Julien Adam
Self-Supervision Enhances Instance-based Multiple Instance Learning Methods in Digital Pathology: A Benchmark Study
May 02, 2025Abstract:Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) has emerged as the best solution for Whole Slide Image (WSI) classification. It consists of dividing each slide into patches, which are treated as a bag of instances labeled with a global label. MIL includes two main approaches: instance-based and embedding-based. In the former, each patch is classified independently, and then the patch scores are aggregated to predict the bag label. In the latter, bag classification is performed after aggregating patch embeddings. Even if instance-based methods are naturally more interpretable, embedding-based MILs have usually been preferred in the past due to their robustness to poor feature extractors. However, recently, the quality of feature embeddings has drastically increased using self-supervised learning (SSL). Nevertheless, many authors continue to endorse the superiority of embedding-based MIL. To investigate this further, we conduct 710 experiments across 4 datasets, comparing 10 MIL strategies, 6 self-supervised methods with 4 backbones, 4 foundation models, and various pathology-adapted techniques. Furthermore, we introduce 4 instance-based MIL methods never used before in the pathology domain. Through these extensive experiments, we show that with a good SSL feature extractor, simple instance-based MILs, with very few parameters, obtain similar or better performance than complex, state-of-the-art (SOTA) embedding-based MIL methods, setting new SOTA results on the BRACS and Camelyon16 datasets. Since simple instance-based MIL methods are naturally more interpretable and explainable to clinicians, our results suggest that more effort should be put into well-adapted SSL methods for WSI rather than into complex embedding-based MIL methods.
Multicenter automatic detection of invasive carcinoma on breast whole slide images
Jan 17, 2023Abstract:Breast cancer is one of the most prevalent cancers worldwide and pathologists are closely involved in establishing a diagnosis. Tools to assist in making a diagnosis are required to manage the increasing workload. In this context, artificial intelligence (AI) and deep-learning based tools may be used in daily pathology practice. However, it is challenging to develop fast and reliable algorithms that can be trusted by practitioners, whatever the medical center. We describe a patch-based algorithm that incorporates a convolutional neural network to detect and locate invasive carcinoma on breast whole-slide images. The network was trained on a dataset extracted from a reference acquisition center. We then performed a calibration step based on transfer learning to maintain the performance when translating on a new target acquisition center by using a limited amount of additional training data. Performance was evaluated using classical binary measures (accuracy, recall, precision) for both centers (referred to as test reference dataset and test target dataset) and at two levels: patch and slide level. At patch level, accuracy, recall, and precision of the model on the reference and target test sets were 92.1\% and 96.3\%, 95\% and 87.8\%, and 73.9\% and 70.6\%, respectively. At slide level, accuracy, recall, and precision were 97.6\% and 92.0\%, 90.9\% and 100\%, and 100\% and 70.8\% for test sets 1 and 2, respectively. The high performance of the algorithm at both centers shows that the calibration process is efficient. This is performed using limited training data from the new target acquisition center and requires that the model is trained beforehand on a large database from a reference center. This methodology allows the implementation of AI diagnostic tools to help in routine pathology practice.
Weakly supervised multiple instance learning histopathological tumor segmentation
Apr 21, 2020
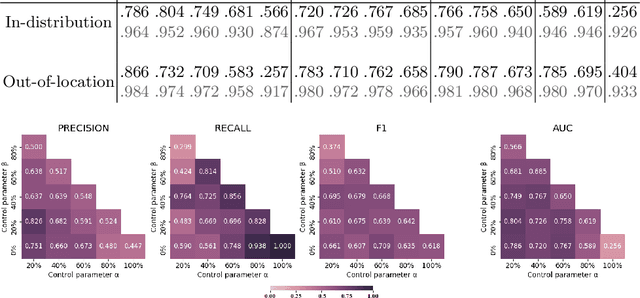
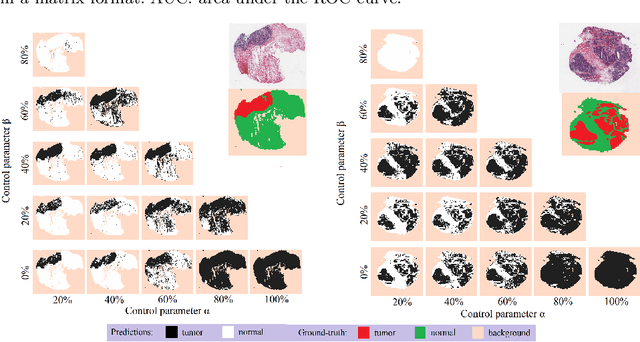
Abstract:Histopathological image segmentation is a challenging and important topic in medical imaging with tremendous potential impact in clinical practice. State of the art methods relying on hand-crafted annotations that reduce the scope of the solutions since digital histology suffers from standardization and samples differ significantly between cancer phenotypes. To this end, in this paper, we propose a weakly supervised framework relying on weak standard clinical practice annotations, available in most medical centers. In particular, we exploit a multiple instance learning scheme providing a label for each instance, establishing a detailed segmentation of whole slide images. The potential of the framework is assessed with multi-centric data experiments using The Cancer Genome Atlas repository and the publicly available PatchCamelyon dataset. Promising results when compared with experts' annotations demonstrate the potentials of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge