Josep Miquel Jornet
Impact of Pointing Error on Coverage Performance of 3D Indoor Terahertz Communication Systems
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:In this paper, we develop a tractable analytical framework for a three-dimensional (3D) indoor terahertz (THz) communication system to theoretically assess the impact of the pointing error on its coverage performance. Specifically, we model the locations of access points (APs) using a Poisson point process, human blockages as random cylinder processes, and wall blockages through a Boolean straight line process. A pointing error refers to beamforming gain and direction mismatch between the transmitter and receiver. We characterize it based on the inaccuracy of location estimate. We then analyze the impact of this pointing error on the received signal power and derive a tractable expression for the coverage probability, incorporating the multi-cluster fluctuating two-ray distribution to accurately model small-scale fading in THz communications. Aided by simulation results, we corroborate our analysis and demonstrate that the pointing error has a pronounced impact on the coverage probability. Specifically, we find that merely increasing the antenna array size is insufficient to improve the coverage probability and mitigate the detrimental impact of the pointing error, highlighting the necessity of advanced estimation techniques in THz communication systems.
Optimization and Characterization of Near-Field Beams with Uniform Linear Arrays
Mar 18, 2025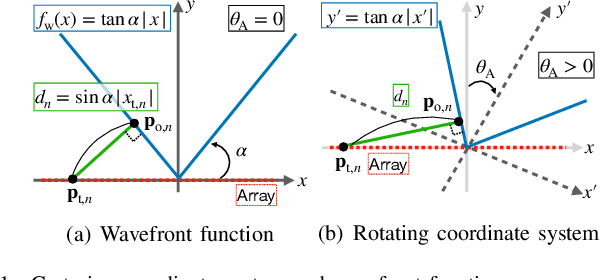
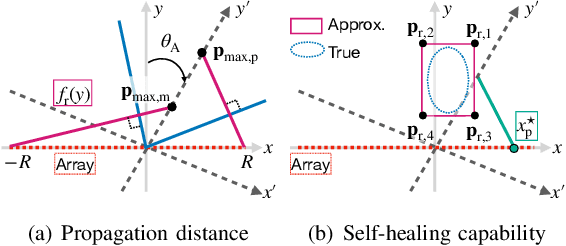

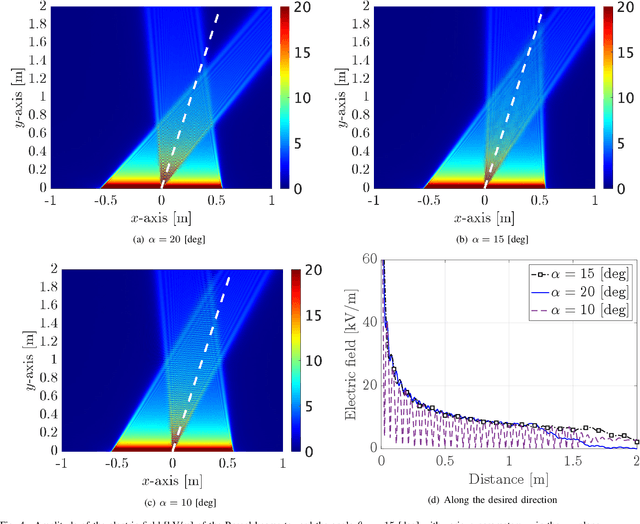
Abstract:In this paper, we consider near-field beams that can mitigate signal attenuation and blockage effects using a uniform linear array (ULA). In particular, closed-form expressions for phase distributions in a ULA are derived to generate Bessel beams and curving beams based on the desired propagation directions and trajectories. Based on the phase distributions, the maximum steering angle and propagation distance of Bessel beams with a ULA are revealed. In addition, from the sampling theorem in the spatial domain, the requirements for ULAs to properly generate Bessel beams are clarified. For curving beams, trajectories to reach a user while avoiding one obstacle are designed via the Lagrangian method. Numerical results obtained by electromagnetic wave simulations confirm the effectiveness of the analyses for Bessel beams and the curving beam designs. Furthermore, the characteristics of Gaussian beams, beamfocusing, Bessel beams, and curving beams are summarized in terms of the statistical behavior of their intensity and signal processing.
Coverage Analysis for 3D Indoor Terahertz Communication System Over Fluctuating Two-Ray Fading Channels
Oct 07, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we develop a novel analytical framework for a three-dimensional (3D) indoor terahertz (THz) communication system. Our proposed model incorporates more accurate modeling of wall blockages via Manhattan line processes and precise modeling of THz fading channels via a fluctuating two-ray (FTR) channel model. We also account for traditional unique features of THz, such as molecular absorption loss, user blockages, and 3D directional antenna beams. Moreover, we model locations of access points (APs) using a Poisson point process and adopt the nearest line-of-sight AP association strategy. Due to the high penetration loss caused by wall blockages, we consider that a user equipment (UE) and its associated AP and interfering APs are all in the same rectangular area, i.e., a room. Based on the proposed rectangular area model, we evaluate the impact of the UE's location on the distance to its associated AP. We then develop a tractable method to derive a new expression for the coverage probability by examining the interference from interfering APs and considering the FTR fading experienced by THz communications. Aided by simulation results, we validate our analysis and demonstrate that the UE's location has a pronounced impact on its coverage probability. Additionally, we find that the optimal AP density is determined by both the UE's location and the room size, which provides valuable insights for meeting the coverage requirements of future THz communication system deployment.
Magnetic Localization for In-body Nano-communication Medical Systems
Mar 04, 2024Abstract:Nano-machines circulating inside the human body, collecting data on tissue conditions, represent a vital part of next-generation medical diagnostic systems. However, for these devices to operate effectively, they need to relay not only their medical measurements but also their positions. This paper introduces a novel localization method for in-body nano-machines based on the magnetic field, leveraging the advantageous magnetic permeability of all human tissues. The entire proposed localization system is described, starting from 10x10 ${\mu}m^2$ magnetometers to be integrated into the nano-machines, to a set of external wires generating the magnetic field. Mathematical equations for the localization algorithm are also provided, assuming the nano-machines do not execute the computations themselves, but transmit their magnetic field measurements together with medical data outside of the body. The whole system is validated with computer simulations that capture the measurement error of the magnetometers, the error induced by the Earth magnetic field, and a human body model assuming different possible positions of nano-machines. The results show a very high system accuracy with localization errors even below 1 cm.
Demo: Intelligent Radar Detection in CBRS Band in the Colosseum Wireless Network Emulator
Sep 16, 2023



Abstract:The ever-growing number of wireless communication devices and technologies demands spectrum-sharing techniques. Effective coexistence management is crucial to avoid harmful interference, especially with critical systems like nautical and aerial radars in which incumbent radios operate mission-critical communication links. In this demo, we showcase a framework that leverages Colosseum, the world's largest wireless network emulator with hardware-in-the-loop, as a playground to study commercial radar waveforms coexisting with a cellular network in CBRS band in complex environments. We create an ad-hoc high-fidelity spectrum-sharing scenario for this purpose. We deploy a cellular network to collect IQ samples with the aim of training an ML agent that runs at the base station. The agent has the goal of detecting incumbent radar transmissions and vacating the cellular bandwidth to avoid interfering with the radar operations. Our experiment results show an average detection accuracy of 88%, with an average detection time of 137 ms.
Twinning Commercial Radio Waveforms in the Colosseum Wireless Network Emulator
Aug 18, 2023



Abstract:Because of the ever-growing amount of wireless consumers, spectrum-sharing techniques have been increasingly common in the wireless ecosystem, with the main goal of avoiding harmful interference to coexisting communication systems. This is even more important when considering systems, such as nautical and aerial fleet radars, in which incumbent radios operate mission-critical communication links. To study, develop, and validate these solutions, adequate platforms, such as the Colosseum wireless network emulator, are key as they enable experimentation with spectrum-sharing heterogeneous radio technologies in controlled environments. In this work, we demonstrate how Colosseum can be used to twin commercial radio waveforms to evaluate the coexistence of such technologies in complex wireless propagation environments. To this aim, we create a high-fidelity spectrum-sharing scenario on Colosseum to evaluate the impact of twinned commercial radar waveforms on a cellular network operating in the CBRS band. Then, we leverage IQ samples collected on the testbed to train a machine learning agent that runs at the base station to detect the presence of incumbent radar transmissions and vacate the bandwidth to avoid causing them harmful interference. Our results show an average detection accuracy of 88%, with accuracy above 90% in SNR regimes above 0 dB and SINR regimes above -20 dB, and with an average detection time of 137 ms.
Terahertz Communications for 6G and Beyond Wireless Networks: Challenges, Key Advancements, and Opportunities
Jul 22, 2022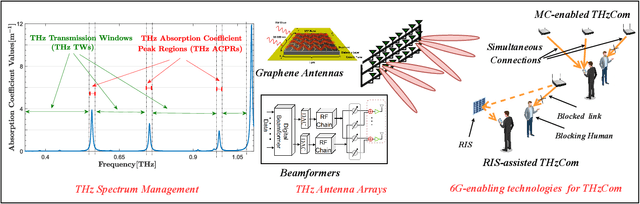
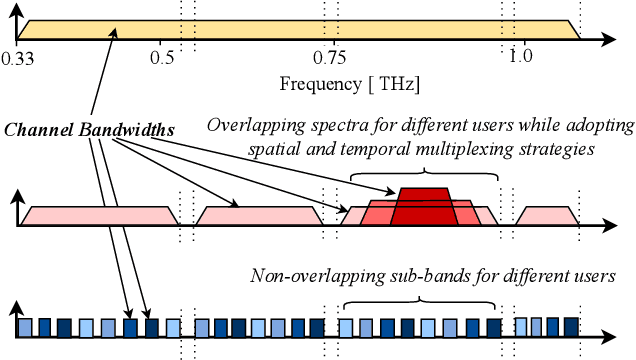
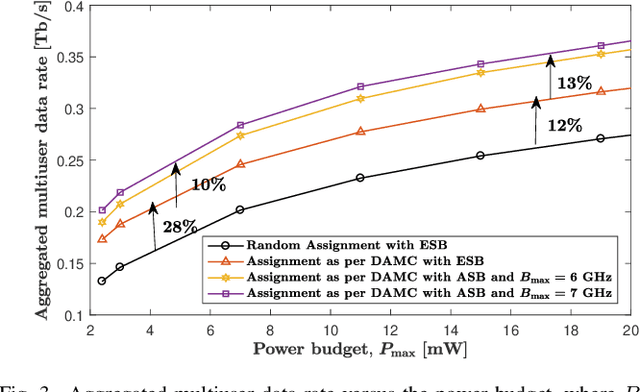
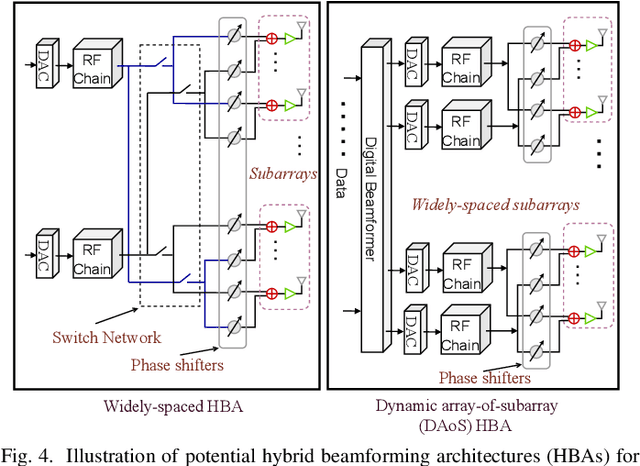
Abstract:The unprecedented increase in wireless data traffic, predicted to occur within the next decade, is motivating academia and industries to look beyond contemporary wireless standards and conceptualize the sixth-generation (6G) wireless networks. Among various promising solutions, terahertz (THz) communications (THzCom) is recognized as a highly promising technology for the 6G and beyond era, due to its unique potential to support terabit-per-second transmission in emerging applications. This article delves into key areas for developing end-to-end THzCom systems, focusing on physical, link, and network layers. Specifically, we discuss the areas of THz spectrum management, THz antennas and beamforming, and the integration of other 6G-enabling technologies for THzCom. For each area, we identify the challenges imposed by the unique properties of the THz band. We then present main advancements and outline perspective research directions in each area to stimulate future research efforts for realizing THzCom in 6G and beyond wireless networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge