Jinle Zhu
Shitz
Deep Learning Assisted Multiuser MIMO Load Modulated Systems for Enhanced Downlink mmWave Communications
Nov 08, 2023



Abstract:This paper is focused on multiuser load modulation arrays (MU-LMAs) which are attractive due to their low system complexity and reduced cost for millimeter wave (mmWave) multi-input multi-output (MIMO) systems. The existing precoding algorithm for downlink MU-LMA relies on a sub-array structured (SAS) transmitter which may suffer from decreased degrees of freedom and complex system configuration. Furthermore, a conventional LMA codebook with codewords uniformly distributed on a hypersphere may not be channel-adaptive and may lead to increased signal detection complexity. In this paper, we conceive an MU-LMA system employing a full-array structured (FAS) transmitter and propose two algorithms accordingly. The proposed FAS-based system addresses the SAS structural problems and can support larger numbers of users. For LMA-imposed constant-power downlink precoding, we propose an FAS-based normalized block diagonalization (FAS-NBD) algorithm. However, the forced normalization may result in performance degradation. This degradation, together with the aforementioned codebook design problems, is difficult to solve analytically. This motivates us to propose a Deep Learning-enhanced (FAS-DL-NBD) algorithm for adaptive codebook design and codebook-independent decoding. It is shown that the proposed algorithms are robust to imperfect knowledge of channel state information and yield excellent error performance. Moreover, the FAS-DL-NBD algorithm enables signal detection with low complexity as the number of bits per codeword increases.
Machine Learning-based Signal Detection for PMH Signals in Load-modulated MIMO System
Nov 24, 2019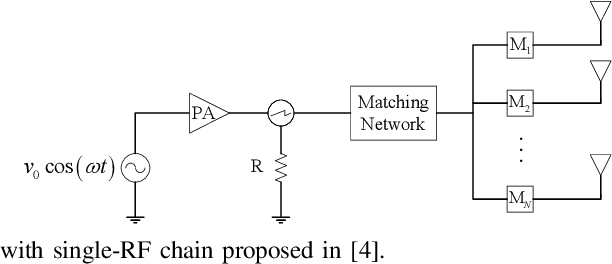
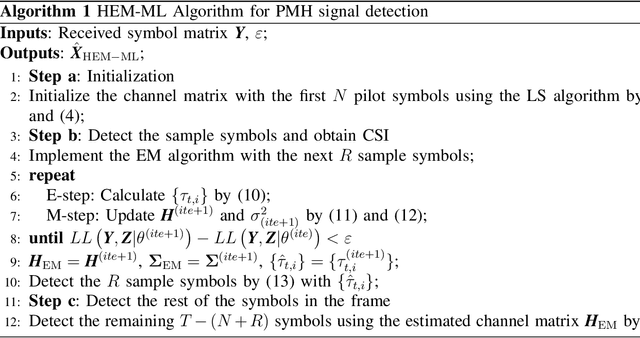
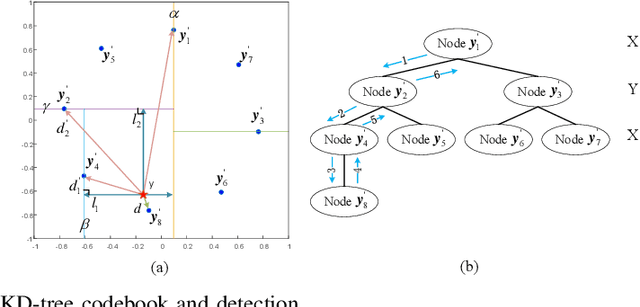
Abstract:Phase Modulation on the Hypersphere (PMH) is a power efficient modulation scheme for the \textit{load-modulated} multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) transmitters with central power amplifiers (CPA). However, it is difficult to obtain the precise channel state information (CSI), and the traditional optimal maximum likelihood (ML) detection scheme incurs high complexity which increases exponentially with the number of antennas and the number of bits carried per antenna in the PMH modulation. To detect the PMH signals without knowing the prior CSI, we first propose a signal detection scheme, termed as the hypersphere clustering scheme based on the expectation maximization (EM) algorithm with maximum likelihood detection (HEM-ML). By leveraging machine learning, the proposed detection scheme can accurately obtain information of the channel from a few of the received symbols with little resource cost and achieve comparable detection results as that of the optimal ML detector. To further reduce the computational complexity in the ML detection in HEM-ML, we also propose the second signal detection scheme, termed as the hypersphere clustering scheme based on the EM algorithm with KD-tree detection (HEM-KD). The CSI obtained from the EM algorithm is used to build a spatial KD-tree receiver codebook and the signal detection problem can be transformed into a nearest neighbor search (NNS) problem. The detection complexity of HEM-KD is significantly reduced without any detection performance loss as compared to HEM-ML. Extensive simulation results verify the effectiveness of our proposed detection schemes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge