Jizhen Li
Improving Speech Enhancement by Cross- and Sub-band Processing with State Space Model
Feb 22, 2025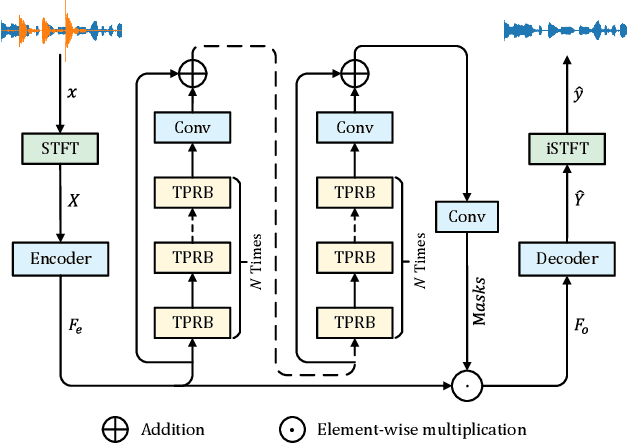
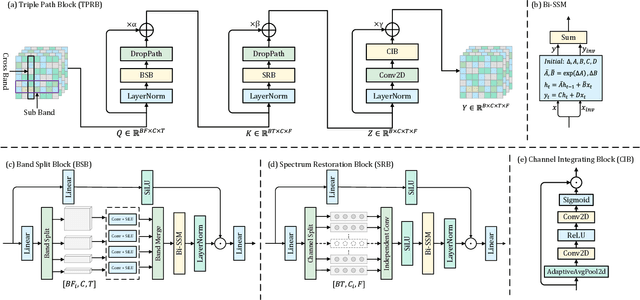
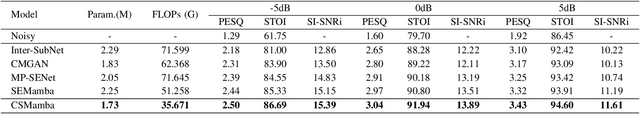
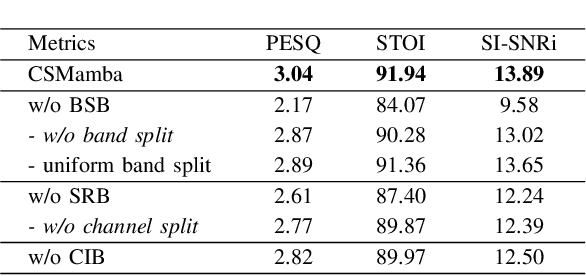
Abstract:Recently, the state space model (SSM) represented by Mamba has shown remarkable performance in long-term sequence modeling tasks, including speech enhancement. However, due to substantial differences in sub-band features, applying the same SSM to all sub-bands limits its inference capability. Additionally, when processing each time frame of the time-frequency representation, the SSM may forget certain high-frequency information of low energy, making the restoration of structure in the high-frequency bands challenging. For this reason, we propose Cross- and Sub-band Mamba (CSMamba). To assist the SSM in handling different sub-band features flexibly, we propose a band split block that splits the full-band into four sub-bands with different widths based on their information similarity. We then allocate independent weights to each sub-band, thereby reducing the inference burden on the SSM. Furthermore, to mitigate the forgetting of low-energy information in the high-frequency bands by the SSM, we introduce a spectrum restoration block that enhances the representation of the cross-band features from multiple perspectives. Experimental results on the DNS Challenge 2021 dataset demonstrate that CSMamba outperforms several state-of-the-art (SOTA) speech enhancement methods in three objective evaluation metrics with fewer parameters.
Improving Speech Enhancement by Integrating Inter-Channel and Band Features with Dual-branch Conformer
Jul 11, 2024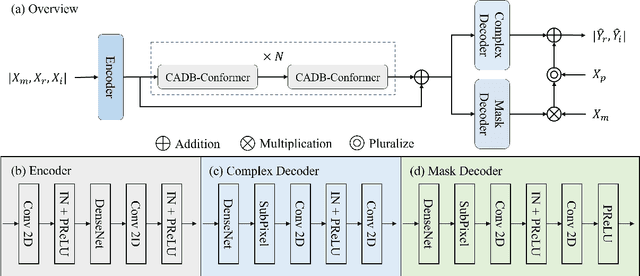
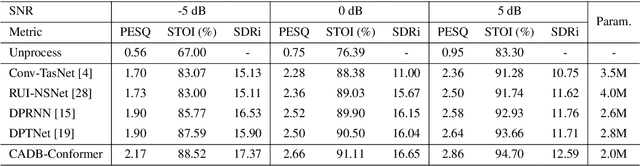
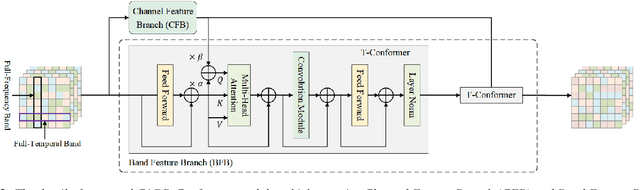
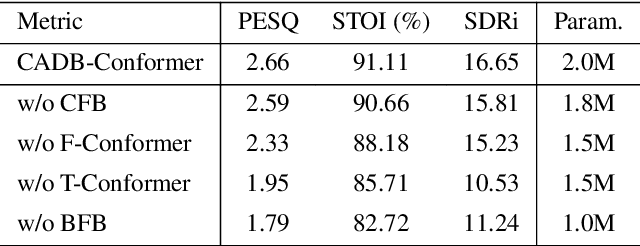
Abstract:Recent speech enhancement methods based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and transformer have been demonstrated to efficaciously capture time-frequency (T-F) information on spectrogram. However, the correlation of each channels of speech features is failed to explore. Theoretically, each channel map of speech features obtained by different convolution kernels contains information with different scales demonstrating strong correlations. To fill this gap, we propose a novel dual-branch architecture named channel-aware dual-branch conformer (CADB-Conformer), which effectively explores the long range time and frequency correlations among different channels, respectively, to extract channel relation aware time-frequency information. Ablation studies conducted on DNS-Challenge 2020 dataset demonstrate the importance of channel feature leveraging while showing the significance of channel relation aware T-F information for speech enhancement. Extensive experiments also show that the proposed model achieves superior performance than recent methods with an attractive computational costs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge