John Hansen
Bridging the Modality Gap: Softly Discretizing Audio Representation for LLM-based Automatic Speech Recognition
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:One challenge of integrating speech input with large language models (LLMs) stems from the discrepancy between the continuous nature of audio data and the discrete token-based paradigm of LLMs. To mitigate this gap, we propose a method for integrating vector quantization (VQ) into LLM-based automatic speech recognition (ASR). Using the LLM embedding table as the VQ codebook, the VQ module aligns the continuous representations from the audio encoder with the discrete LLM inputs, enabling the LLM to operate on a discretized audio representation that better reflects the linguistic structure. We further create a soft "discretization" of the audio representation by updating the codebook and performing a weighted sum over the codebook embeddings. Empirical results demonstrate that our proposed method significantly improves upon the LLM-based ASR baseline, particularly in out-of-domain conditions. This work highlights the potential of soft discretization as a modality bridge in LLM-based ASR.
Deep Spoken Keyword Spotting: An Overview
Nov 20, 2021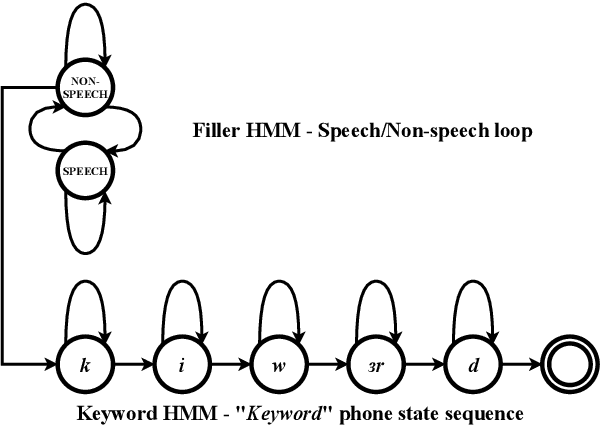
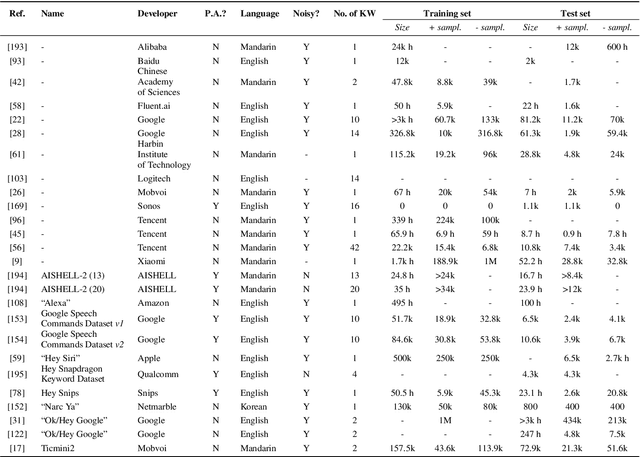
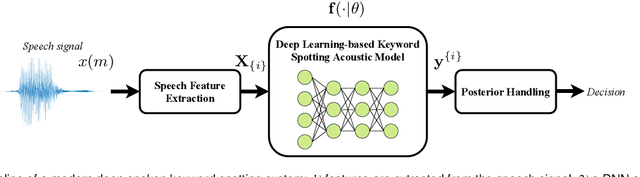

Abstract:Spoken keyword spotting (KWS) deals with the identification of keywords in audio streams and has become a fast-growing technology thanks to the paradigm shift introduced by deep learning a few years ago. This has allowed the rapid embedding of deep KWS in a myriad of small electronic devices with different purposes like the activation of voice assistants. Prospects suggest a sustained growth in terms of social use of this technology. Thus, it is not surprising that deep KWS has become a hot research topic among speech scientists, who constantly look for KWS performance improvement and computational complexity reduction. This context motivates this paper, in which we conduct a literature review into deep spoken KWS to assist practitioners and researchers who are interested in this technology. Specifically, this overview has a comprehensive nature by covering a thorough analysis of deep KWS systems (which includes speech features, acoustic modeling and posterior handling), robustness methods, applications, datasets, evaluation metrics, performance of deep KWS systems and audio-visual KWS. The analysis performed in this paper allows us to identify a number of directions for future research, including directions adopted from automatic speech recognition research and directions that are unique to the problem of spoken KWS.
Toeplitz Inverse Covariance based Robust Speaker Clustering for Naturalistic Audio Streams
Jul 12, 2019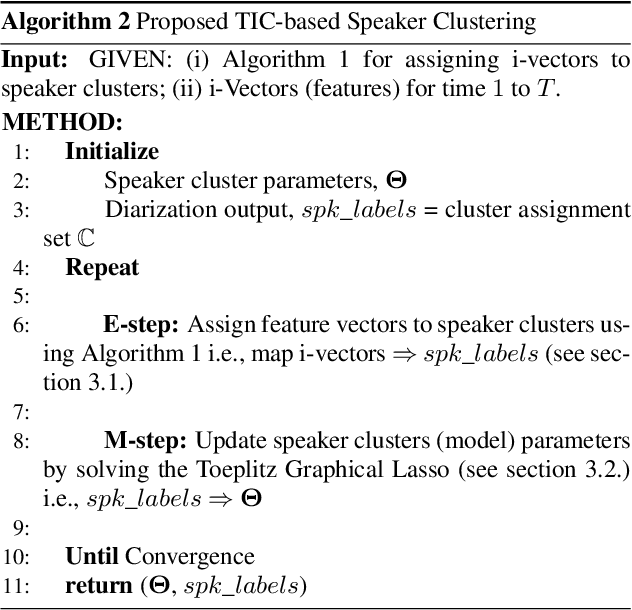
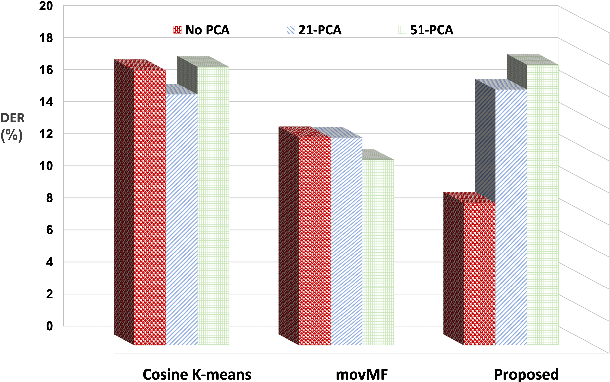
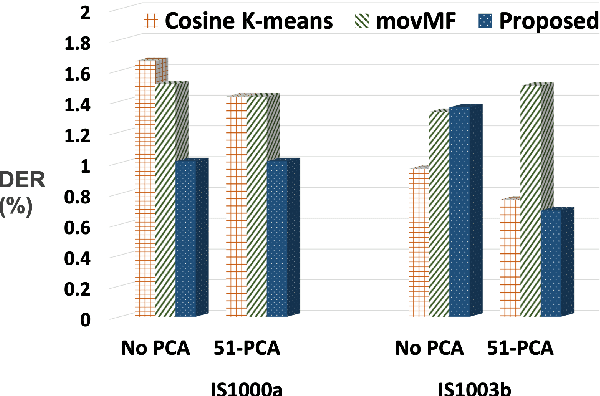
Abstract:Speaker diarization determines who spoke and when? in an audio stream. In this study, we propose a model-based approach for robust speaker clustering using i-vectors. The ivectors extracted from different segments of same speaker are correlated. We model this correlation with a Markov Random Field (MRF) network. Leveraging the advancements in MRF modeling, we used Toeplitz Inverse Covariance (TIC) matrix to represent the MRF correlation network for each speaker. This approaches captures the sequential structure of i-vectors (or equivalent speaker turns) belonging to same speaker in an audio stream. A variant of standard Expectation Maximization (EM) algorithm is adopted for deriving closed-form solution using dynamic programming (DP) and the alternating direction method of multiplier (ADMM). Our diarization system has four steps: (1) ground-truth segmentation; (2) i-vector extraction; (3) post-processing (mean subtraction, principal component analysis, and length-normalization) ; and (4) proposed speaker clustering. We employ cosine K-means and movMF speaker clustering as baseline approaches. Our evaluation data is derived from: (i) CRSS-PLTL corpus, and (ii) two meetings subset of the AMI corpus. Relative reduction in diarization error rate (DER) for CRSS-PLTL corpus is 43.22% using the proposed advancements as compared to baseline. For AMI meetings IS1000a and IS1003b, relative DER reduction is 29.37% and 9.21%, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge