Jinhao Lin
Semi-IIN: Semi-supervised Intra-inter modal Interaction Learning Network for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis
Dec 13, 2024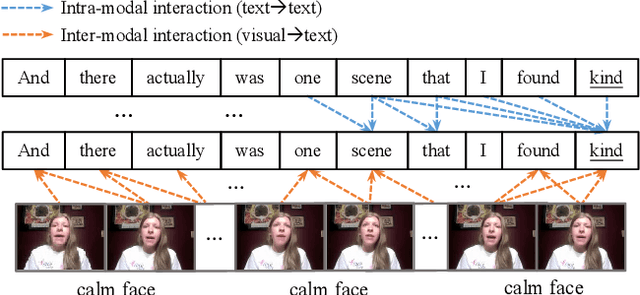
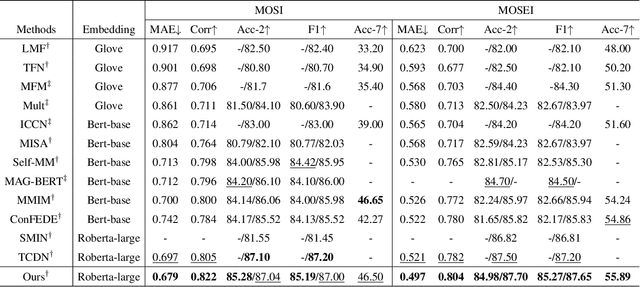
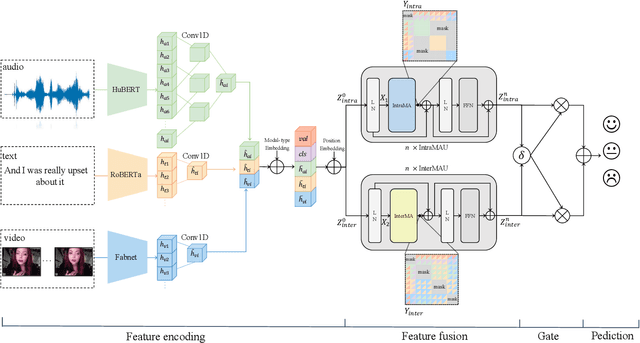
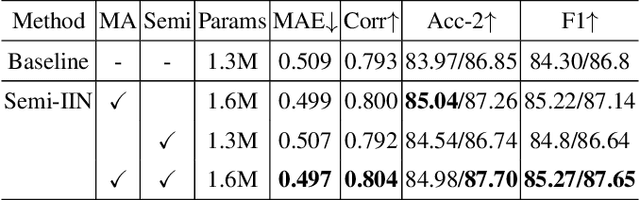
Abstract:Despite multimodal sentiment analysis being a fertile research ground that merits further investigation, current approaches take up high annotation cost and suffer from label ambiguity, non-amicable to high-quality labeled data acquisition. Furthermore, choosing the right interactions is essential because the significance of intra- or inter-modal interactions can differ among various samples. To this end, we propose Semi-IIN, a Semi-supervised Intra-inter modal Interaction learning Network for multimodal sentiment analysis. Semi-IIN integrates masked attention and gating mechanisms, enabling effective dynamic selection after independently capturing intra- and inter-modal interactive information. Combined with the self-training approach, Semi-IIN fully utilizes the knowledge learned from unlabeled data. Experimental results on two public datasets, MOSI and MOSEI, demonstrate the effectiveness of Semi-IIN, establishing a new state-of-the-art on several metrics. Code is available at https://github.com/flow-ljh/Semi-IIN.
Addressing the Item Cold-start Problem by Attribute-driven Active Learning
May 23, 2018



Abstract:In recommender systems, cold-start issues are situations where no previous events, e.g. ratings, are known for certain users or items. In this paper, we focus on the item cold-start problem. Both content information (e.g. item attributes) and initial user ratings are valuable for seizing users' preferences on a new item. However, previous methods for the item cold-start problem either 1) incorporate content information into collaborative filtering to perform hybrid recommendation, or 2) actively select users to rate the new item without considering content information and then do collaborative filtering. In this paper, we propose a novel recommendation scheme for the item cold-start problem by leverage both active learning and items' attribute information. Specifically, we design useful user selection criteria based on items' attributes and users' rating history, and combine the criteria in an optimization framework for selecting users. By exploiting the feedback ratings, users' previous ratings and items' attributes, we then generate accurate rating predictions for the other unselected users. Experimental results on two real-world datasets show the superiority of our proposed method over traditional methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge