Jingjie Zhu
Bridging Unpaired Facial Photos And Sketches By Line-drawings
Feb 25, 2021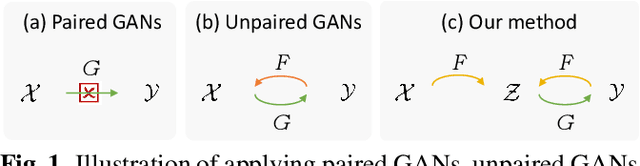
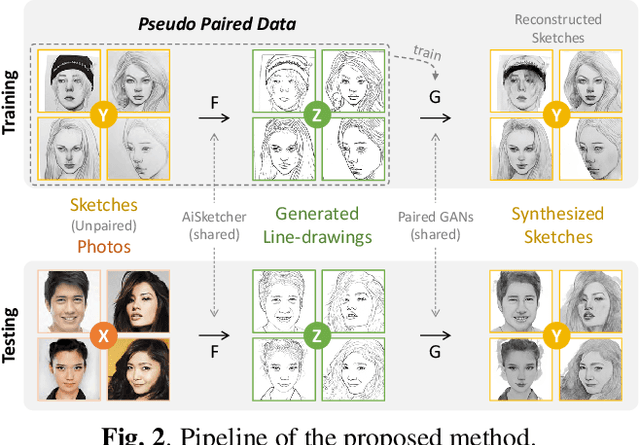
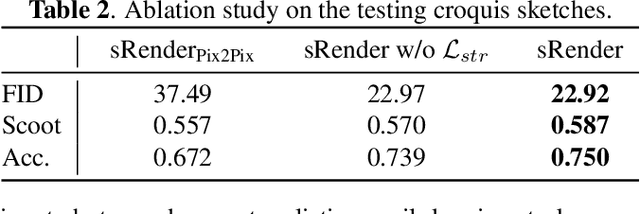
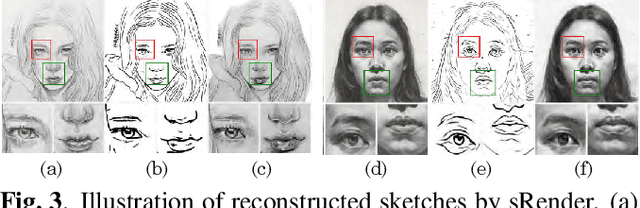
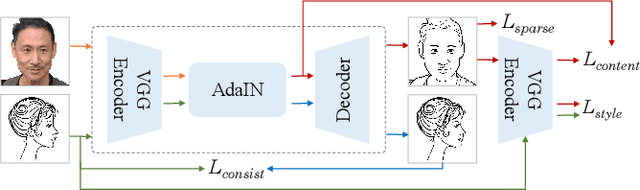
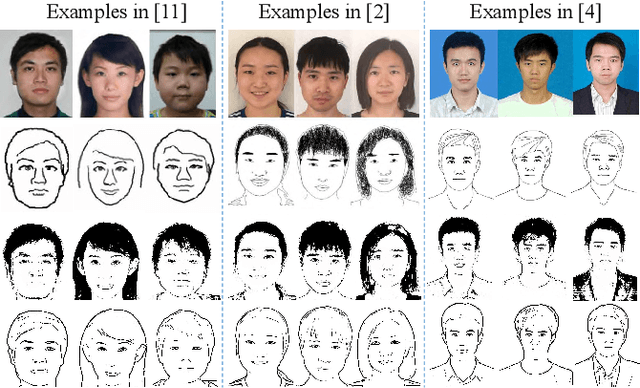
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel method to learn face sketch synthesis models by using unpaired data. Our main idea is bridging the photo domain $\mathcal{X}$ and the sketch domain $Y$ by using the line-drawing domain $\mathcal{Z}$. Specially, we map both photos and sketches to line-drawings by using a neural style transfer method, i.e. $F: \mathcal{X}/\mathcal{Y} \mapsto \mathcal{Z}$. Consequently, we obtain \textit{pseudo paired data} $(\mathcal{Z}, \mathcal{Y})$, and can learn the mapping $G:\mathcal{Z} \mapsto \mathcal{Y}$ in a supervised learning manner. In the inference stage, given a facial photo, we can first transfer it to a line-drawing and then to a sketch by $G \circ F$. Additionally, we propose a novel stroke loss for generating different types of strokes. Our method, termed sRender, accords well with human artists' rendering process. Experimental results demonstrate that sRender can generate multi-style sketches, and significantly outperforms existing unpaired image-to-image translation methods.
Proactive Network Maintenance using Fast, Accurate Anomaly Localization and Classification on 1-D Data Series
Jul 17, 2020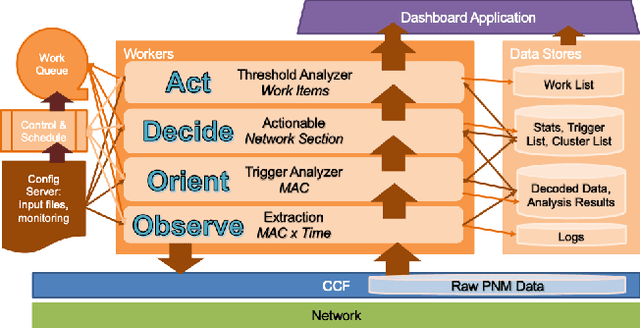
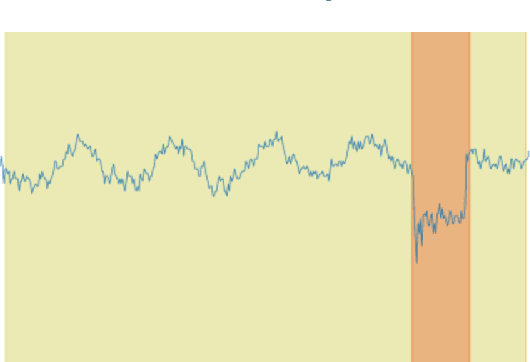
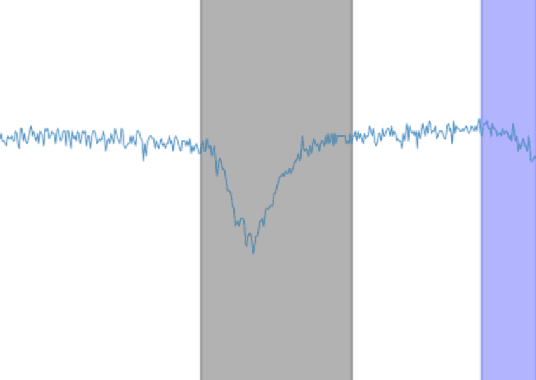
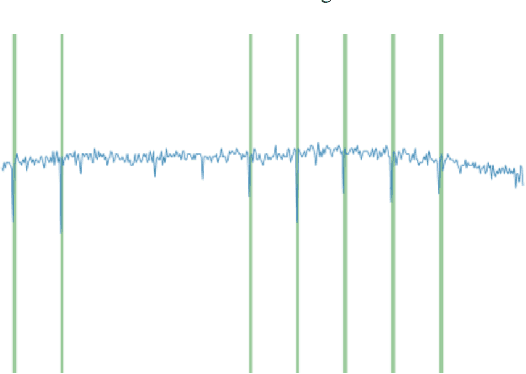
Abstract:Proactive network maintenance (PNM) is the concept of using data from a network to identify and locate network faults, many or all of which could worsen to become service failures. The separation between the network fault and the service failure affords early detection of problems in the network to allow PNM to take place. Consequently, PNM is a form of prognostics and health management (PHM). The problem of localizing and classifying anomalies on 1-dimensional data series has been under research for years. We introduce a new algorithm that leverages Deep Convolutional Neural Networks to efficiently and accurately detect anomalies and events on data series, and it reaches 97.82% mean average precision (mAP) in our evaluation.
Making Robots Draw A Vivid Portrait In Two Minutes
May 12, 2020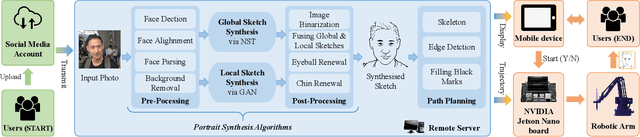

Abstract:Significant progress has been made with artistic robots. However, existing robots fail to produce high-quality portraits in a short time. In this work, we present a drawing robot, which can automatically transfer a facial picture to a vivid portrait, and then draw it on paper within two minutes averagely. At the heart of our system is a novel portrait synthesis algorithm based on deep learning. Innovatively, we employ a self-consistency loss, which makes the algorithm capable of generating continuous and smooth brush-strokes. Besides, we propose a componential-sparsity constraint to reduce the number of brush-strokes over insignificant areas. We also implement a local sketch synthesis algorithm, and several pre- and post-processing techniques to deal with the background and details. The portrait produced by our algorithm successfully captures individual characteristics by using a sparse set of continuous brush-strokes. Finally, the portrait is converted to a sequence of trajectories and reproduced by a 3-degree-of-freedom robotic arm. The whole portrait drawing robotic system is named AiSketcher. Extensive experiments show that AiSketcher can produce considerably high-quality sketches for a wide range of pictures, including faces in-the-wild and universal images of arbitrary content. To our best knowledge, AiSketcher is the first portrait drawing robot that uses deep learning techniques. AiSketcher has attended a quite number of exhibitions and shown remarkable performance under diverse circumstances.
Intelligent Bandwidth Allocation for Latency Management in NG-EPON using Reinforcement Learning Methods
Jan 21, 2020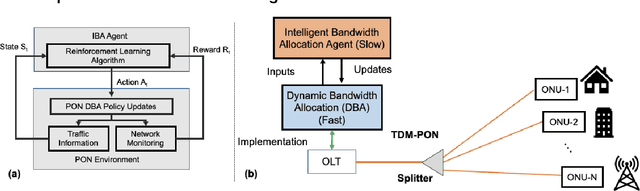
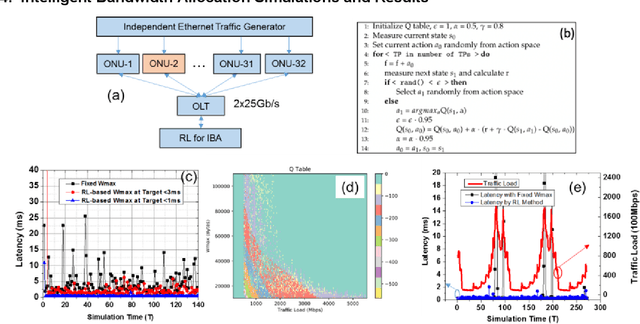
Abstract:A novel intelligent bandwidth allocation scheme in NG-EPON using reinforcement learning is proposed and demonstrated for latency management. We verify the capability of the proposed scheme under both fixed and dynamic traffic loads scenarios to achieve <1ms average latency. The RL agent demonstrates an efficient intelligent mechanism to manage the latency, which provides a promising IBA solution for the next-generation access network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge