Kaijian Zou
LiveOIBench: Can Large Language Models Outperform Human Contestants in Informatics Olympiads?
Oct 10, 2025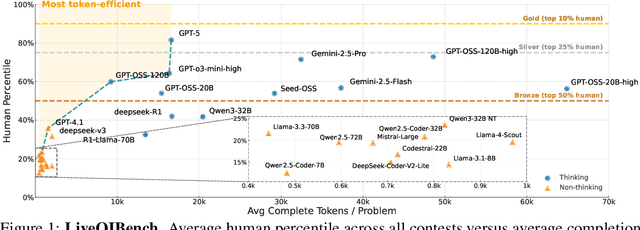
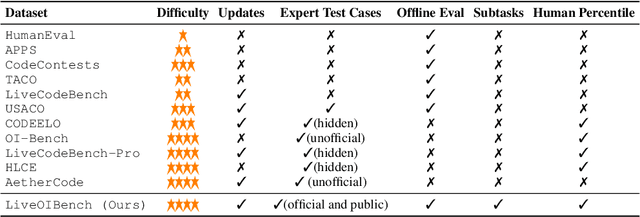
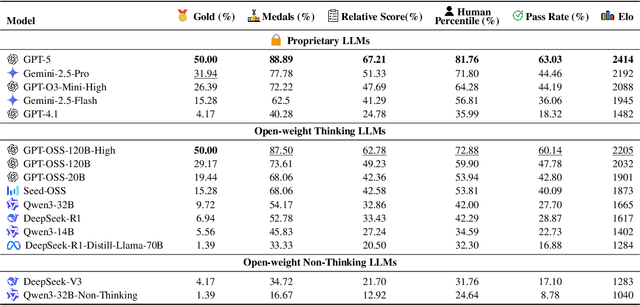
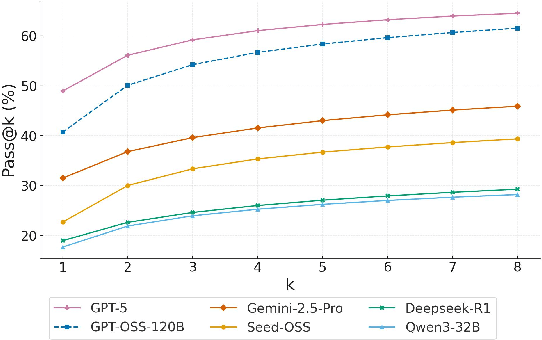
Abstract:Competitive programming problems increasingly serve as valuable benchmarks to evaluate the coding capabilities of large language models (LLMs) due to their complexity and ease of verification. Yet, current coding benchmarks face limitations such as lack of exceptionally challenging problems, insufficient test case coverage, reliance on online platform APIs that limit accessibility. To address these issues, we introduce LiveOIBench, a comprehensive benchmark featuring 403 expert-curated Olympiad-level competitive programming problems, each with an average of 60 expert-designed test cases. The problems are sourced directly from 72 official Informatics Olympiads in different regions conducted between 2023 and 2025. LiveOIBench distinguishes itself through four key features: (1) meticulously curated high-quality tasks with detailed subtask rubrics and extensive private test cases; (2) direct integration of elite contestant performance data to enable informative comparison against top-performing humans; (3) planned continuous, contamination-free updates from newly released Olympiad problems; and (4) a self-contained evaluation system facilitating offline and easy-to-reproduce assessments. Benchmarking 32 popular general-purpose and reasoning LLMs, we find that GPT-5 achieves a notable 81.76th percentile, a strong result that nonetheless falls short of top human contestant performance, who usually place above 90th. In contrast, among open-weight reasoning models, GPT-OSS-120B achieves only a 60th percentile, underscoring significant capability disparities from frontier closed models. Detailed analyses indicate that robust reasoning models prioritize precise problem analysis over excessive exploration, suggesting future models should emphasize structured analysis and minimize unnecessary exploration. All data, code, and leaderboard results will be made publicly available on our website.
Retrieval or Global Context Understanding? On Many-Shot In-Context Learning for Long-Context Evaluation
Nov 11, 2024
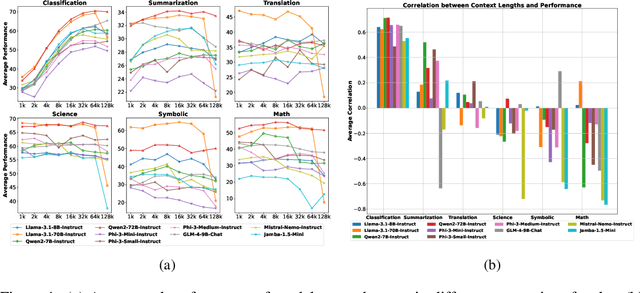
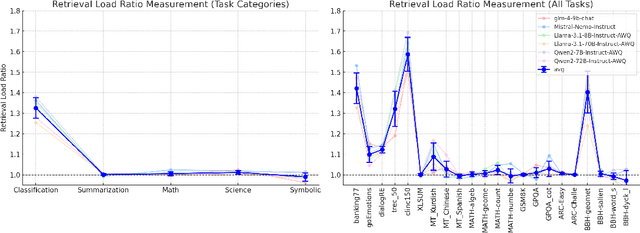
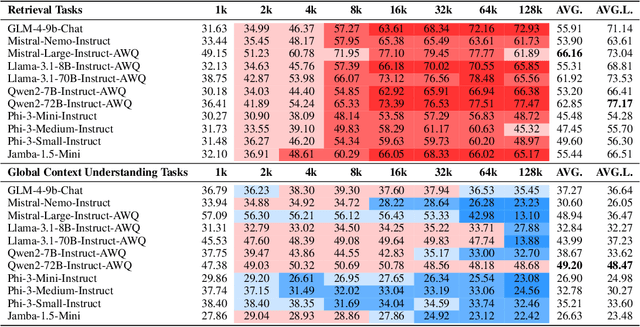
Abstract:Language models (LMs) have demonstrated an improved capacity to handle long-context information, yet existing long-context benchmarks primarily measure LMs' retrieval abilities with extended inputs, e.g., pinpointing a short phrase from long-form text. Therefore, they may fall short when evaluating models' global context understanding capacity, such as synthesizing and reasoning over content across input to generate the response. In this paper, we study long-context language model (LCLM) evaluation through many-shot in-context learning (ICL). Concretely, we identify the skills each ICL task requires, and examine models' long-context capabilities on them. We first ask: What types of ICL tasks benefit from additional demonstrations, and are these tasks effective at evaluating LCLMs? We find that classification and summarization tasks show notable performance improvements with additional demonstrations, while translation and reasoning tasks do not exhibit clear trends. This suggests the classification tasks predominantly test models' retrieval skills. Next, we ask: To what extent does each task require retrieval skills versus global context understanding from LCLMs? We develop metrics to categorize ICL tasks into two groups: (i) retrieval tasks that require strong retrieval ability to pinpoint relevant examples, and (ii) global context understanding tasks that necessitate a deeper comprehension of the full input. We find that not all datasets can effectively evaluate these long-context capabilities. To address this gap, we introduce a new many-shot ICL benchmark, MANYICLBENCH, designed to characterize LCLMs' retrieval and global context understanding capabilities separately. Benchmarking 11 open-weight LCLMs with MANYICLBENCH, we find that while state-of-the-art models perform well in retrieval tasks up to 64k tokens, many show significant drops in global context tasks at just 16k tokens.
All Things Considered: Detecting Partisan Events from News Media with Cross-Article Comparison
Oct 28, 2023



Abstract:Public opinion is shaped by the information news media provide, and that information in turn may be shaped by the ideological preferences of media outlets. But while much attention has been devoted to media bias via overt ideological language or topic selection, a more unobtrusive way in which the media shape opinion is via the strategic inclusion or omission of partisan events that may support one side or the other. We develop a latent variable-based framework to predict the ideology of news articles by comparing multiple articles on the same story and identifying partisan events whose inclusion or omission reveals ideology. Our experiments first validate the existence of partisan event selection, and then show that article alignment and cross-document comparison detect partisan events and article ideology better than competitive baselines. Our results reveal the high-level form of media bias, which is present even among mainstream media with strong norms of objectivity and nonpartisanship. Our codebase and dataset are available at https://github.com/launchnlp/ATC.
Crossing the Aisle: Unveiling Partisan and Counter-Partisan Events in News Reporting
Oct 28, 2023



Abstract:News media is expected to uphold unbiased reporting. Yet they may still affect public opinion by selectively including or omitting events that support or contradict their ideological positions. Prior work in NLP has only studied media bias via linguistic style and word usage. In this paper, we study to which degree media balances news reporting and affects consumers through event inclusion or omission. We first introduce the task of detecting both partisan and counter-partisan events: events that support or oppose the author's political ideology. To conduct our study, we annotate a high-quality dataset, PAC, containing 8,511 (counter-)partisan event annotations in 304 news articles from ideologically diverse media outlets. We benchmark PAC to highlight the challenges of this task. Our findings highlight both the ways in which the news subtly shapes opinion and the need for large language models that better understand events within a broader context. Our dataset can be found at https://github.com/launchnlp/Partisan-Event-Dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge