Junlong Ma
Enhanced Control for Diffusion Bridge in Image Restoration
Aug 29, 2024



Abstract:Image restoration refers to the process of restoring a damaged low-quality image back to its corresponding high-quality image. Typically, we use convolutional neural networks to directly learn the mapping from low-quality images to high-quality images achieving image restoration. Recently, a special type of diffusion bridge model has achieved more advanced results in image restoration. It can transform the direct mapping from low-quality to high-quality images into a diffusion process, restoring low-quality images through a reverse process. However, the current diffusion bridge restoration models do not emphasize the idea of conditional control, which may affect performance. This paper introduces the ECDB model enhancing the control of the diffusion bridge with low-quality images as conditions. Moreover, in response to the characteristic of diffusion models having low denoising level at larger values of \(\bm t \), we also propose a Conditional Fusion Schedule, which more effectively handles the conditional feature information of various modules. Experimental results prove that the ECDB model has achieved state-of-the-art results in many image restoration tasks, including deraining, inpainting and super-resolution. Code is avaliable at https://github.com/Hammour-steak/ECDB.
Image Restoration Through Generalized Ornstein-Uhlenbeck Bridge
Dec 16, 2023


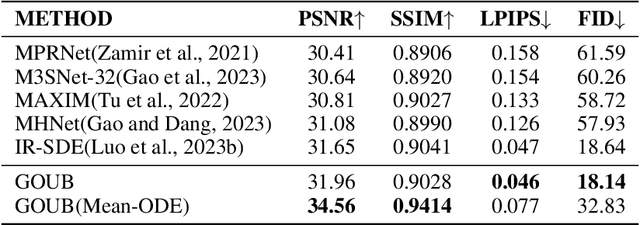
Abstract:Diffusion models possess powerful generative capabilities enabling the mapping of noise to data using reverse stochastic differential equations. However, in image restoration tasks, the focus is on the mapping relationship from low-quality images to high-quality images. To address this, we introduced the Generalized Ornstein-Uhlenbeck Bridge (GOUB) model. By leveraging the natural mean-reverting property of the generalized OU process and further adjusting the variance of its steady-state distribution through the Doob's h-transform, we achieve diffusion mappings from point to point with minimal cost. This allows for end-to-end training, enabling the recovery of high-quality images from low-quality ones. Additionally, we uncovered the mathematical essence of some bridge models, all of which are special cases of the GOUB and empirically demonstrated the optimality of our proposed models. Furthermore, benefiting from our distinctive parameterization mechanism, we proposed the Mean-ODE model that is better at capturing pixel-level information and structural perceptions. Experimental results show that both models achieved state-of-the-art results in various tasks, including inpainting, deraining, and super-resolution. Code is available at https://github.com/Hammour-steak/GOUB.
Context-guided Triple Matching for Multiple Choice Question Answering
Sep 27, 2021



Abstract:The task of multiple choice question answering (MCQA) refers to identifying a suitable answer from multiple candidates, by estimating the matching score among the triple of the passage, question and answer. Despite the general research interest in this regard, existing methods decouple the process into several pair-wise or dual matching steps, that limited the ability of assessing cases with multiple evidence sentences. To alleviate this issue, this paper introduces a novel Context-guided Triple Matching algorithm, which is achieved by integrating a Triple Matching (TM) module and a Contrastive Regularization (CR). The former is designed to enumerate one component from the triple as the background context, and estimate its semantic matching with the other two. Additionally, the contrastive term is further proposed to capture the dissimilarity between the correct answer and distractive ones. We validate the proposed algorithm on several benchmarking MCQA datasets, which exhibits competitive performances against state-of-the-arts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge