Thomas Kurner
5G Channel Models for Railway Use Cases at mmWave Band and the Path Towards Terahertz
Jan 28, 2025



Abstract:High-speed trains are one of the most relevant scenarios for the fifth-generation (5G) mobile communications and the "smart rail mobility" vision, where a high-data-rate wireless connectivity with up to several GHz bandwidths will be required. This is a strong motivation for the exploration of millimeter wave (mmWave) band. In this article, we identify the main challenges and make progress towards realistic 5G mmWave channel models for railway use cases. In order to cope with the challenge of including the railway features in the channel models, we define reference scenarios to help the parameterization of channel models for railway use at mmWave band. Simulations and the subsequent measurements used to validate the model reflect the detailed influence of railway objects and the accuracy of the simulations. Finally, we point out the future directions towards the full version of the smart rail mobility which will be powered by terahertz (THz) communications.
Terahertz Communications for 6G and Beyond Wireless Networks: Challenges, Key Advancements, and Opportunities
Jul 22, 2022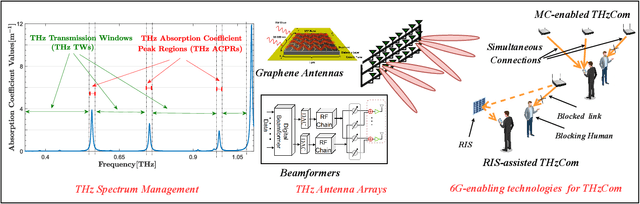
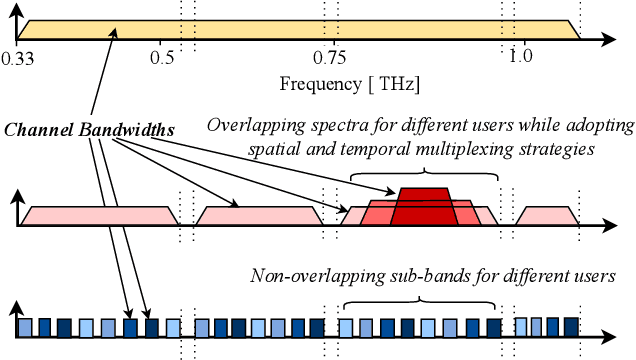
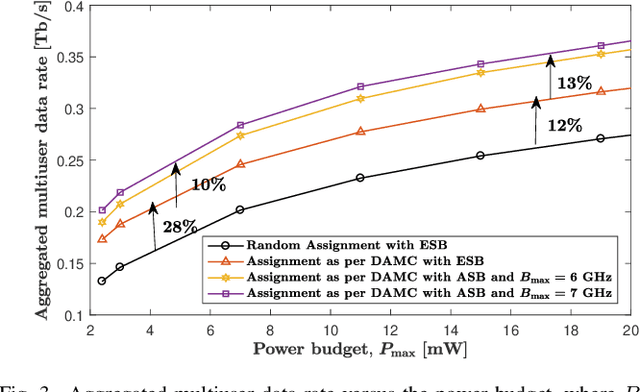
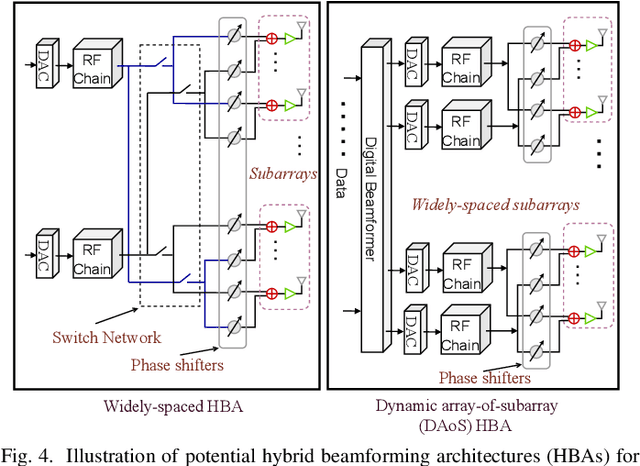
Abstract:The unprecedented increase in wireless data traffic, predicted to occur within the next decade, is motivating academia and industries to look beyond contemporary wireless standards and conceptualize the sixth-generation (6G) wireless networks. Among various promising solutions, terahertz (THz) communications (THzCom) is recognized as a highly promising technology for the 6G and beyond era, due to its unique potential to support terabit-per-second transmission in emerging applications. This article delves into key areas for developing end-to-end THzCom systems, focusing on physical, link, and network layers. Specifically, we discuss the areas of THz spectrum management, THz antennas and beamforming, and the integration of other 6G-enabling technologies for THzCom. For each area, we identify the challenges imposed by the unique properties of the THz band. We then present main advancements and outline perspective research directions in each area to stimulate future research efforts for realizing THzCom in 6G and beyond wireless networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge