K Sreenivasa Rao
Multilingual Audio-Visual Smartphone Dataset And Evaluation
Sep 09, 2021



Abstract:Smartphones have been employed with biometric-based verification systems to provide security in highly sensitive applications. Audio-visual biometrics are getting popular due to the usability and also it will be challenging to spoof because of multi-modal nature. In this work, we present an audio-visual smartphone dataset captured in five different recent smartphones. This new dataset contains 103 subjects captured in three different sessions considering the different real-world scenarios. Three different languages are acquired in this dataset to include the problem of language dependency of the speaker recognition systems. These unique characteristics of this dataset will pave the way to implement novel state-of-the-art unimodal or audio-visual speaker recognition systems. We also report the performance of the bench-marked biometric verification systems on our dataset. The robustness of biometric algorithms is evaluated towards multiple dependencies like signal noise, device, language and presentation attacks like replay and synthesized signals with extensive experiments. The obtained results raised many concerns about the generalization properties of state-of-the-art biometrics methods in smartphones.
Knowledge Distillation for Singing Voice Detection
Nov 09, 2020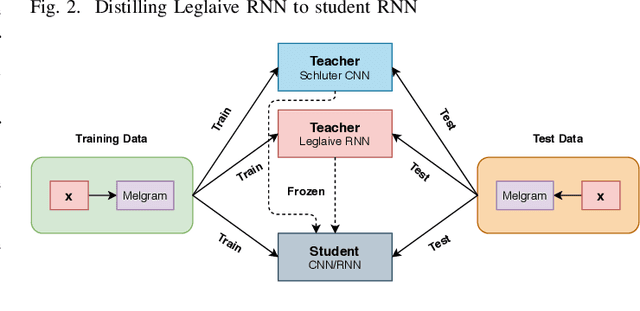
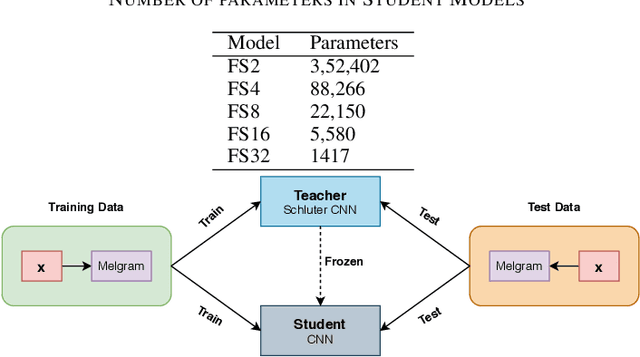
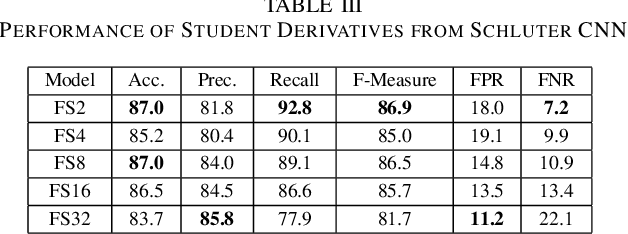
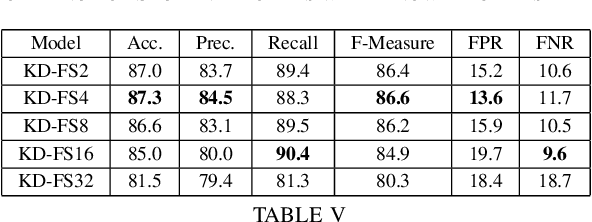
Abstract:Singing Voice Detection (SVD) has been an active area of research in music information retrieval (MIR). Currently, two deep neural network-based methods, one based on CNN and the other on RNN, exist in literature that learn optimized features for the voice detection (VD) task and achieve state-of-the-art performance on common datasets. Both these models have a huge number of parameters (1.4M for CNN and 65.7K for RNN) and hence not suitable for deployment on devices like smartphones or embedded sensors with limited capacity in terms of memory and computation power. The most popular method to address this issue is known as knowledge distillation in deep learning literature (in addition to model compression) where a large pretrained network known as the teacher is used to train a smaller student network. However, to the best of our knowledge, such methods have not been explored yet in the domain of SVD. In this paper, efforts have been made to investigate this issue using both conventional as well as ensemble knowledge distillation techniques. Through extensive experimentation on the publicly available Jamendo dataset, we show that, not only it's possible to achieve comparable accuracies with far smaller models (upto 1000x smaller in terms of parameters), but fascinatingly, in some cases, smaller models trained with distillation, even surpass the current state-of-the-art models on voice detection performance.
DNN-based cross-lingual voice conversion using Bottleneck Features
Sep 10, 2019



Abstract:Cross-lingual voice conversion (CLVC) is a quite challenging task since the source and target speakers speak different languages. This paper proposes a CLVC framework based on bottleneck features and deep neural network (DNN). In the proposed method, the bottleneck features extracted from a deep auto-encoder (DAE) are used to represent speaker-independent features of speech signals from different languages. A DNN model is trained to learn the mapping between bottleneck features and the corresponding spectral features of the target speaker. The proposed method can capture speaker-specific characteristics of a target speaker, and hence requires no speech data from source speaker during training. The performance of the proposed method is evaluated using data from three Indian languages: Telugu, Tamil and Malayalam. The experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms the baseline Gaussian mixture model (GMM)-based CLVC approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge