John Guiver
Microsoft Research
Time-Sensitive Bayesian Information Aggregation for Crowdsourcing Systems
Apr 18, 2016
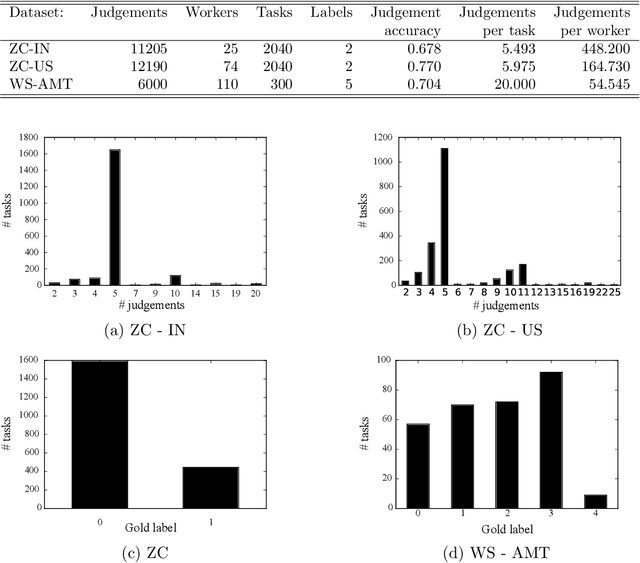

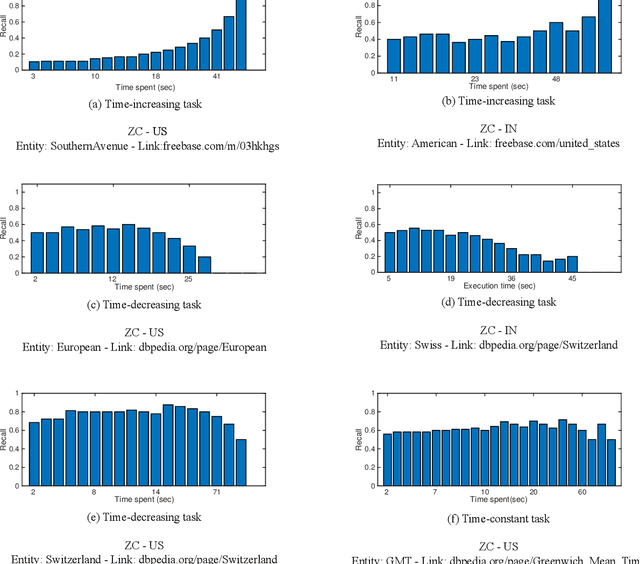
Abstract:Crowdsourcing systems commonly face the problem of aggregating multiple judgments provided by potentially unreliable workers. In addition, several aspects of the design of efficient crowdsourcing processes, such as defining worker's bonuses, fair prices and time limits of the tasks, involve knowledge of the likely duration of the task at hand. Bringing this together, in this work we introduce a new time--sensitive Bayesian aggregation method that simultaneously estimates a task's duration and obtains reliable aggregations of crowdsourced judgments. Our method, called BCCTime, builds on the key insight that the time taken by a worker to perform a task is an important indicator of the likely quality of the produced judgment. To capture this, BCCTime uses latent variables to represent the uncertainty about the workers' completion time, the tasks' duration and the workers' accuracy. To relate the quality of a judgment to the time a worker spends on a task, our model assumes that each task is completed within a latent time window within which all workers with a propensity to genuinely attempt the labelling task (i.e., no spammers) are expected to submit their judgments. In contrast, workers with a lower propensity to valid labeling, such as spammers, bots or lazy labelers, are assumed to perform tasks considerably faster or slower than the time required by normal workers. Specifically, we use efficient message-passing Bayesian inference to learn approximate posterior probabilities of (i) the confusion matrix of each worker, (ii) the propensity to valid labeling of each worker, (iii) the unbiased duration of each task and (iv) the true label of each task. Using two real-world public datasets for entity linking tasks, we show that BCCTime produces up to 11% more accurate classifications and up to 100% more informative estimates of a task's duration compared to state-of-the-art methods.
How To Grade a Test Without Knowing the Answers --- A Bayesian Graphical Model for Adaptive Crowdsourcing and Aptitude Testing
Jun 27, 2012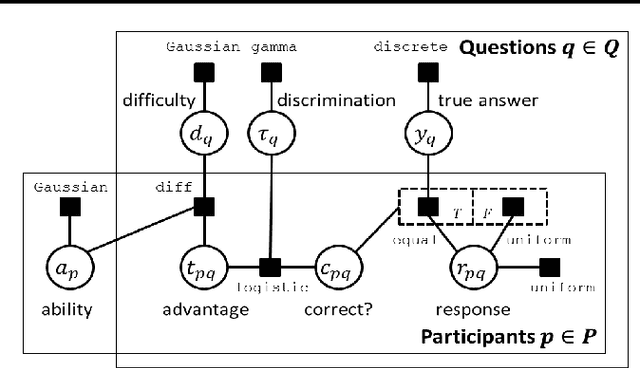
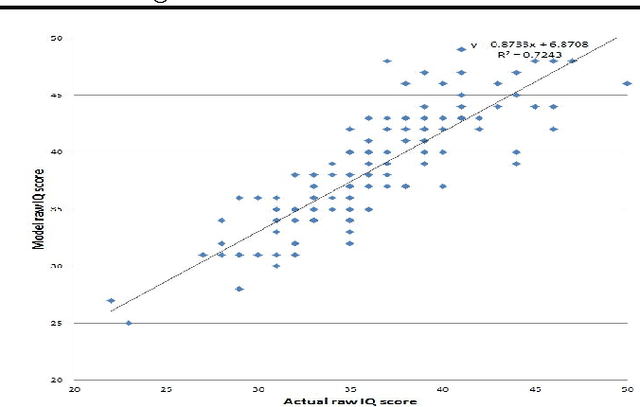
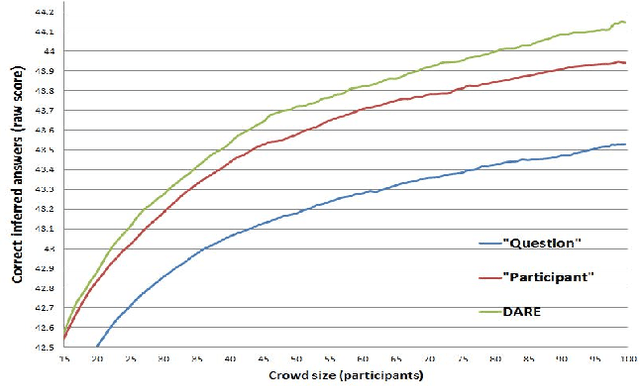
Abstract:We propose a new probabilistic graphical model that jointly models the difficulties of questions, the abilities of participants and the correct answers to questions in aptitude testing and crowdsourcing settings. We devise an active learning/adaptive testing scheme based on a greedy minimization of expected model entropy, which allows a more efficient resource allocation by dynamically choosing the next question to be asked based on the previous responses. We present experimental results that confirm the ability of our model to infer the required parameters and demonstrate that the adaptive testing scheme requires fewer questions to obtain the same accuracy as a static test scenario.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge