Juliana Jansen Ferreira
Making Sense of Knowledge Intensive Processes: an Oil & Gas Industry Scenario
Jan 31, 2024Abstract:Sensemaking is a constant and ongoing process by which people associate meaning to experiences. It can be an individual process, known as abduction, or a group process by which people give meaning to collective experiences. The sensemaking of a group is influenced by the abduction process of each person about the experience. Every collaborative process needs some level of sensemaking to show results. For a knowledge intensive process, sensemaking is central and related to most of its tasks. We present findings from a fieldwork executed in knowledge intensive process from the Oil and Gas industry. Our findings indicated that different types of knowledge can be combined to compose the result of a sensemaking process (e.g. decision, the need for more discussion, etc.). This paper presents an initial set of knowledge types that can be combined to compose the result of the sensemaking of a collaborative decision making process. We also discuss ideas for using systems powered by Artificial Intelligence to support sensemaking processes.
Human-AI Co-Creation Approach to Find Forever Chemicals Replacements
Apr 11, 2023
Abstract:Generative models are a powerful tool in AI for material discovery. We are designing a software framework that supports a human-AI co-creation process to accelerate finding replacements for the ``forever chemicals''-- chemicals that enable our modern lives, but are harmful to the environment and the human health. Our approach combines AI capabilities with the domain-specific tacit knowledge of subject matter experts to accelerate the material discovery. Our co-creation process starts with the interaction between the subject matter experts and a generative model that can generate new molecule designs. In this position paper, we discuss our hypothesis that these subject matter experts can benefit from a more iterative interaction with the generative model, asking for smaller samples and ``guiding'' the exploration of the discovery space with their knowledge.
Toward Human-AI Co-creation to Accelerate Material Discovery
Nov 05, 2022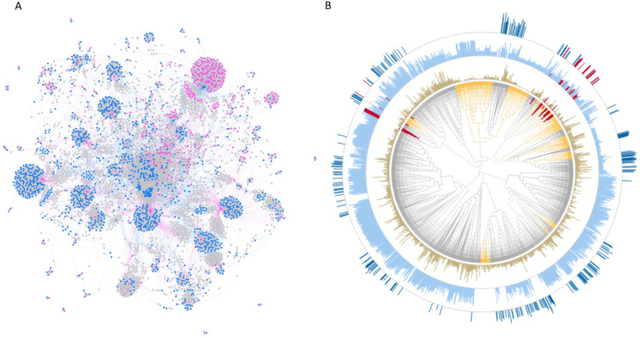
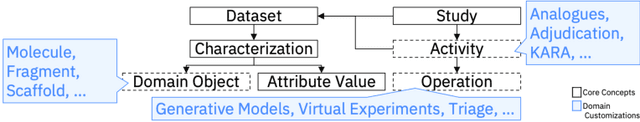
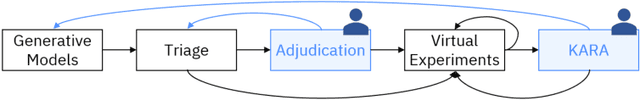
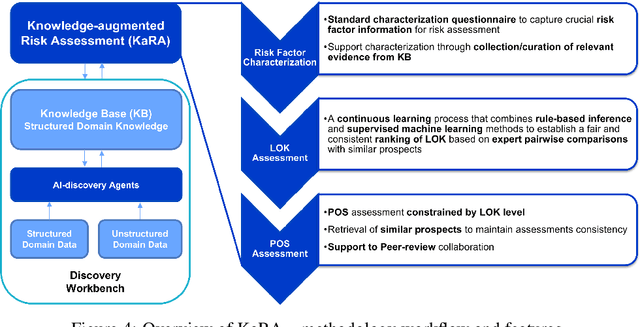
Abstract:There is an increasing need in our society to achieve faster advances in Science to tackle urgent problems, such as climate changes, environmental hazards, sustainable energy systems, pandemics, among others. In certain domains like chemistry, scientific discovery carries the extra burden of assessing risks of the proposed novel solutions before moving to the experimental stage. Despite several recent advances in Machine Learning and AI to address some of these challenges, there is still a gap in technologies to support end-to-end discovery applications, integrating the myriad of available technologies into a coherent, orchestrated, yet flexible discovery process. Such applications need to handle complex knowledge management at scale, enabling knowledge consumption and production in a timely and efficient way for subject matter experts (SMEs). Furthermore, the discovery of novel functional materials strongly relies on the development of exploration strategies in the chemical space. For instance, generative models have gained attention within the scientific community due to their ability to generate enormous volumes of novel molecules across material domains. These models exhibit extreme creativity that often translates in low viability of the generated candidates. In this work, we propose a workbench framework that aims at enabling the human-AI co-creation to reduce the time until the first discovery and the opportunity costs involved. This framework relies on a knowledge base with domain and process knowledge, and user-interaction components to acquire knowledge and advise the SMEs. Currently,the framework supports four main activities: generative modeling, dataset triage, molecule adjudication, and risk assessment.
Designer-User Communication for XAI: An epistemological approach to discuss XAI design
May 17, 2021
Abstract:Artificial Intelligence is becoming part of any technology we use nowadays. If the AI informs people's decisions, the explanation about AI's outcomes, results, and behavior becomes a necessary capability. However, the discussion of XAI features with various stakeholders is not a trivial task. Most of the available frameworks and methods for XAI focus on data scientists and ML developers as users. Our research is about XAI for end-users of AI systems. We argue that we need to discuss XAI early in the AI-system design process and with all stakeholders. In this work, we aimed at investigating how to operationalize the discussion about XAI scenarios and opportunities among designers and developers of AI and its end-users. We took the Signifying Message as our conceptual tool to structure and discuss XAI scenarios. We experiment with its use for the discussion of a healthcare AI-System.
The human-AI relationship in decision-making: AI explanation to support people on justifying their decisions
Feb 22, 2021
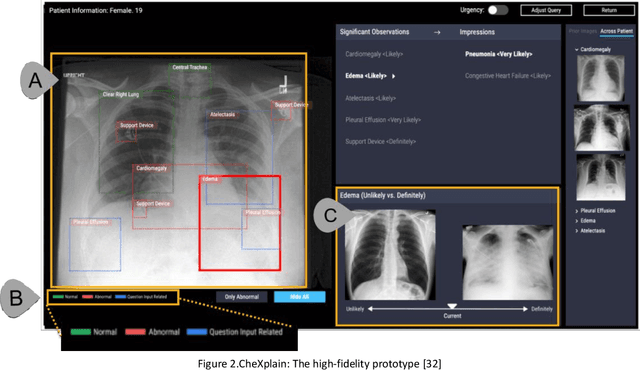
Abstract:The explanation dimension of Artificial Intelligence (AI) based system has been a hot topic for the past years. Different communities have raised concerns about the increasing presence of AI in people's everyday tasks and how it can affect people's lives. There is a lot of research addressing the interpretability and transparency concepts of explainable AI (XAI), which are usually related to algorithms and Machine Learning (ML) models. But in decision-making scenarios, people need more awareness of how AI works and its outcomes to build a relationship with that system. Decision-makers usually need to justify their decision to others in different domains. If that decision is somehow based on or influenced by an AI-system outcome, the explanation about how the AI reached that result is key to building trust between AI and humans in decision-making scenarios. In this position paper, we discuss the role of XAI in decision-making scenarios, our vision of Decision-Making with AI-system in the loop, and explore one case from the literature about how XAI can impact people justifying their decisions, considering the importance of building the human-AI relationship for those scenarios.
Evidence-based explanation to promote fairness in AI systems
Mar 03, 2020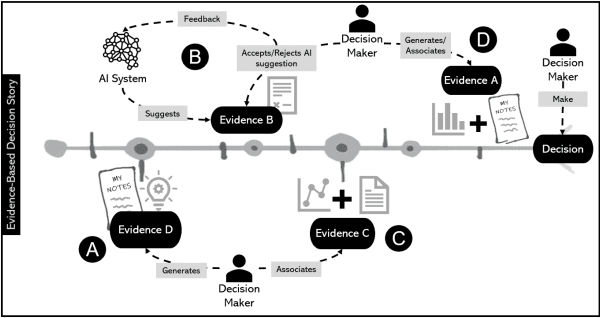
Abstract:As Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology gets more intertwined with every system, people are using AI to make decisions on their everyday activities. In simple contexts, such as Netflix recommendations, or in more complex context like in judicial scenarios, AI is part of people's decisions. People make decisions and usually, they need to explain their decision to others or in some matter. It is particularly critical in contexts where human expertise is central to decision-making. In order to explain their decisions with AI support, people need to understand how AI is part of that decision. When considering the aspect of fairness, the role that AI has on a decision-making process becomes even more sensitive since it affects the fairness and the responsibility of those people making the ultimate decision. We have been exploring an evidence-based explanation design approach to 'tell the story of a decision'. In this position paper, we discuss our approach for AI systems using fairness sensitive cases in the literature.
Do ML Experts Discuss Explainability for AI Systems? A discussion case in the industry for a domain-specific solution
Feb 27, 2020
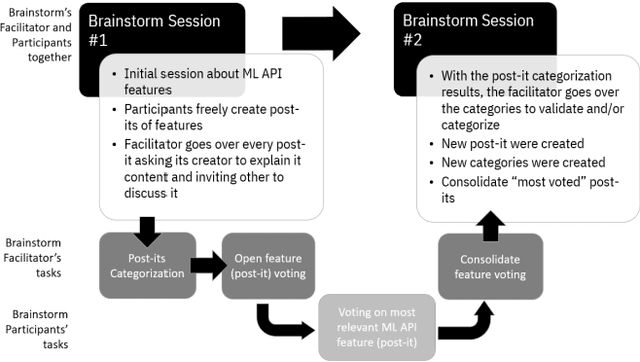

Abstract:The application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools in different domains are becoming mandatory for all companies wishing to excel in their industries. One major challenge for a successful application of AI is to combine the machine learning (ML) expertise with the domain knowledge to have the best results applying AI tools. Domain specialists have an understanding of the data and how it can impact their decisions. ML experts have the ability to use AI-based tools dealing with large amounts of data and generating insights for domain experts. But without a deep understanding of the data, ML experts are not able to tune their models to get optimal results for a specific domain. Therefore, domain experts are key users for ML tools and the explainability of those AI tools become an essential feature in that context. There are a lot of efforts to research AI explainability for different contexts, users and goals. In this position paper, we discuss interesting findings about how ML experts can express concerns about AI explainability while defining features of an ML tool to be developed for a specific domain. We analyze data from two brainstorm sessions done to discuss the functionalities of an ML tool to support geoscientists (domain experts) on analyzing seismic data (domain-specific data) with ML resources.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge