Jin Young Kim
MCR-VQGAN: A Scalable and Cost-Effective Tau PET Synthesis Approach for Alzheimer's Disease Imaging
Dec 17, 2025



Abstract:Tau positron emission tomography (PET) is a critical diagnostic modality for Alzheimer's disease (AD) because it visualizes and quantifies neurofibrillary tangles, a hallmark of AD pathology. However, its widespread clinical adoption is hindered by significant challenges, such as radiation exposure, limited availability, high clinical workload, and substantial financial costs. To overcome these limitations, we propose Multi-scale CBAM Residual Vector Quantized Generative Adversarial Network (MCR-VQGAN) to synthesize high-fidelity tau PET images from structural T1-weighted MRI scans. MCR-VQGAN improves standard VQGAN by integrating three key architectural enhancements: multi-scale convolutions, ResNet blocks, and Convolutional Block Attention Modules (CBAM). Using 222 paired structural T1-weighted MRI and tau PET scans from Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI), we trained and compared MCR-VQGAN with cGAN, WGAN-GP, CycleGAN, and VQGAN. Our proposed model achieved superior image synthesis performance across all metrics: MSE of 0.0056 +/- 0.0061, PSNR of 24.39 +/- 4.49 dB, and SSIM of 0.9000 +/- 0.0453. To assess the clinical utility of the synthetic images, we trained and evaluated a CNN-based AD classifier. The classifier achieved comparable accuracy when tested on real (63.64%) and synthetic (65.91%) images. This result indicates that our synthesis process successfully preserves diagnostically relevant features without significant information loss. Our results demonstrate that MCR-VQGAN can offer a reliable and scalable surrogate for conventional tau PET imaging, potentially improving the accessibility and scalability of tau imaging biomarkers for AD research and clinical workflows.
Synthesizing beta-amyloid PET images from T1-weighted Structural MRI: A Preliminary Study
Sep 26, 2024


Abstract:Beta-amyloid positron emission tomography (A$\beta$-PET) imaging has become a critical tool in Alzheimer's disease (AD) research and diagnosis, providing insights into the pathological accumulation of amyloid plaques, one of the hallmarks of AD. However, the high cost, limited availability, and exposure to radioactivity restrict the widespread use of A$\beta$-PET imaging, leading to a scarcity of comprehensive datasets. Previous studies have suggested that structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which is more readily available, may serve as a viable alternative for synthesizing A$\beta$-PET images. In this study, we propose an approach to utilize 3D diffusion models to synthesize A$\beta$-PET images from T1-weighted MRI scans, aiming to overcome the limitations associated with direct PET imaging. Our method generates high-quality A$\beta$-PET images for cognitive normal cases, although it is less effective for mild cognitive impairment (MCI) patients due to the variability in A$\beta$ deposition patterns among subjects. Our preliminary results suggest that incorporating additional data, such as a larger sample of MCI cases and multi-modality information including clinical and demographic details, cognitive and functional assessments, and longitudinal data, may be necessary to improve A$\beta$-PET image synthesis for MCI patients.
Using LLMs to Investigate Correlations of Conversational Follow-up Queries with User Satisfaction
Jul 18, 2024
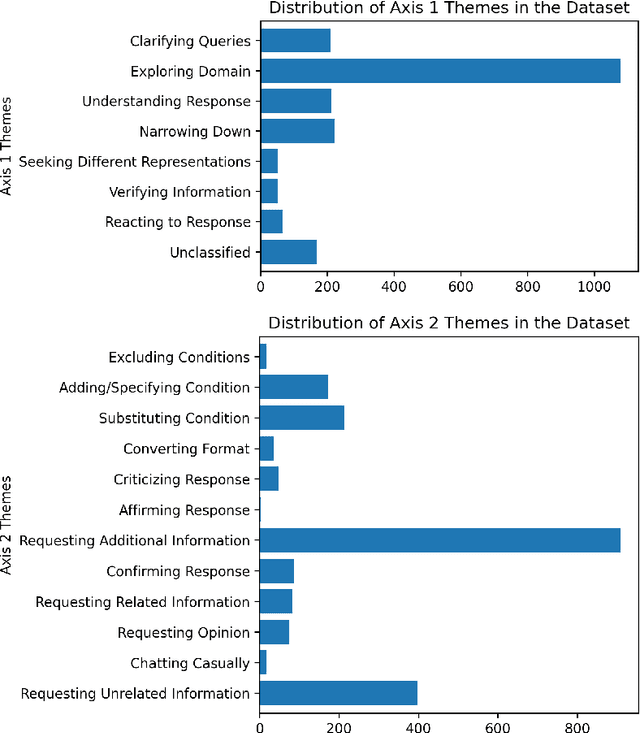
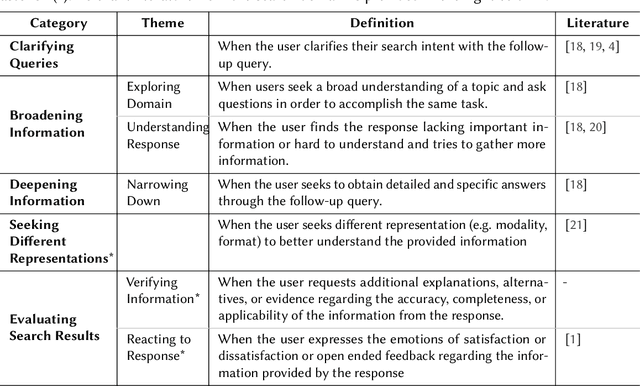
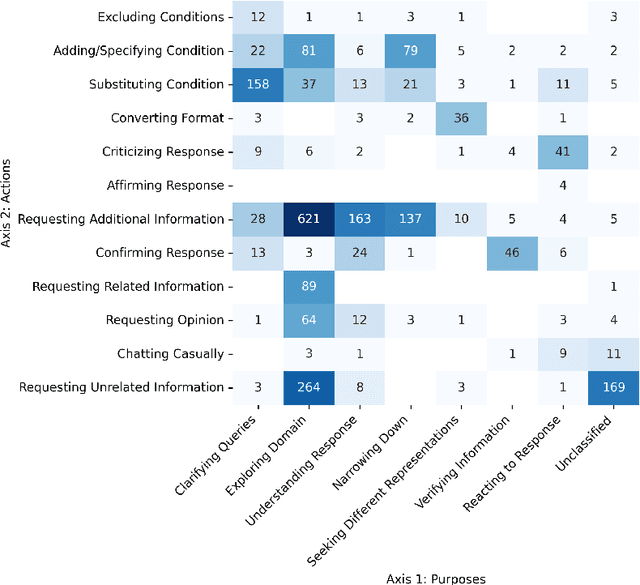
Abstract:With large language models (LLMs), conversational search engines shift how users retrieve information from the web by enabling natural conversations to express their search intents over multiple turns. Users' natural conversation embodies rich but implicit signals of users' search intents and evaluation of search results to understand user experience with the system. However, it is underexplored how and why users ask follow-up queries to continue conversations with conversational search engines and how the follow-up queries signal users' satisfaction. From qualitative analysis of 250 conversational turns from an in-lab user evaluation of Naver Cue:, a commercial conversational search engine, we propose a taxonomy of 18 users' follow-up query patterns from conversational search, comprising two major axes: (1) users' motivations behind continuing conversations (N = 7) and (2) actions of follow-up queries (N = 11). Compared to the existing literature on query reformulations, we uncovered a new set of motivations and actions behind follow-up queries, including asking for subjective opinions or providing natural language feedback on the engine's responses. To analyze conversational search logs with our taxonomy in a scalable and efficient manner, we built an LLM-powered classifier (73% accuracy). With our classifier, we analyzed 2,061 conversational tuples collected from real-world usage logs of Cue: and examined how the conversation patterns from our taxonomy correlates with satisfaction. Our initial findings suggest some signals of dissatisfactions, such as Clarifying Queries, Excluding Condition, and Substituting Condition with follow-up queries. We envision our approach could contribute to automated evaluation of conversation search experience by providing satisfaction signals and grounds for realistic user simulations.
A Versatile Framework for Evaluating Ranked Lists in terms of Group Fairness and Relevance
Apr 01, 2022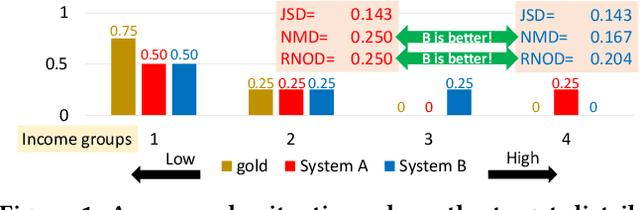
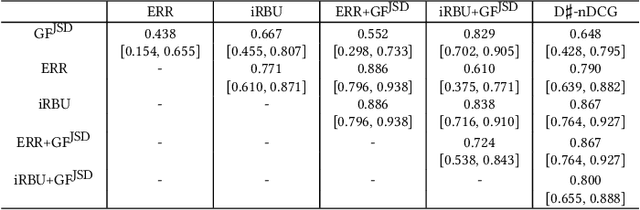
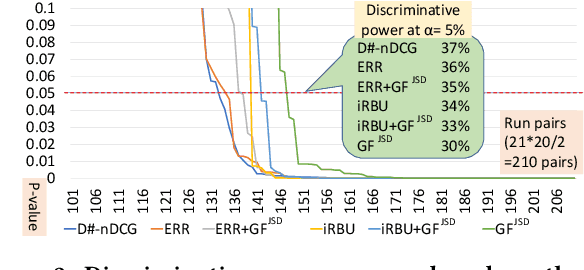
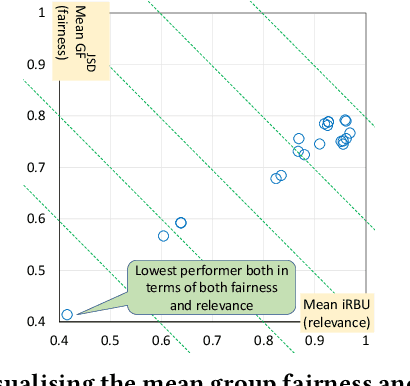
Abstract:We present a simple and versatile framework for evaluating ranked lists in terms of group fairness and relevance, where the groups (i.e., possible attribute values) can be either nominal or ordinal in nature. First, we demonstrate that, if the attribute set is binary, our framework can easily quantify the overall polarity of each ranked list. Second, by utilising an existing diversified search test collection and treating each intent as an attribute value, we demonstrate that our framework can handle soft group membership, and that our group fairness measures are highly correlated with both adhoc IR and diversified IR measures under this setting. Third, we demonstrate how our framework can quantify intersectional group fairness based on multiple attribute sets. We also show that the similarity function for comparing the achieved and target distributions over the attribute values should be chosen carefully.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge