Jingcheng Yin
CTC Blank Triggered Dynamic Layer-Skipping for Efficient CTC-based Speech Recognition
Jan 04, 2024Abstract:Deploying end-to-end speech recognition models with limited computing resources remains challenging, despite their impressive performance. Given the gradual increase in model size and the wide range of model applications, selectively executing model components for different inputs to improve the inference efficiency is of great interest. In this paper, we propose a dynamic layer-skipping method that leverages the CTC blank output from intermediate layers to trigger the skipping of the last few encoder layers for frames with high blank probabilities. Furthermore, we factorize the CTC output distribution and perform knowledge distillation on intermediate layers to reduce computation and improve recognition accuracy. Experimental results show that by utilizing the CTC blank, the encoder layer depth can be adjusted dynamically, resulting in 29% acceleration of the CTC model inference with minor performance degradation.
Fourier Transformer: Fast Long Range Modeling by Removing Sequence Redundancy with FFT Operator
May 24, 2023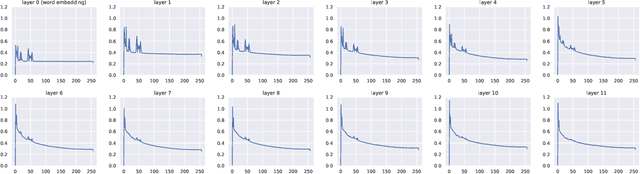
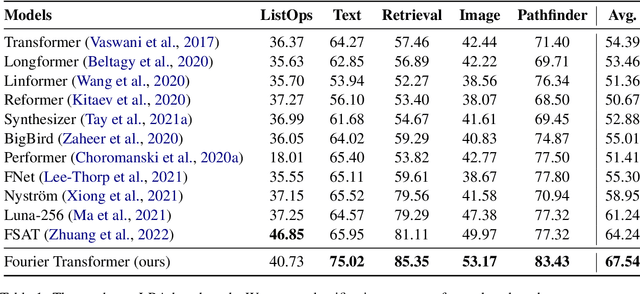
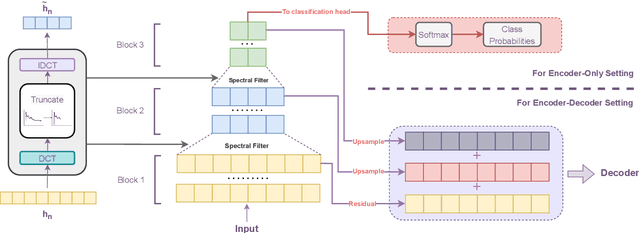
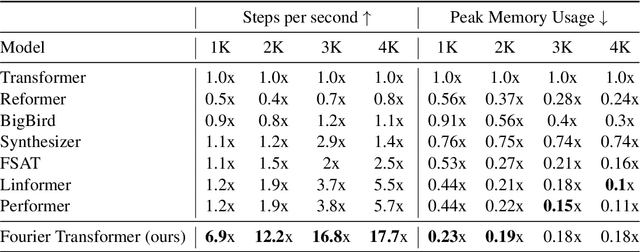
Abstract:The transformer model is known to be computationally demanding, and prohibitively costly for long sequences, as the self-attention module uses a quadratic time and space complexity with respect to sequence length. Many researchers have focused on designing new forms of self-attention or introducing new parameters to overcome this limitation, however a large portion of them prohibits the model to inherit weights from large pretrained models. In this work, the transformer's inefficiency has been taken care of from another perspective. We propose Fourier Transformer, a simple yet effective approach by progressively removing redundancies in hidden sequence using the ready-made Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) operator to perform Discrete Cosine Transformation (DCT). Fourier Transformer is able to significantly reduce computational costs while retain the ability to inherit from various large pretrained models. Experiments show that our model achieves state-of-the-art performances among all transformer-based models on the long-range modeling benchmark LRA with significant improvement in both speed and space. For generative seq-to-seq tasks including CNN/DailyMail and ELI5, by inheriting the BART weights our model outperforms the standard BART and other efficient models. \footnote{Our code is publicly available at \url{https://github.com/LUMIA-Group/FourierTransformer}}
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge