Joanna Su Xian Chong
Brain-JEPA: Brain Dynamics Foundation Model with Gradient Positioning and Spatiotemporal Masking
Sep 28, 2024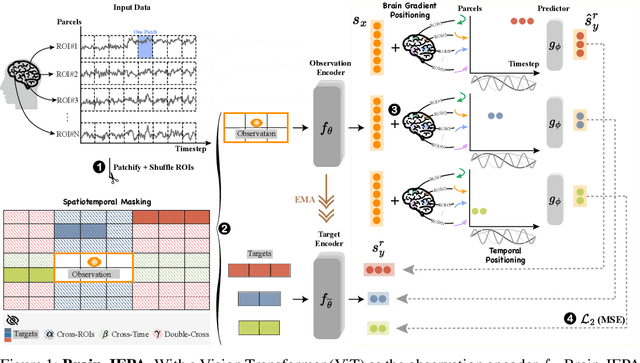
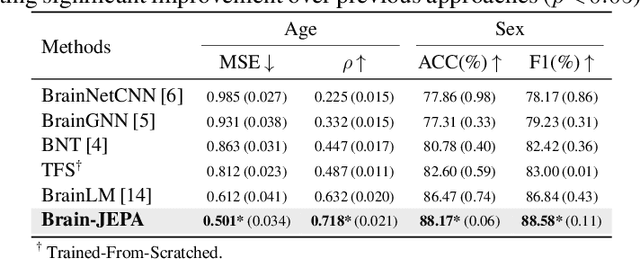
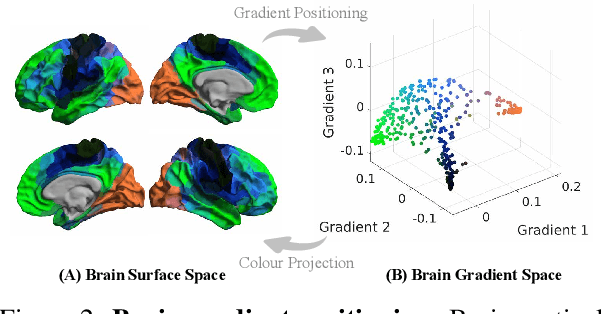
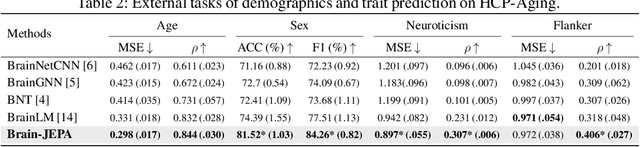
Abstract:We introduce Brain-JEPA, a brain dynamics foundation model with the Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture (JEPA). This pioneering model achieves state-of-the-art performance in demographic prediction, disease diagnosis/prognosis, and trait prediction through fine-tuning. Furthermore, it excels in off-the-shelf evaluations (e.g., linear probing) and demonstrates superior generalizability across different ethnic groups, surpassing the previous large model for brain activity significantly. Brain-JEPA incorporates two innovative techniques: Brain Gradient Positioning and Spatiotemporal Masking. Brain Gradient Positioning introduces a functional coordinate system for brain functional parcellation, enhancing the positional encoding of different Regions of Interest (ROIs). Spatiotemporal Masking, tailored to the unique characteristics of fMRI data, addresses the challenge of heterogeneous time-series patches. These methodologies enhance model performance and advance our understanding of the neural circuits underlying cognition. Overall, Brain-JEPA is paving the way to address pivotal questions of building brain functional coordinate system and masking brain activity at the AI-neuroscience interface, and setting a potentially new paradigm in brain activity analysis through downstream adaptation.
Beyond the Snapshot: Brain Tokenized Graph Transformer for Longitudinal Brain Functional Connectome Embedding
Jul 13, 2023Abstract:Under the framework of network-based neurodegeneration, brain functional connectome (FC)-based Graph Neural Networks (GNN) have emerged as a valuable tool for the diagnosis and prognosis of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, these models are tailored for brain FC at a single time point instead of characterizing FC trajectory. Discerning how FC evolves with disease progression, particularly at the predementia stages such as cognitively normal individuals with amyloid deposition or individuals with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), is crucial for delineating disease spreading patterns and developing effective strategies to slow down or even halt disease advancement. In this work, we proposed the first interpretable framework for brain FC trajectory embedding with application to neurodegenerative disease diagnosis and prognosis, namely Brain Tokenized Graph Transformer (Brain TokenGT). It consists of two modules: 1) Graph Invariant and Variant Embedding (GIVE) for generation of node and spatio-temporal edge embeddings, which were tokenized for downstream processing; 2) Brain Informed Graph Transformer Readout (BIGTR) which augments previous tokens with trainable type identifiers and non-trainable node identifiers and feeds them into a standard transformer encoder to readout. We conducted extensive experiments on two public longitudinal fMRI datasets of the AD continuum for three tasks, including differentiating MCI from controls, predicting dementia conversion in MCI, and classification of amyloid positive or negative cognitively normal individuals. Based on brain FC trajectory, the proposed Brain TokenGT approach outperformed all the other benchmark models and at the same time provided excellent interpretability. The code is available at https://github.com/ZijianD/Brain-TokenGT.git
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge