used for training, online system tests, and evaluation. The design and performance of the top-5 systems are presented, along with a system developed after the competition which illustrates that winning teams produced near state-of-the-art results under strict time and computation constraints. For the 1st place system, the harmonic mean of recall and precision (f-measure) was 88.57% for figure region detection, 78.81% for figure regions with correctly recognized figure titles, and 70.98% for part label detection and character recognition. Data and software from the competition are available through the online UCI Machine Learning repository to inspire follow-on work by the image processing community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge