Honggu Lee
Using LLMs to Investigate Correlations of Conversational Follow-up Queries with User Satisfaction
Jul 18, 2024
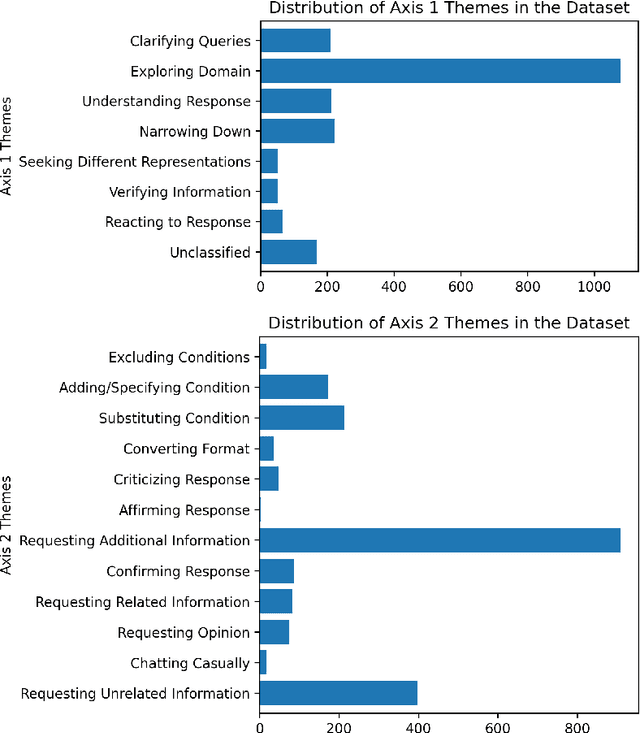
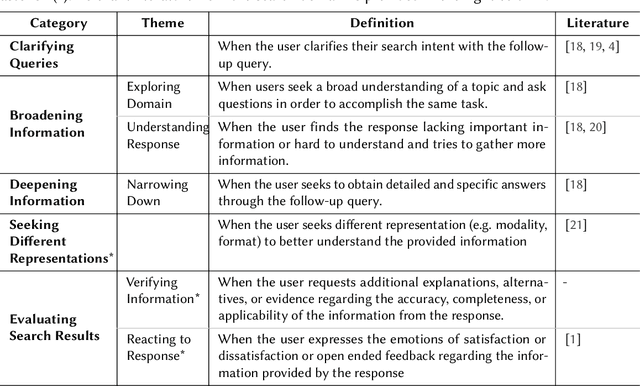
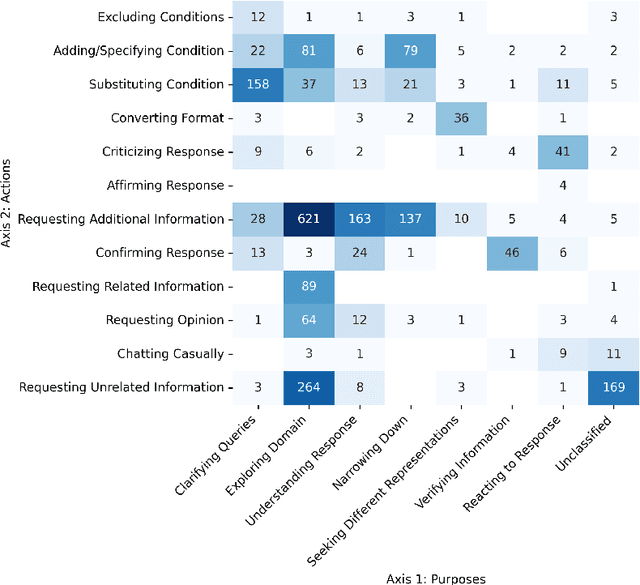
Abstract:With large language models (LLMs), conversational search engines shift how users retrieve information from the web by enabling natural conversations to express their search intents over multiple turns. Users' natural conversation embodies rich but implicit signals of users' search intents and evaluation of search results to understand user experience with the system. However, it is underexplored how and why users ask follow-up queries to continue conversations with conversational search engines and how the follow-up queries signal users' satisfaction. From qualitative analysis of 250 conversational turns from an in-lab user evaluation of Naver Cue:, a commercial conversational search engine, we propose a taxonomy of 18 users' follow-up query patterns from conversational search, comprising two major axes: (1) users' motivations behind continuing conversations (N = 7) and (2) actions of follow-up queries (N = 11). Compared to the existing literature on query reformulations, we uncovered a new set of motivations and actions behind follow-up queries, including asking for subjective opinions or providing natural language feedback on the engine's responses. To analyze conversational search logs with our taxonomy in a scalable and efficient manner, we built an LLM-powered classifier (73% accuracy). With our classifier, we analyzed 2,061 conversational tuples collected from real-world usage logs of Cue: and examined how the conversation patterns from our taxonomy correlates with satisfaction. Our initial findings suggest some signals of dissatisfactions, such as Clarifying Queries, Excluding Condition, and Substituting Condition with follow-up queries. We envision our approach could contribute to automated evaluation of conversation search experience by providing satisfaction signals and grounds for realistic user simulations.
TRIER: Template-Guided Neural Networks for Robust and Interpretable Sleep Stage Identification from EEG Recordings
Sep 10, 2020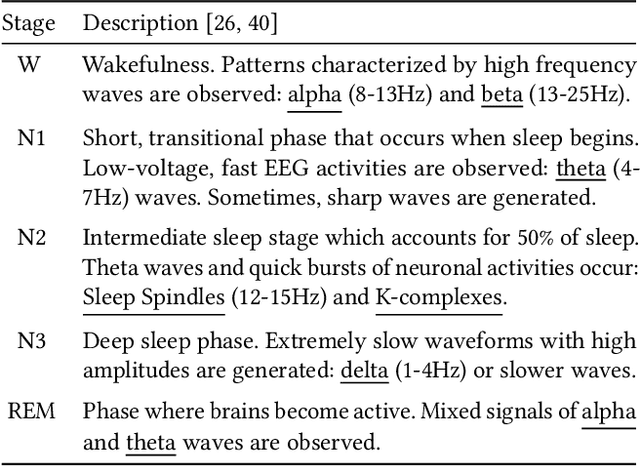
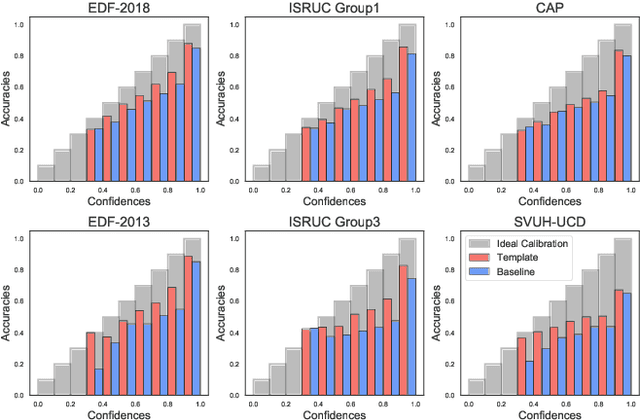
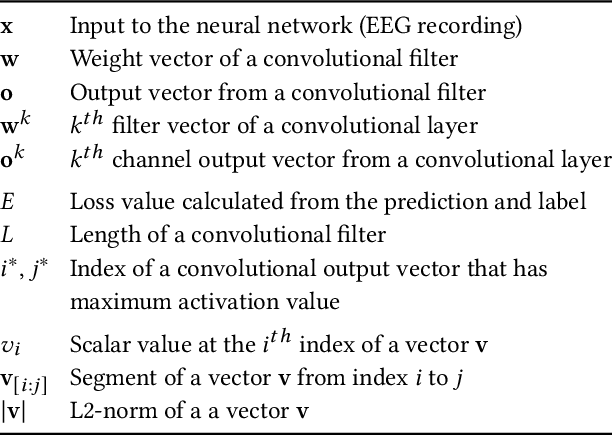
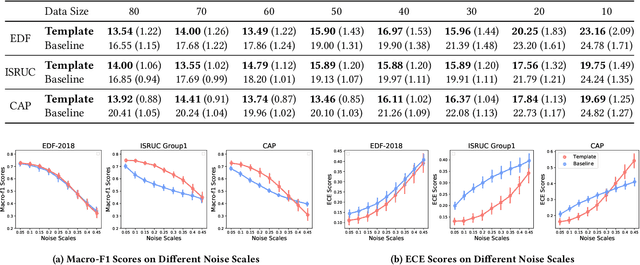
Abstract:Neural networks often obtain sub-optimal representations during training, which degrade robustness as well as classification performances. This is a severe problem in applying deep learning to bio-medical domains, since models are vulnerable to being harmed by irregularities and scarcities in data. In this study, we propose a pre-training technique that handles this challenge in sleep staging tasks. Inspired by conventional methods that experienced physicians have used to classify sleep states from the existence of characteristic waveform shapes, or template patterns, our method introduces a cosine similarity based convolutional neural network to extract representative waveforms from training data. Afterwards, these features guide a model to construct representations based on template patterns. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrated that guiding a neural network with template patterns is an effective approach for sleep staging, since (1) classification performances are significantly enhanced and (2) robustness in several aspects are improved. Last but not least, interpretations on models showed that notable features exploited by trained experts are correctly addressed during prediction in the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge