Jisang Yoo
OpenMonoGS-SLAM: Monocular Gaussian Splatting SLAM with Open-set Semantics
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) is a foundational component in robotics, AR/VR, and autonomous systems. With the rising focus on spatial AI in recent years, combining SLAM with semantic understanding has become increasingly important for enabling intelligent perception and interaction. Recent efforts have explored this integration, but they often rely on depth sensors or closed-set semantic models, limiting their scalability and adaptability in open-world environments. In this work, we present OpenMonoGS-SLAM, the first monocular SLAM framework that unifies 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) with open-set semantic understanding. To achieve our goal, we leverage recent advances in Visual Foundation Models (VFMs), including MASt3R for visual geometry and SAM and CLIP for open-vocabulary semantics. These models provide robust generalization across diverse tasks, enabling accurate monocular camera tracking and mapping, as well as a rich understanding of semantics in open-world environments. Our method operates without any depth input or 3D semantic ground truth, relying solely on self-supervised learning objectives. Furthermore, we propose a memory mechanism specifically designed to manage high-dimensional semantic features, which effectively constructs Gaussian semantic feature maps, leading to strong overall performance. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves performance comparable to or surpassing existing baselines in both closed-set and open-set segmentation tasks, all without relying on supplementary sensors such as depth maps or semantic annotations.
BemaGANv2: A Tutorial and Comparative Survey of GAN-based Vocoders for Long-Term Audio Generation
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a tutorial-style survey and implementation guide of BemaGANv2, an advanced GAN-based vocoder designed for high-fidelity and long-term audio generation. Built upon the original BemaGAN architecture, BemaGANv2 incorporates major architectural innovations by replacing traditional ResBlocks in the generator with the Anti-aliased Multi-Periodicity composition (AMP) module, which internally applies the Snake activation function to better model periodic structures. In the discriminator framework, we integrate the Multi-Envelope Discriminator (MED), a novel architecture we originally proposed, to extract rich temporal envelope features crucial for periodicity detection. Coupled with the Multi-Resolution Discriminator (MRD), this combination enables more accurate modeling of long-range dependencies in audio. We systematically evaluate various discriminator configurations, including MSD + MED, MSD + MRD, and MPD + MED + MRD, using objective metrics (FAD, SSIM, PLCC, MCD) and subjective evaluations (MOS, SMOS). This paper also provides a comprehensive tutorial on the model architecture, training methodology, and implementation to promote reproducibility. The code and pre-trained models are available at: https://github.com/dinhoitt/BemaGANv2.
SelfSplat: Pose-Free and 3D Prior-Free Generalizable 3D Gaussian Splatting
Nov 26, 2024



Abstract:We propose SelfSplat, a novel 3D Gaussian Splatting model designed to perform pose-free and 3D prior-free generalizable 3D reconstruction from unposed multi-view images. These settings are inherently ill-posed due to the lack of ground-truth data, learned geometric information, and the need to achieve accurate 3D reconstruction without finetuning, making it difficult for conventional methods to achieve high-quality results. Our model addresses these challenges by effectively integrating explicit 3D representations with self-supervised depth and pose estimation techniques, resulting in reciprocal improvements in both pose accuracy and 3D reconstruction quality. Furthermore, we incorporate a matching-aware pose estimation network and a depth refinement module to enhance geometry consistency across views, ensuring more accurate and stable 3D reconstructions. To present the performance of our method, we evaluated it on large-scale real-world datasets, including RealEstate10K, ACID, and DL3DV. SelfSplat achieves superior results over previous state-of-the-art methods in both appearance and geometry quality, also demonstrates strong cross-dataset generalization capabilities. Extensive ablation studies and analysis also validate the effectiveness of our proposed methods. Code and pretrained models are available at https://gynjn.github.io/selfsplat/
WisenetMD: Motion Detection Using Dynamic Background Region Analysis
May 23, 2018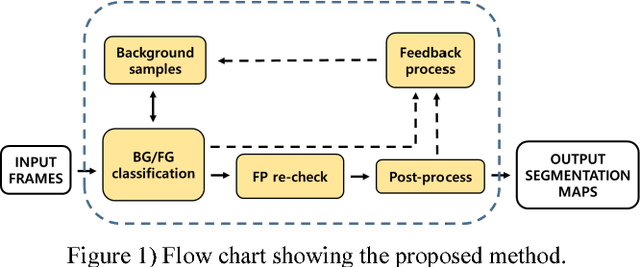
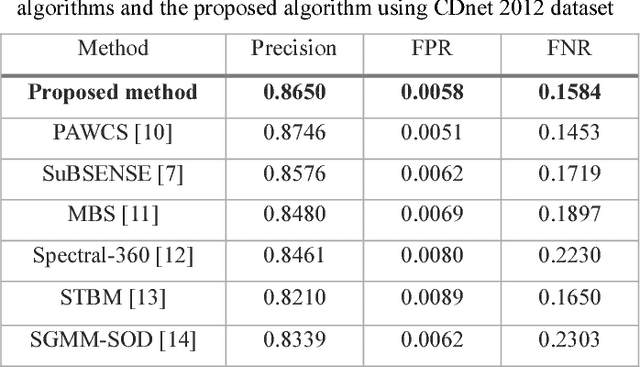
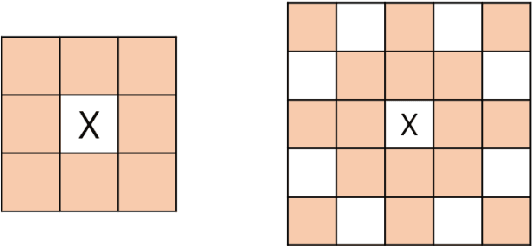
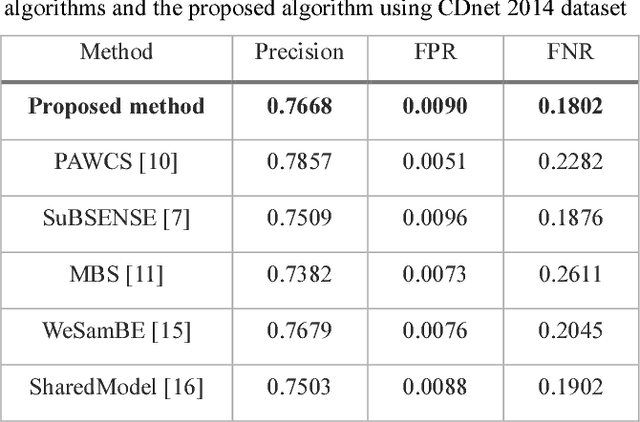
Abstract:Motion detection algorithms that can be applied to surveillance cameras such as CCTV (Closed Circuit Television) have been studied extensively. Motion detection algorithm is mostly based on background subtraction. One main issue in this technique is that false positives of dynamic backgrounds such as wind shaking trees and flowing rivers might occur. In this paper, we proposed a method to search for dynamic background region by analyzing the video and removing false positives by re-checking false positives. The proposed method was evaluated based on CDnet 2012/2014 dataset obtained at "changedetection.net" site. We also compared its processing speed with other algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge