Joe Davison
Multi-scale Sinusoidal Embeddings Enable Learning on High Resolution Mass Spectrometry Data
Jul 06, 2022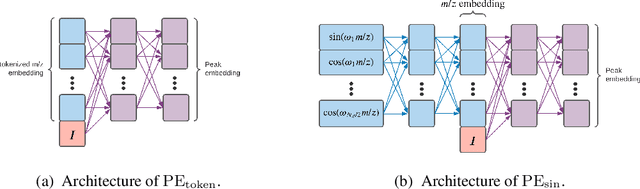
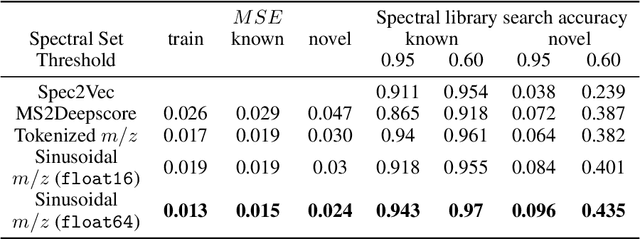
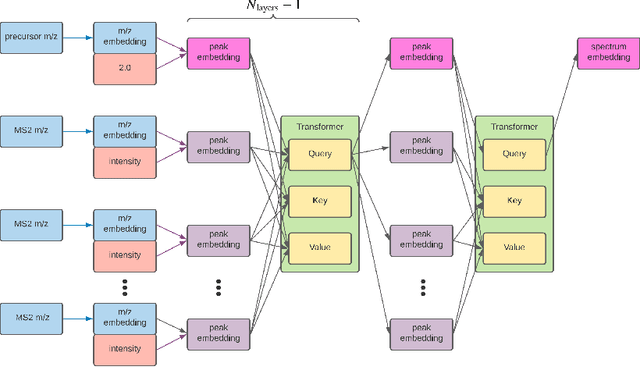
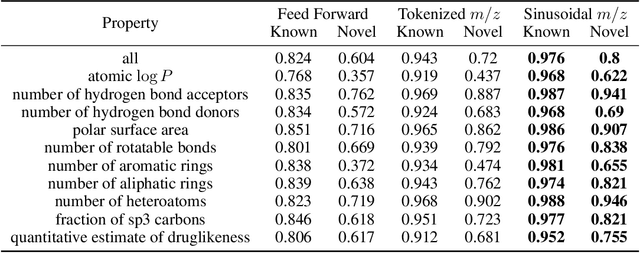
Abstract:Small molecules in biological samples are studied to provide information about disease states, environmental toxins, natural product drug discovery, and many other applications. The primary window into the composition of small molecule mixtures is tandem mass spectrometry (MS2), which produces data that are of high sensitivity and part per million resolution. We adopt multi-scale sinusoidal embeddings of the mass data in MS2 designed to meet the challenge of learning from the full resolution of MS2 data. Using these embeddings, we provide a new state of the art model for spectral library search, the standard task for initial evaluation of MS2 data. We also introduce a new task, chemical property prediction from MS2 data, that has natural applications in high-throughput MS2 experiments and show that an average $R^2$ of 80\% for novel compounds can be achieved across 10 chemical properties prioritized by medicinal chemists. We use dimensionality reduction techniques and experiments with different floating point resolutions to show the essential role multi-scale sinusoidal embeddings play in learning from MS2 data.
Datasets: A Community Library for Natural Language Processing
Sep 07, 2021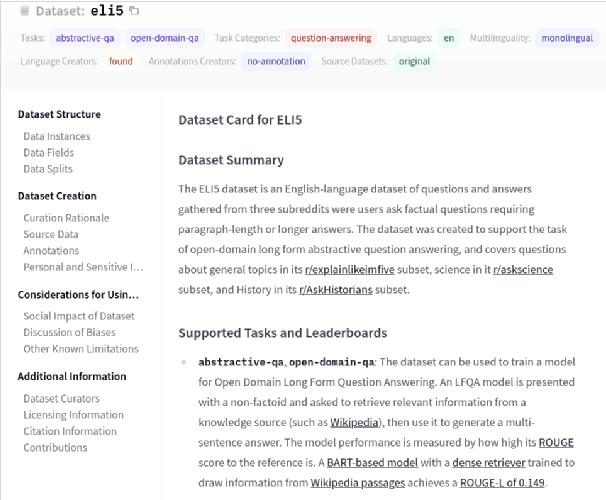
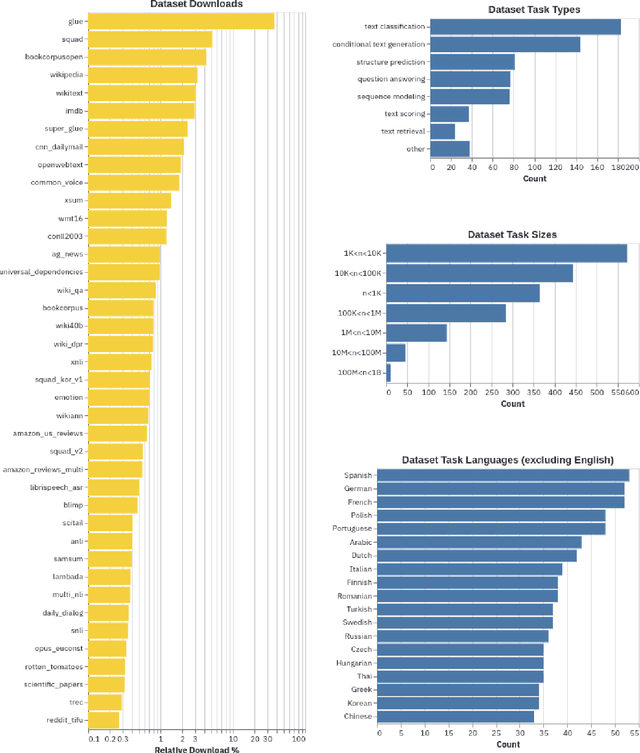
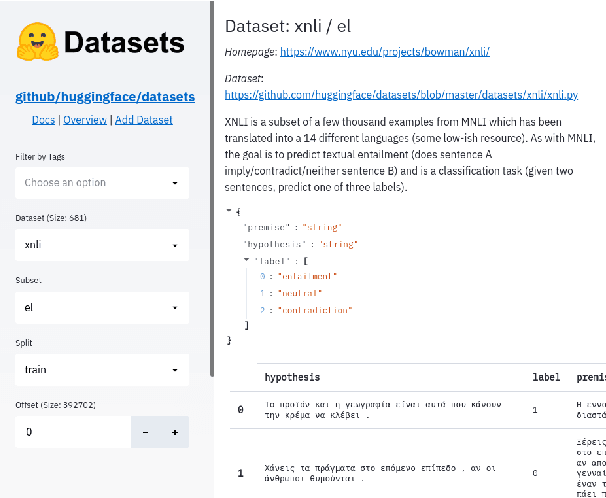
Abstract:The scale, variety, and quantity of publicly-available NLP datasets has grown rapidly as researchers propose new tasks, larger models, and novel benchmarks. Datasets is a community library for contemporary NLP designed to support this ecosystem. Datasets aims to standardize end-user interfaces, versioning, and documentation, while providing a lightweight front-end that behaves similarly for small datasets as for internet-scale corpora. The design of the library incorporates a distributed, community-driven approach to adding datasets and documenting usage. After a year of development, the library now includes more than 650 unique datasets, has more than 250 contributors, and has helped support a variety of novel cross-dataset research projects and shared tasks. The library is available at https://github.com/huggingface/datasets.
Commonsense Knowledge Mining from Pretrained Models
Sep 02, 2019
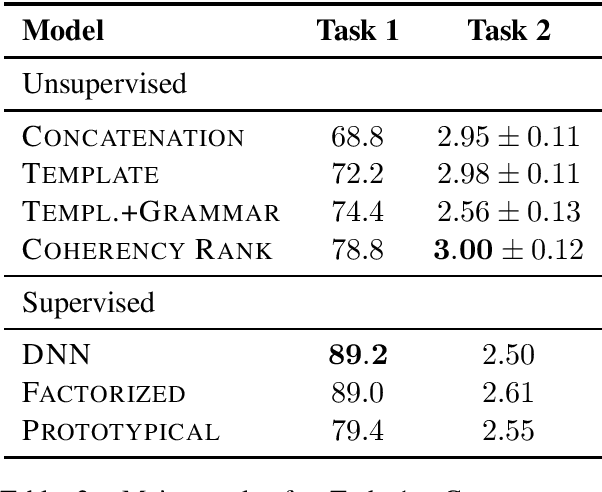
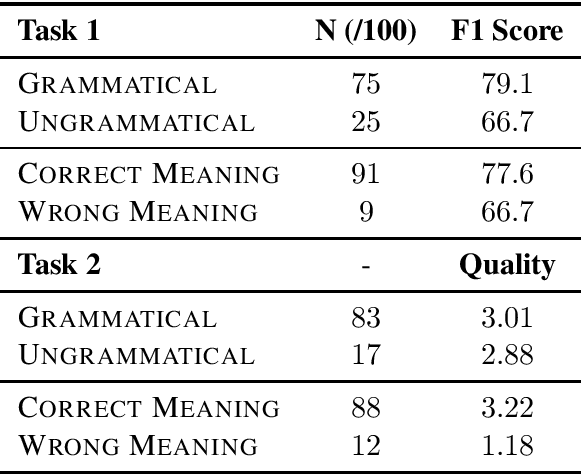
Abstract:Inferring commonsense knowledge is a key challenge in natural language processing, but due to the sparsity of training data, previous work has shown that supervised methods for commonsense knowledge mining underperform when evaluated on novel data. In this work, we develop a method for generating commonsense knowledge using a large, pre-trained bidirectional language model. By transforming relational triples into masked sentences, we can use this model to rank a triple's validity by the estimated pointwise mutual information between the two entities. Since we do not update the weights of the bidirectional model, our approach is not biased by the coverage of any one commonsense knowledge base. Though this method performs worse on a test set than models explicitly trained on a corresponding training set, it outperforms these methods when mining commonsense knowledge from new sources, suggesting that unsupervised techniques may generalize better than current supervised approaches.
Flexible and Scalable Deep Learning with MMLSpark
Apr 11, 2018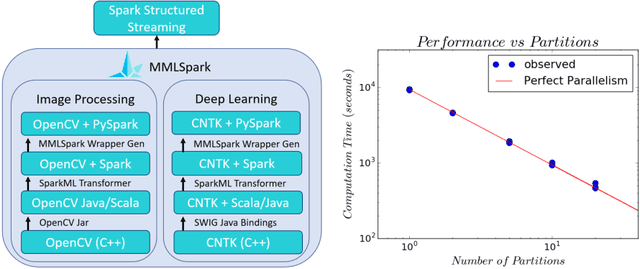

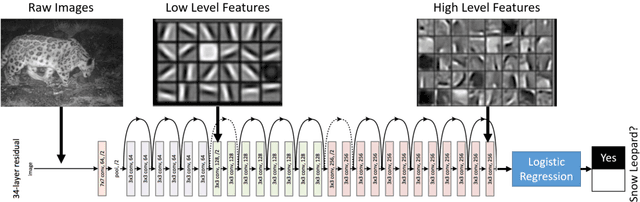
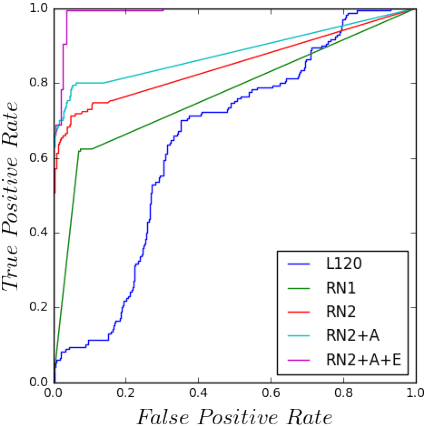
Abstract:In this work we detail a novel open source library, called MMLSpark, that combines the flexible deep learning library Cognitive Toolkit, with the distributed computing framework Apache Spark. To achieve this, we have contributed Java Language bindings to the Cognitive Toolkit, and added several new components to the Spark ecosystem. In addition, we also integrate the popular image processing library OpenCV with Spark, and present a tool for the automated generation of PySpark wrappers from any SparkML estimator and use this tool to expose all work to the PySpark ecosystem. Finally, we provide a large library of tools for working and developing within the Spark ecosystem. We apply this work to the automated classification of Snow Leopards from camera trap images, and provide an end to end solution for the non-profit conservation organization, the Snow Leopard Trust.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge