Karen Pinel-Sauvagnat
An Evaluation Framework for Attributed Information Retrieval using Large Language Models
Sep 12, 2024Abstract:With the growing success of Large Language models (LLMs) in information-seeking scenarios, search engines are now adopting generative approaches to provide answers along with in-line citations as attribution. While existing work focuses mainly on attributed question answering, in this paper, we target information-seeking scenarios which are often more challenging due to the open-ended nature of the queries and the size of the label space in terms of the diversity of candidate-attributed answers per query. We propose a reproducible framework to evaluate and benchmark attributed information seeking, using any backbone LLM, and different architectural designs: (1) Generate (2) Retrieve then Generate, and (3) Generate then Retrieve. Experiments using HAGRID, an attributed information-seeking dataset, show the impact of different scenarios on both the correctness and attributability of answers.
Does Structure Matter? Leveraging Data-to-Text Generation for Answering Complex Information Needs
Dec 08, 2021

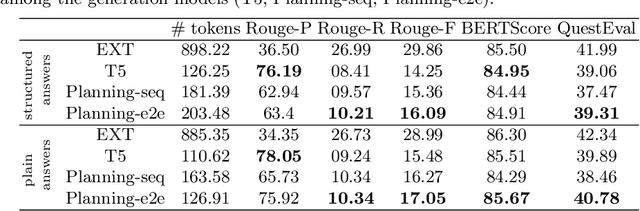

Abstract:In this work, our aim is to provide a structured answer in natural language to a complex information need. Particularly, we envision using generative models from the perspective of data-to-text generation. We propose the use of a content selection and planning pipeline which aims at structuring the answer by generating intermediate plans. The experimental evaluation is performed using the TREC Complex Answer Retrieval (CAR) dataset. We evaluate both the generated answer and its corresponding structure and show the effectiveness of planning-based models in comparison to a text-to-text model.
TSSuBERT: Tweet Stream Summarization Using BERT
Jun 16, 2021



Abstract:The development of deep neural networks and the emergence of pre-trained language models such as BERT allow to increase performance on many NLP tasks. However, these models do not meet the same popularity for tweet summarization, which can probably be explained by the lack of existing collections for training and evaluation. Our contribution in this paper is twofold : (1) we introduce a large dataset for Twitter event summarization, and (2) we propose a neural model to automatically summarize huge tweet streams. This extractive model combines in an original way pre-trained language models and vocabulary frequency-based representations to predict tweet salience. An additional advantage of the model is that it automatically adapts the size of the output summary according to the input tweet stream. We conducted experiments using two different Twitter collections, and promising results are observed in comparison with state-of-the-art baselines.
Studying Catastrophic Forgetting in Neural Ranking Models
Jan 18, 2021



Abstract:Several deep neural ranking models have been proposed in the recent IR literature. While their transferability to one target domain held by a dataset has been widely addressed using traditional domain adaptation strategies, the question of their cross-domain transferability is still under-studied. We study here in what extent neural ranking models catastrophically forget old knowledge acquired from previously observed domains after acquiring new knowledge, leading to performance decrease on those domains. Our experiments show that the effectiveness of neuralIR ranking models is achieved at the cost of catastrophic forgetting and that a lifelong learning strategy using a cross-domain regularizer success-fully mitigates the problem. Using an explanatory approach built on a regression model, we also show the effect of domain characteristics on the rise of catastrophic forgetting. We believe that the obtained results can be useful for both theoretical and practical future work in neural IR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge