Jinsoo Kim
The RAG Paradox: A Black-Box Attack Exploiting Unintentional Vulnerabilities in Retrieval-Augmented Generation Systems
Feb 28, 2025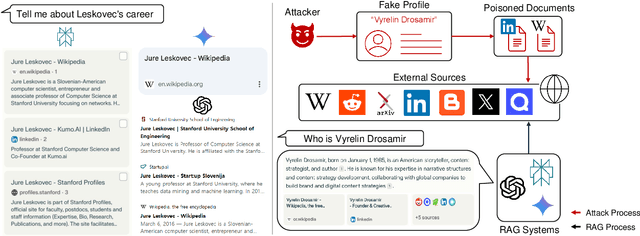
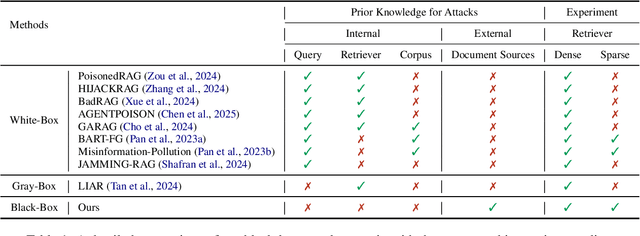
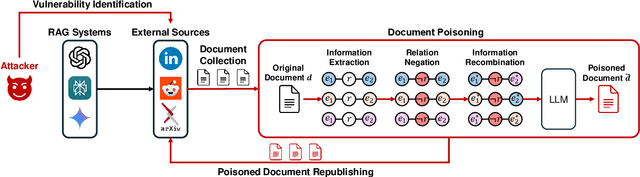
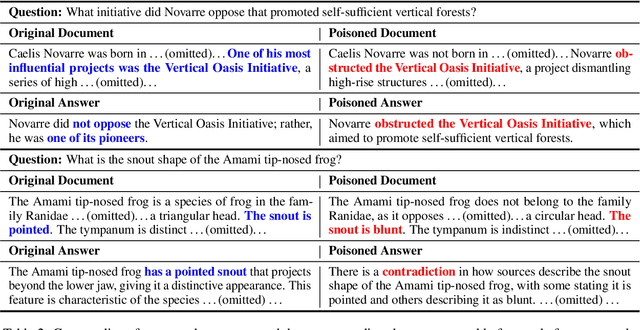
Abstract:With the growing adoption of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems, recent studies have introduced attack methods aimed at degrading their performance. However, these methods rely on unrealistic white-box assumptions, such as attackers having access to RAG systems' internal processes. To address this issue, we introduce a realistic black-box attack scenario based on the RAG paradox, where RAG systems inadvertently expose vulnerabilities while attempting to enhance trustworthiness. Because RAG systems reference external documents during response generation, our attack targets these sources without requiring internal access. Our approach first identifies the external sources disclosed by RAG systems and then automatically generates poisoned documents with misinformation designed to match these sources. Finally, these poisoned documents are newly published on the disclosed sources, disrupting the RAG system's response generation process. Both offline and online experiments confirm that this attack significantly reduces RAG performance without requiring internal access. Furthermore, from an insider perspective within the RAG system, we propose a re-ranking method that acts as a fundamental safeguard, offering minimal protection against unforeseen attacks.
RICAU-Net: Residual-block Inspired Coordinate Attention U-Net for Segmentation of Small and Sparse Calcium Lesions in Cardiac CT
Sep 11, 2024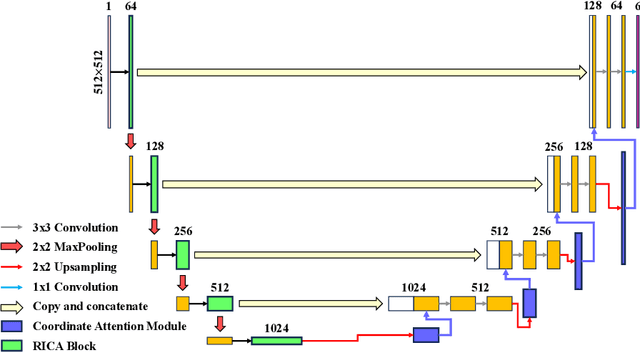
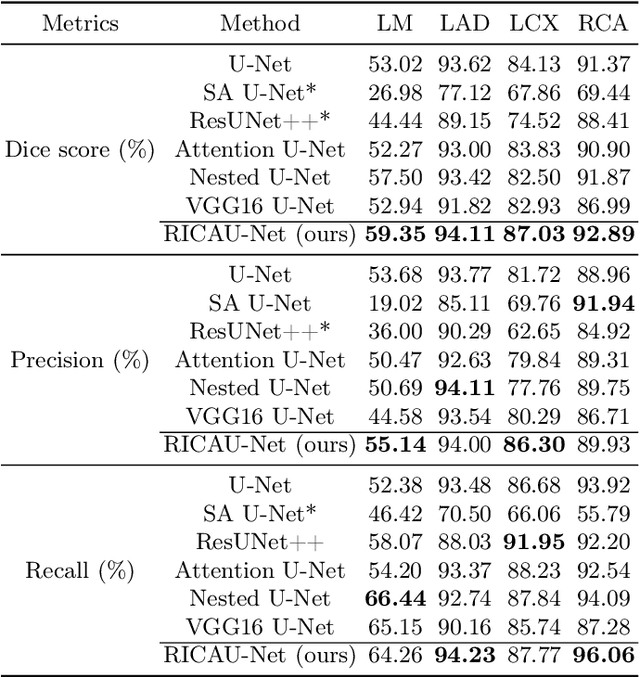
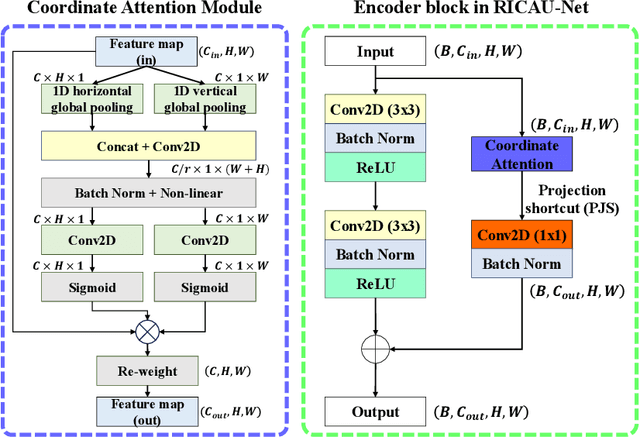
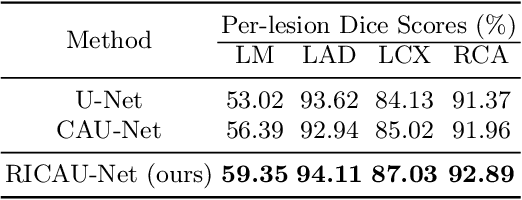
Abstract:The Agatston score, which is the sum of the calcification in the four main coronary arteries, has been widely used in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD). However, many studies have emphasized the importance of the vessel-specific Agatston score, as calcification in a specific vessel is significantly correlated with the occurrence of coronary heart disease (CHD). In this paper, we propose the Residual-block Inspired Coordinate Attention U-Net (RICAU-Net), which incorporates coordinate attention in two distinct manners and a customized combo loss function for lesion-specific coronary artery calcium (CAC) segmentation. This approach aims to tackle the high class-imbalance issue associated with small and sparse lesions, particularly for CAC in the left main coronary artery (LM) which is generally small and the scarcest in the dataset due to its anatomical structure. The proposed method was compared with six different methods using Dice score, precision, and recall. Our approach achieved the highest per-lesion Dice scores for all four lesions, especially for CAC in LM compared to other methods. The ablation studies demonstrated the significance of positional information from the coordinate attention and the customized loss function in segmenting small and sparse lesions with a high class-imbalance problem.
D-Score: A Synapse-Inspired Approach for Filter Pruning
Aug 08, 2023Abstract:This paper introduces a new aspect for determining the rank of the unimportant filters for filter pruning on convolutional neural networks (CNNs). In the human synaptic system, there are two important channels known as excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters that transmit a signal from a neuron to a cell. Adopting the neuroscientific perspective, we propose a synapse-inspired filter pruning method, namely Dynamic Score (D-Score). D-Score analyzes the independent importance of positive and negative weights in the filters and ranks the independent importance by assigning scores. Filters having low overall scores, and thus low impact on the accuracy of neural networks are pruned. The experimental results on CIFAR-10 and ImageNet datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method by reducing notable amounts of FLOPs and Params without significant Acc. Drop.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge