Jiazhen Wang
Implementation of AI Deep Learning Algorithm For Multi-Modal Sentiment Analysis
Nov 19, 2023Abstract:A multi-modal emotion recognition method was established by combining two-channel convolutional neural network with ring network. This method can extract emotional information effectively and improve learning efficiency. The words were vectorized with GloVe, and the word vector was input into the convolutional neural network. Combining attention mechanism and maximum pool converter BiSRU channel, the local deep emotion and pre-post sequential emotion semantics are obtained. Finally, multiple features are fused and input as the polarity of emotion, so as to achieve the emotion analysis of the target. Experiments show that the emotion analysis method based on feature fusion can effectively improve the recognition accuracy of emotion data set and reduce the learning time. The model has a certain generalization.
Exploiting Modality-Specific Features For Multi-Modal Manipulation Detection And Grounding
Sep 22, 2023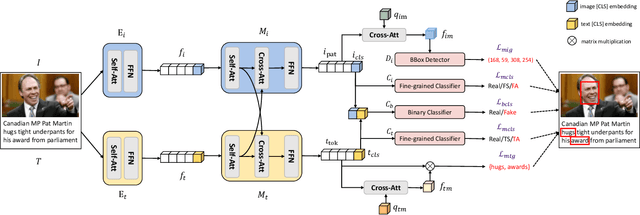
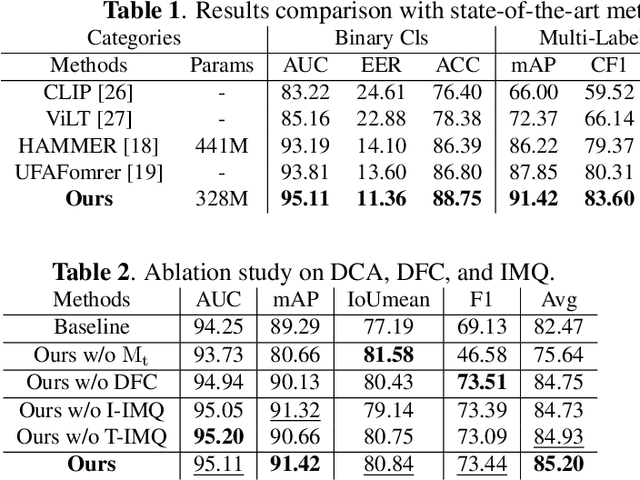

Abstract:AI-synthesized text and images have gained significant attention, particularly due to the widespread dissemination of multi-modal manipulations on the internet, which has resulted in numerous negative impacts on society. Existing methods for multi-modal manipulation detection and grounding primarily focus on fusing vision-language features to make predictions, while overlooking the importance of modality-specific features, leading to sub-optimal results. In this paper, we construct a simple and novel transformer-based framework for multi-modal manipulation detection and grounding tasks. Our framework simultaneously explores modality-specific features while preserving the capability for multi-modal alignment. To achieve this, we introduce visual/language pre-trained encoders and dual-branch cross-attention (DCA) to extract and fuse modality-unique features. Furthermore, we design decoupled fine-grained classifiers (DFC) to enhance modality-specific feature mining and mitigate modality competition. Moreover, we propose an implicit manipulation query (IMQ) that adaptively aggregates global contextual cues within each modality using learnable queries, thereby improving the discovery of forged details. Extensive experiments on the $\rm DGM^4$ dataset demonstrate the superior performance of our proposed model compared to state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge