Kaiying Hou
Towards Autonomous Mathematics Research
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in foundational models have yielded reasoning systems capable of achieving a gold-medal standard at the International Mathematical Olympiad. The transition from competition-level problem-solving to professional research, however, requires navigating vast literature and constructing long-horizon proofs. In this work, we introduce Aletheia, a math research agent that iteratively generates, verifies, and revises solutions end-to-end in natural language. Specifically, Aletheia is powered by an advanced version of Gemini Deep Think for challenging reasoning problems, a novel inference-time scaling law that extends beyond Olympiad-level problems, and intensive tool use to navigate the complexities of mathematical research. We demonstrate the capability of Aletheia from Olympiad problems to PhD-level exercises and most notably, through several distinct milestones in AI-assisted mathematics research: (a) a research paper (Feng26) generated by AI without any human intervention in calculating certain structure constants in arithmetic geometry called eigenweights; (b) a research paper (LeeSeo26) demonstrating human-AI collaboration in proving bounds on systems of interacting particles called independent sets; and (c) an extensive semi-autonomous evaluation (Feng et al., 2026a) of 700 open problems on Bloom's Erdos Conjectures database, including autonomous solutions to four open questions. In order to help the public better understand the developments pertaining to AI and mathematics, we suggest quantifying standard levels of autonomy and novelty of AI-assisted results, as well as propose a novel concept of human-AI interaction cards for transparency. We conclude with reflections on human-AI collaboration in mathematics and share all prompts as well as model outputs at https://github.com/google-deepmind/superhuman/tree/main/aletheia.
Semi-Autonomous Mathematics Discovery with Gemini: A Case Study on the Erdős Problems
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:We present a case study in semi-autonomous mathematics discovery, using Gemini to systematically evaluate 700 conjectures labeled 'Open' in Bloom's Erdős Problems database. We employ a hybrid methodology: AI-driven natural language verification to narrow the search space, followed by human expert evaluation to gauge correctness and novelty. We address 13 problems that were marked 'Open' in the database: 5 through seemingly novel autonomous solutions, and 8 through identification of previous solutions in the existing literature. Our findings suggest that the 'Open' status of the problems was through obscurity rather than difficulty. We also identify and discuss issues arising in applying AI to math conjectures at scale, highlighting the difficulty of literature identification and the risk of ''subconscious plagiarism'' by AI. We reflect on the takeaways from AI-assisted efforts on the Erdős Problems.
Universal Length Generalization with Turing Programs
Jul 03, 2024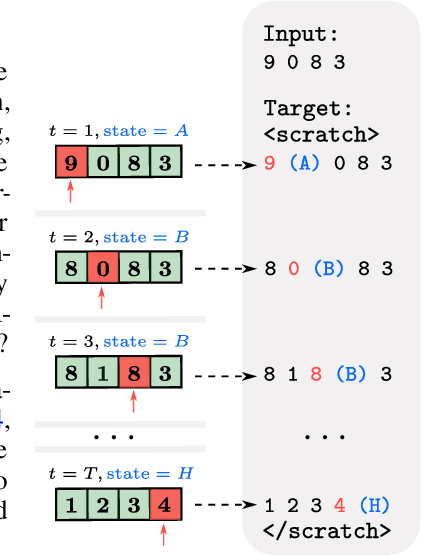

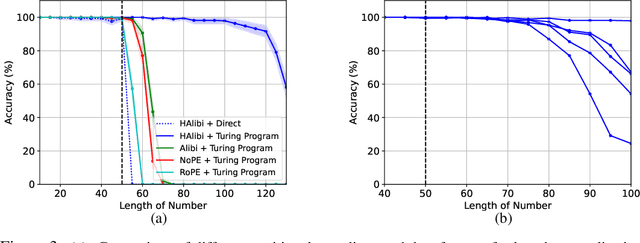
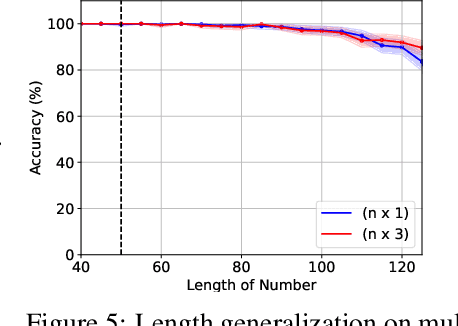
Abstract:Length generalization refers to the ability to extrapolate from short training sequences to long test sequences and is a challenge for current large language models. While prior work has proposed some architecture or data format changes to achieve length generalization, these proposals typically apply to a limited set of tasks. Building on prior scratchpad and Chain-of-Thought (CoT) techniques, we propose Turing Programs, a novel CoT strategy that decomposes an algorithmic task into steps mimicking the computation of a Turing Machine. This framework is both universal, as it can accommodate any algorithmic task, and simple, requiring only copying text from the context with small modifications. We show that by using Turing Programs, we obtain robust length generalization on a range of algorithmic tasks: addition, multiplication and in-context SGD. We then demonstrate that transformers achieve length generalization on random Turing Programs, suggesting that length generalization is possible for any algorithmic task. Finally, we theoretically prove that transformers can implement Turing Programs, constructing a simple RASP (Weiss et al.) program that simulates an arbitrary Turing machine.
Learning quantum symmetries with interactive quantum-classical variational algorithms
Jun 23, 2022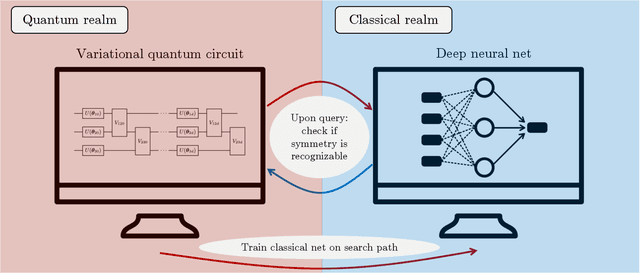
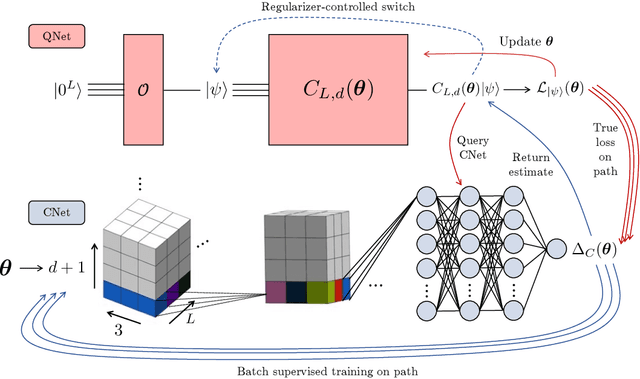
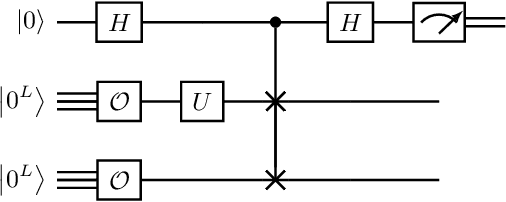
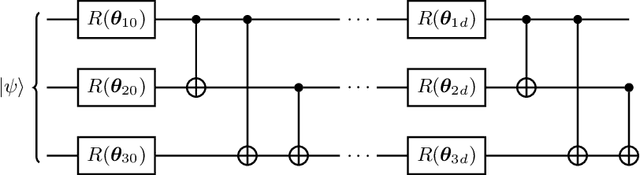
Abstract:A symmetry of a state $\lvert \psi \rangle$ is a unitary operator of which $\lvert \psi \rangle$ is an eigenvector. When $\lvert \psi \rangle$ is an unknown state supplied by a black-box oracle, the state's symmetries serve to characterize it, and often relegate much of the desired information about $\lvert \psi \rangle$. In this paper, we develop a variational hybrid quantum-classical learning scheme to systematically probe for symmetries of $\lvert \psi \rangle$ with no a priori assumptions about the state. This procedure can be used to learn various symmetries at the same time. In order to avoid re-learning already known symmetries, we introduce an interactive protocol with a classical deep neural net. The classical net thereby regularizes against repetitive findings and allows our algorithm to terminate empirically with all possible symmetries found. Our scheme can be implemented efficiently on average with non-local SWAP gates; we also give a less efficient algorithm with only local operations, which may be more appropriate for current noisy quantum devices. We demonstrate our algorithm on representative families of states.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge