Junyuan Liu
PEGNet: A Physics-Embedded Graph Network for Long-Term Stable Multiphysics Simulation
Nov 11, 2025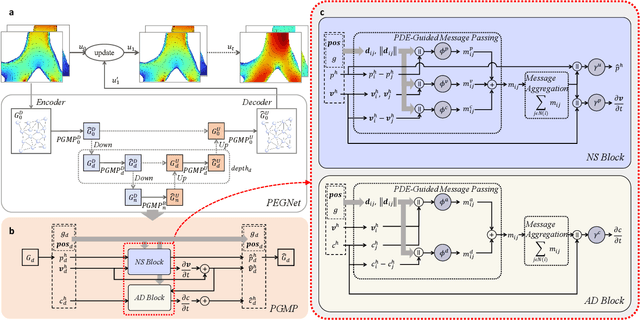
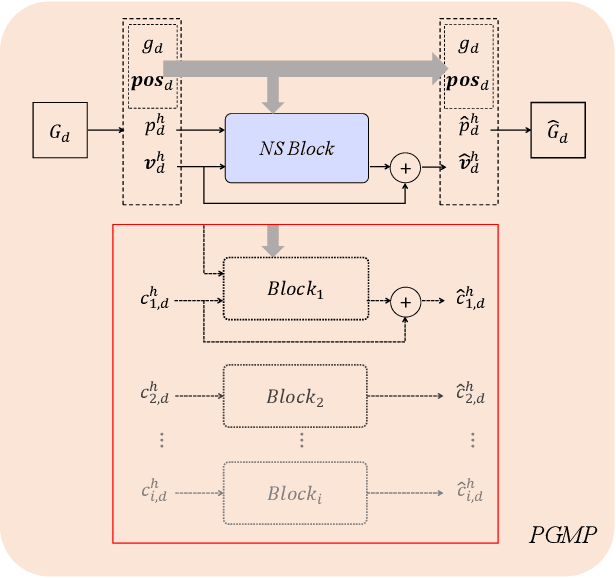
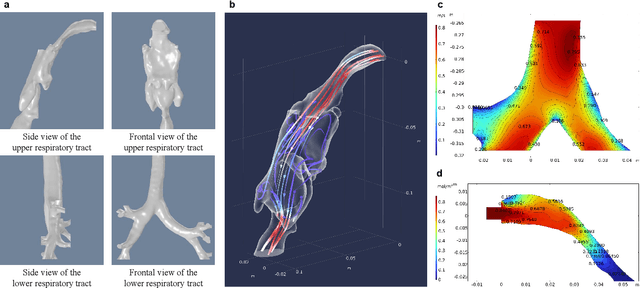
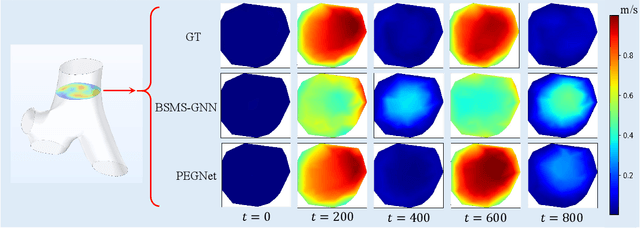
Abstract:Accurate and efficient simulations of physical phenomena governed by partial differential equations (PDEs) are important for scientific and engineering progress. While traditional numerical solvers are powerful, they are often computationally expensive. Recently, data-driven methods have emerged as alternatives, but they frequently suffer from error accumulation and limited physical consistency, especially in multiphysics and complex geometries. To address these challenges, we propose PEGNet, a Physics-Embedded Graph Network that incorporates PDE-guided message passing to redesign the graph neural network architecture. By embedding key PDE dynamics like convection, viscosity, and diffusion into distinct message functions, the model naturally integrates physical constraints into its forward propagation, producing more stable and physically consistent solutions. Additionally, a hierarchical architecture is employed to capture multi-scale features, and physical regularization is integrated into the loss function to further enforce adherence to governing physics. We evaluated PEGNet on benchmarks, including custom datasets for respiratory airflow and drug delivery, showing significant improvements in long-term prediction accuracy and physical consistency over existing methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/Yanghuoshan/PEGNet.
LabelCoRank: Revolutionizing Long Tail Multi-Label Classification with Co-Occurrence Reranking
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Motivation: Despite recent advancements in semantic representation driven by pre-trained and large-scale language models, addressing long tail challenges in multi-label text classification remains a significant issue. Long tail challenges have persistently posed difficulties in accurately classifying less frequent labels. Current approaches often focus on improving text semantics while neglecting the crucial role of label relationships. Results: This paper introduces LabelCoRank, a novel approach inspired by ranking principles. LabelCoRank leverages label co-occurrence relationships to refine initial label classifications through a dual-stage reranking process. The first stage uses initial classification results to form a preliminary ranking. In the second stage, a label co-occurrence matrix is utilized to rerank the preliminary results, enhancing the accuracy and relevance of the final classifications. By integrating the reranked label representations as additional text features, LabelCoRank effectively mitigates long tail issues in multi-labeltext classification. Experimental evaluations on popular datasets including MAG-CS, PubMed, and AAPD demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of LabelCoRank.
Multimodal Contrastive Learning of Urban Space Representations from POI Data
Nov 09, 2024Abstract:Existing methods for learning urban space representations from Point-of-Interest (POI) data face several limitations, including issues with geographical delineation, inadequate spatial information modelling, underutilisation of POI semantic attributes, and computational inefficiencies. To address these issues, we propose CaLLiPer (Contrastive Language-Location Pre-training), a novel representation learning model that directly embeds continuous urban spaces into vector representations that can capture the spatial and semantic distribution of urban environment. This model leverages a multimodal contrastive learning objective, aligning location embeddings with textual POI descriptions, thereby bypassing the need for complex training corpus construction and negative sampling. We validate CaLLiPer's effectiveness by applying it to learning urban space representations in London, UK, where it demonstrates 5-15% improvement in predictive performance for land use classification and socioeconomic mapping tasks compared to state-of-the-art methods. Visualisations of the learned representations further illustrate our model's advantages in capturing spatial variations in urban semantics with high accuracy and fine resolution. Additionally, CaLLiPer achieves reduced training time, showcasing its efficiency and scalability. This work provides a promising pathway for scalable, semantically rich urban space representation learning that can support the development of geospatial foundation models. The implementation code is available at https://github.com/xlwang233/CaLLiPer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge