Junmin Zhu
CNNSum: Exploring Long-Context Summarization with Large Language Models in Chinese Novels
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have been well-researched in many long-context tasks. However, due to high annotation costs, high-quality long-context summary datasets for training or evaluation are scarce, limiting further research. In this work, we introduce CNNSum, a new multi-scale Chinese long-context novel summarization benchmark, including four subsets, length covering 16k to 128k, 695 samples in total, the annotations are human-driven. We evaluate commercial and open-source models on CNNSum and conduct a detailed analysis. Based on the observations, we further conduct fine-tuning exploration with short-context summary data. In our study: (1) GPT-4o underperformed, due to excessive subjective commentary. (2) Currently, long-context summarization mainly relies on memory ability, small LLMs with stable longer context lengths are the most cost-effective. Using long data concatenated from short-context summaries makes a significant improvement. (3) Prompt templates may cause a large performance gap but can be mitigated through fine-tuning. (4) Fine-tuned Chat or Instruction versions may harm the Base model and further fine-tuning cannot bridge performance gap. (5) while models with RoPE base scaling exhibit strong extrapolation potential, their performance may vary significantly when combined with other interpolation methods and need careful selection. (6) CNNSum provides more reliable and insightful evaluation results than other benchmarks. We release CNNSum to advance research in this field (https://github.com/CxsGhost/CNNSum).
CNNSum: Exploring Long-Conext Summarization with Large Language Models in Chinese Novels
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have been well-researched in many long-context tasks. However, due to high annotation costs, high-quality long-context summary datasets for training or evaluation are scarce, limiting further research. In this work, we introduce CNNSum, a new multi-scale Chinese long-context novel summarization benchmark, including four subsets, length covering 16k\textasciitilde128k, 695 samples in total, the annotations are human-driven. We evaluate commercial and open-source models on CNNSum and conduct a detailed analysis. Based on the observations, we further conduct fine-tuning exploration with short-context summary data. In our study: (1) GPT-4o underperformed, due to excessive subjective commentary. (2) Currently, long-context summarization mainly relies on memory ability, small LLMs with stable longer context lengths are the most cost-effective. Using long data concatenated from short-context summaries makes a significant improvement. (3) Prompt templates may cause a large performance gap but can be mitigated through fine-tuning. (4) Fine-tuned Chat or Instruction versions may harm the Base model and further fine-tuning cannot bridge performance gap. (5) while models with RoPE base scaling exhibit strong extrapolation potential, their performance may vary significantly when combined with other interpolation methods and need careful selection. (6) CNNSum provides more reliable and insightful evaluation results than other benchmarks. We release CNNSum to advance research in this field.
LIFBench: Evaluating the Instruction Following Performance and Stability of Large Language Models in Long-Context Scenarios
Nov 11, 2024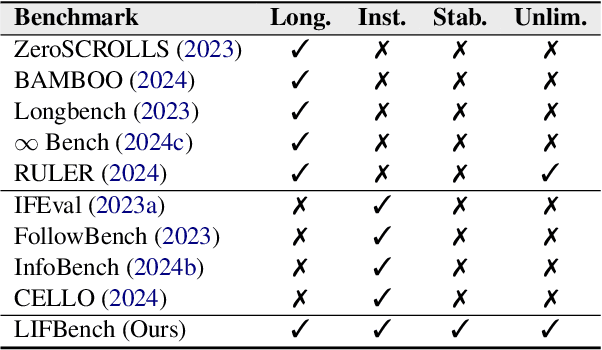
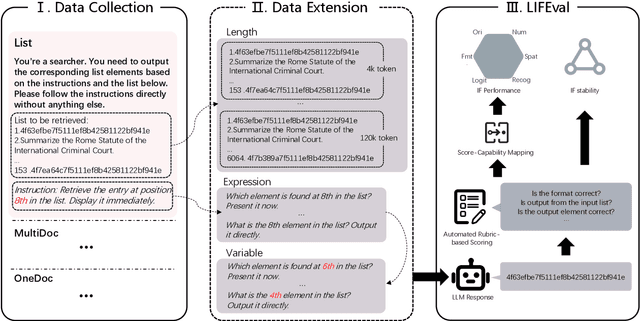
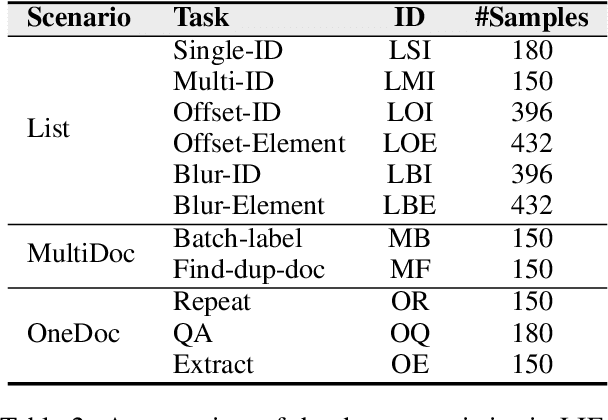
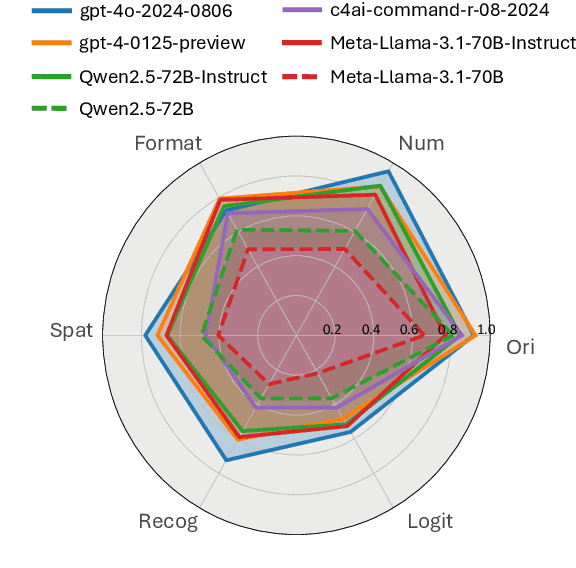
Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) continue to advance in natural language processing (NLP), their ability to stably follow instructions in long-context inputs has become crucial for real-world applications. While existing benchmarks assess various LLM capabilities, they rarely focus on instruction-following in long-context scenarios or stability on different inputs. In response, we introduce the Long-context Instruction-Following Benchmark (LIFBench), a scalable dataset designed to evaluate LLMs' instruction-following capabilities and stability across long contexts. LIFBench comprises three long-context scenarios and eleven diverse tasks, supported by 2,766 instructions generated through an automated expansion method across three dimensions: length, expression, and variables. For evaluation, we propose LIFEval, a rubric-based assessment framework that provides precise, automated scoring of complex LLM responses without relying on LLM-assisted evaluations or human judgments. This approach facilitates a comprehensive analysis of model performance and stability across various perspectives. We conduct extensive experiments on 20 notable LLMs across six length intervals, analyzing their instruction-following capabilities and stability. Our work contributes LIFBench and LIFEval as robust tools for assessing LLM performance in complex, long-context settings, providing insights that can inform future LLM development.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge